1. Overview
Two-wire output is a common signal transmission method in industrial automation and process control systems. In a two-wire configuration, the same pair of wires is used to supply power to the instrument and to transmit output signals. The 8 mA and 16 mA output scheme is frequently adopted, especially in intrinsically safe explosion-proof products, to indicate different operational states.
2. Working Principle
In a two-wire output system, the instrument or sensor does not have an independent power supply. Instead, an external power source delivers energy through the same two wires that also carry the measurement or control signal.
The instrument’s internal circuit adjusts the current in this loop according to its detected state:
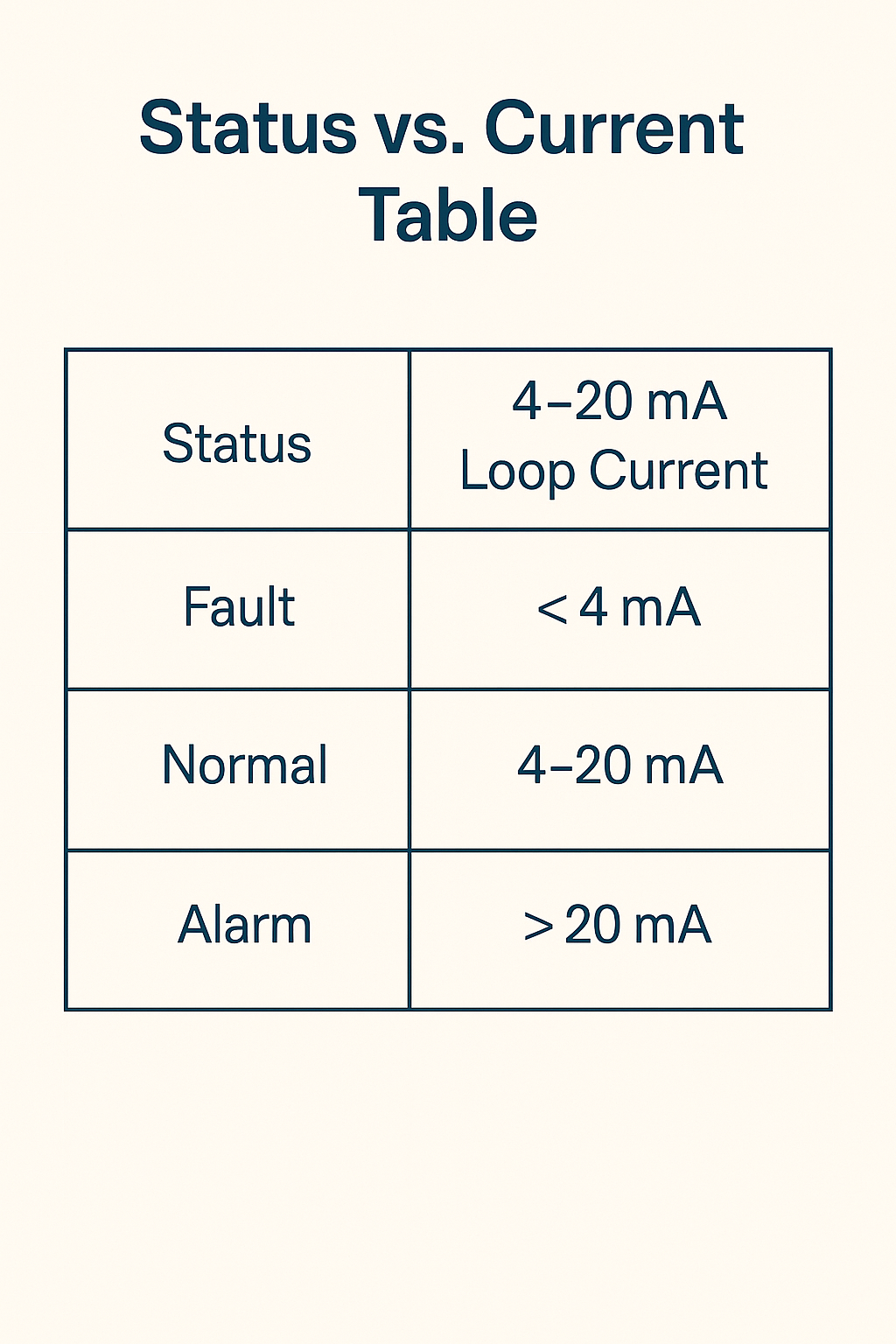
8 mA – Represents a normal or safe condition.
16 mA – Represents an alarm or triggered condition.
~1.8 mA – Indicates a fault or malfunction.
The control system continuously monitors the loop current using a current detection circuit. By interpreting the current level, it can determine the status of the instrument and take appropriate action.
3. Example: Level Switch Application
A tuning fork level switch can be configured with a two-wire 8/16 mA output.
In low-level monitoring mode, 8 mA may indicate material is present, while 16 mA indicates absence.
In high-level monitoring mode, 8 mA may indicate no material contact, while 16 mA indicates material contact.
