1. Overview
In industrial environments, proper installation of combustible and toxic gas detectors is essential for early leak detection, personnel safety, and fire/explosion prevention. This guide provides standard recommendations for installation height, spacing, positioning, and alarm thresholds.

2. Detector Placement Principles
The layout of detectors should be based on gas dispersion patterns after a leak. Detectors must be positioned so that in the event of a leak, gas concentrations can be detected before they reach hazardous levels.
Detectors should be installed near the following typical gas emission sources:
Dynamic seals on gas compressors and liquid pumps
Liquid and gas sampling ports
Drainage points and vent valves
Frequently disassembled flanges or frequently operated valve sets
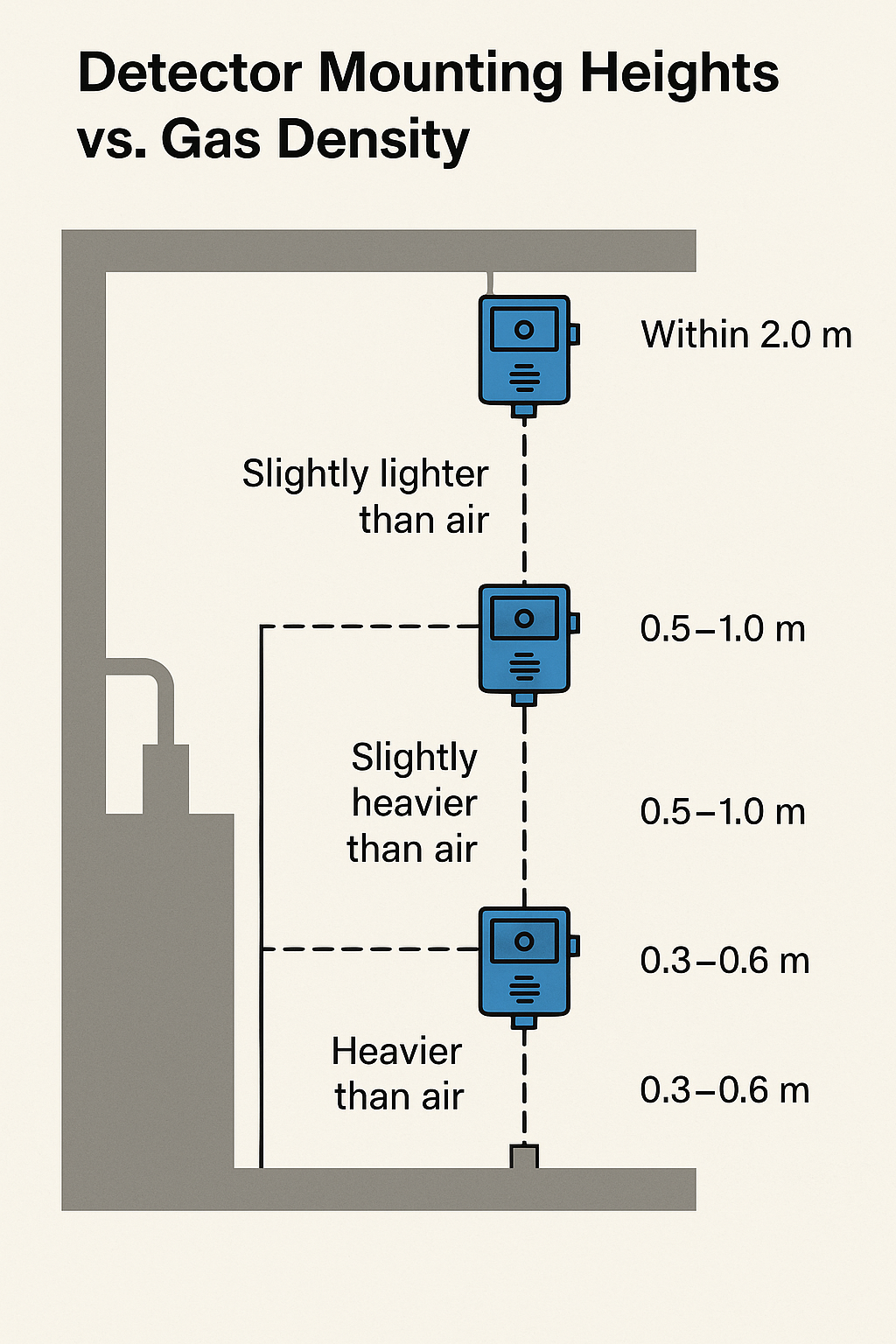
3. Gas Density and Mounting Height
Gas density relative to air determines the appropriate installation height:
| Relative Molecular Weight | Classification | Recommended Mounting Height |
|---|---|---|
| ≥ 1.2 | Heavier than air | 0.3–0.6 m from the floor |
| 1.0 – 1.2 | Slightly heavier | 0.5–1.0 m below the leak source |
| 0.8 – 1.0 | Slightly lighter | 0.5–1.0 m above the leak source |
| ≤ 0.8 | Lighter than air | Within 2.0 m above the leak source or at ceiling level |
Diagram available: Mounting Height vs. Gas Density
4. Spacing Requirements
➤ Outdoor or Open Structures:
Combustible gas detectors: max 10 m from each leak source
Toxic gas detectors: max 4 m from each leak source
➤ Enclosed or Poorly Ventilated Areas:
Combustible gas detectors: max 5 m
Toxic gas detectors: max 2 m

5. Alarm Thresholds
| Gas Type | Level 1 Alarm | Level 2 Alarm |
|---|---|---|
| Combustible Gas | ≤ 25% LEL | ≤ 50% LEL |
| Toxic Gas | ≤ 100% OEL | ≤ 200% OEL |
| Oxygen (Overlimit) | > 23.5% Vol | – |
| Oxygen (Deficiency) | < 19.5% Vol | – |
LEL: Lower Explosive Limit
OEL: Occupational Exposure Limit
6. Signal Handling and Alarm Display
Alarm signals should be sent to manned local control rooms, central control rooms, and fire control stations.
Visual and audible alarms must be installed at operator stations and field areas.
Field alarms should consider site layout, area size, equipment density, and airflow characteristics.

7. Detector Selection Guidelines
| Application | Recommended Detector Type |
|---|---|
| Light hydrocarbons (e.g., methane) | Catalytic combustion or infrared |
| Heavy hydrocarbons (e.g., hexane) | Photoionization (PID) |
| Hydrogen | Catalytic, electrochemical, or thermal conductivity |
| Organic toxic gases | Semiconductor or PID |
| Inorganic toxic gases | Electrochemical |
| Oxygen | Electrochemical |
| Open areas with special conditions | Line-type gas detectors |
| Temperature-change-prone leaks | Infrared imaging detectors |
| Pressure-leakage with sound impact | Acoustic detectors |
| Temporary monitoring | Portable gas detectors |

8. Visual Aids (To Be Added)
Detector Mounting Height Chart
Detector Coverage Radius Illustration
Gas Density vs. Air Comparison Table
