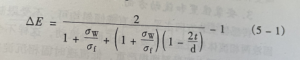When measuring fluids that are easy to adhere to and precipitate substances on the tube wall, if the attached is a conductive material with higher conductivity than the liquid, the signal potential may be short-circuited and cannot work. If it is a non-conductive layer, first pay attention to the contamination of the electrode. If the selected is not easy to adhere to pointed or hemispherical protruding electrodes, replaceable electrodes, scraper-type dirt cleaning electrodes, etc.
The scraper electrode can manually scrape off the dirt outside the sensor on a regular basis. There is also a temporary disconnection of the measuring circuit, a low-voltage and large current flows between the electrodes in a short time, and the adhesion layer of attached grease is removed by incineration. In places prone to adhesion, the flow rate can be increased to achieve the purpose of self-cleaning, and a more convenient and easy-to-clean pipeline connection can be adopted, and the sensor can be cleaned without disassembly.
The non-contact capacitive electrode electromagnetic flowmeter is attached with a non-conductive film layer, and the meter can still work, but if it is a highly conductive layer, it will not work as well.
For the additional indication error of the conductive adhesion layer of the contact electrode of the electromagnetic flowmeter:
If the outside matter layer attached to the lining pipe wall is an oxidized iron rust layer or a metal-based dye whose conductivity is greater than that of the liquid, the measured flow rate will be lower than the actual flow rate; if it is a scale layer such as calcium carbonate, it If the conductivity is lower than the liquid, the measured flow rate will be higher than the actual flow; if the conductivity of the adhesion layer is the same as that of the liquid, the additional error calculated according to formula (5-1) is zero, but this is only limited to the condition that the thickness of the adhesion layer is small.