In both modes, a fault condition is signaled by a drop to approximately 1.8 mA.
This method provides a simple, robust, and energy-efficient way to convey binary status information over a single pair of conductors.
4. Typical Wiring
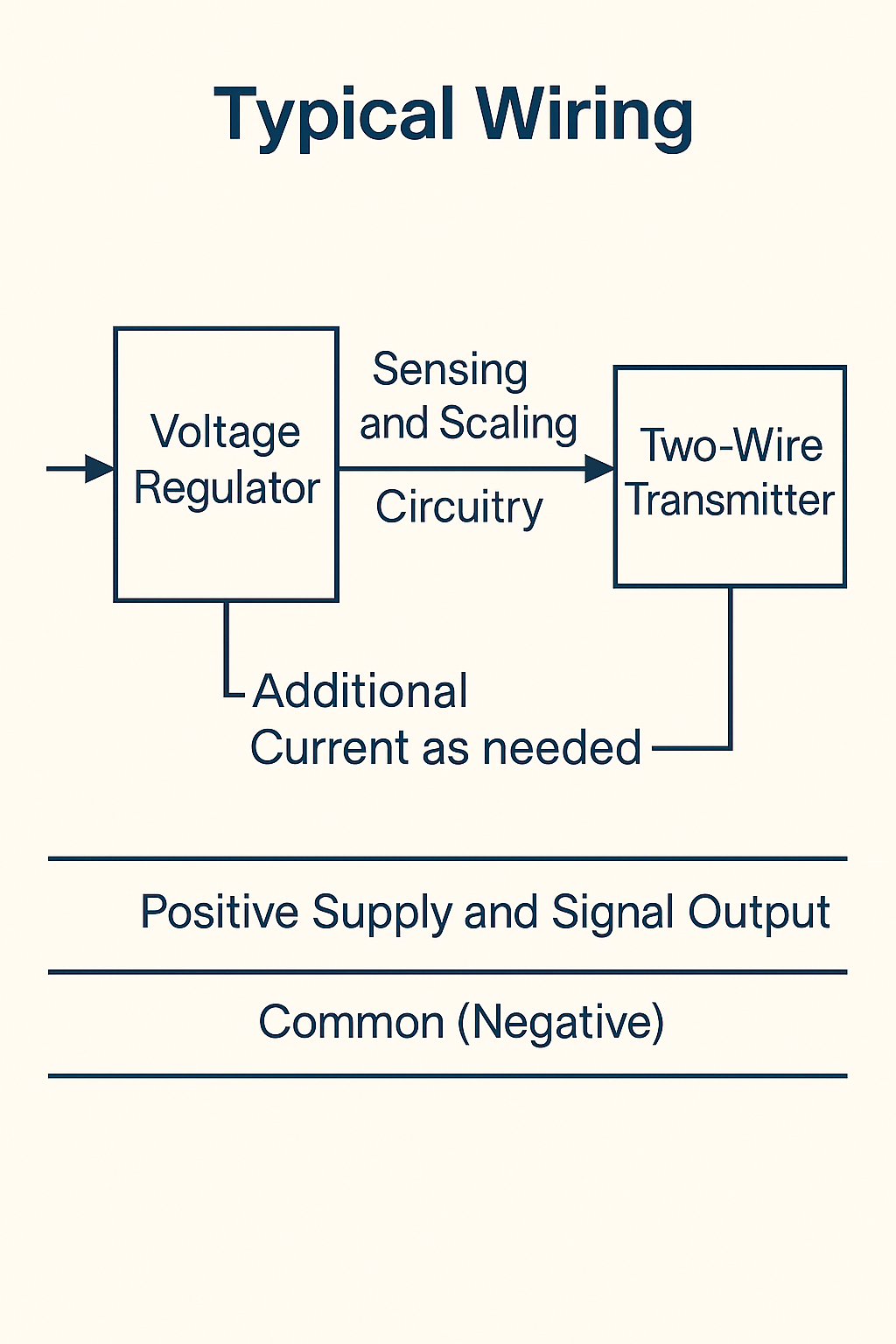
In a typical two-wire output connection:
One conductor serves as the positive supply and signal output.
The other conductor acts as the common (negative).
The external power supply feeds the instrument through these two wires, and the instrument modulates the loop current to send its status to the control system.
5. Advantages
Simplicity – Power and signal share the same wiring.
Reliability – Low susceptibility to noise compared to voltage signals.
Low Power Consumption – Suitable for battery-powered or intrinsically safe systems.
Compatibility – Works with standard current loop monitoring equipment.
6. Application Areas
The 8/16 mA two-wire output method is widely used in:
Level switches (tuning fork, capacitive, optical)
Pressure and temperature limit switches
Safety-critical monitoring in hazardous locations
Intrinsically safe control loops
7. Summary
The 8/16 mA two-wire output is an effective method for transmitting simple binary status signals while powering the instrument from the same pair of wires. Its reliability, low power requirements, and compatibility with intrinsically safe designs make it a preferred choice in many industrial automation and process control applications.
