Flanges are essential components used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment in piping systems. They come in various types and designs to suit different applications, pressure levels, and operational conditions. This article provides a detailed overview of the most common flange types, their designations, and their typical applications.
1. Plate Flange (PL)
- Description: The plate flange is a simple and lightweight flange with a flat surface. It is easy to manufacture and cost-effective.
- Designation: PL
- Applications:
- Suitable for low-pressure piping systems.
- Often used in water, air, and low-temperature fluid pipelines.
- Advantages:
- Cost-effective for low-pressure systems.
- Easy to install and align.
2. Slip-On Flange (SO)
- Description: This flange has a slightly larger inner diameter than the pipe, allowing it to slip over the pipe before welding. The flange is welded both inside and outside to increase its strength.
- Designation: SO
- Applications:
- Medium to high-pressure systems.
- Suitable for applications where moderate pressure containment and temperature resistance are required.
- Advantages:
- Easier to align than other types.
- Economical for many general applications.
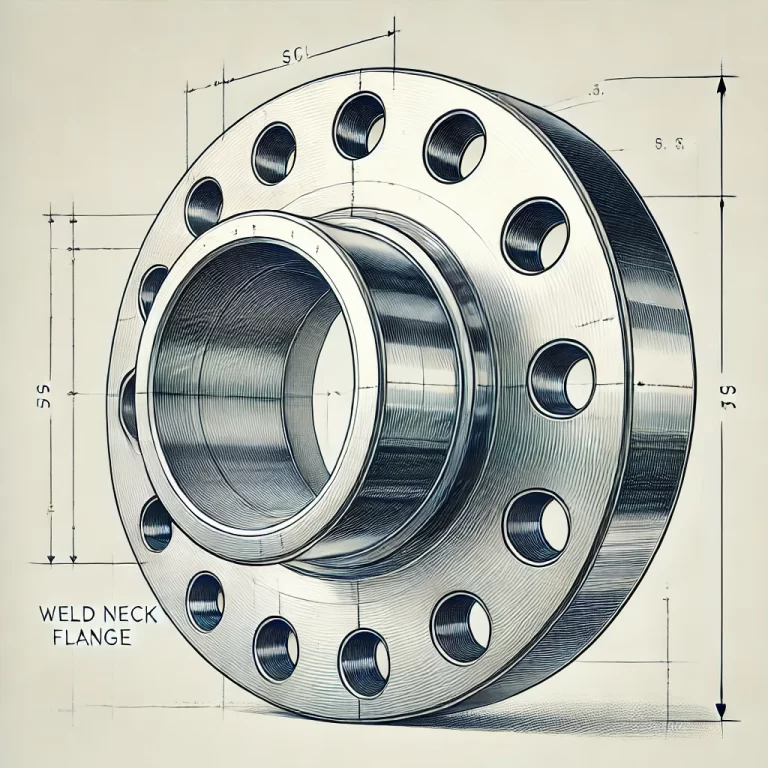
3. Weld Neck Flange (WN)
- Description: This flange features a long tapered hub that gradually transitions to the pipe’s thickness. It is welded directly to the pipe.
- Designation: WN
- Applications:
- High-pressure and high-temperature environments.
- Systems requiring excellent stress distribution and leak prevention, such as in oil and gas industries.
- Advantages:
- Superior strength and fatigue resistance.
- Provides a smoother flow inside the pipe.
4. Socket Weld Flange (SW)
- Description: Socket weld flanges have a recessed area that allows the pipe to fit into the flange. It is secured with a single fillet weld.
- Designation: SW
- Applications:
- Used in small-diameter, high-pressure piping systems.
- Suitable for pipelines transporting hazardous materials.
- Advantages:
- Strong connection for small-diameter pipes.
- Provides a smooth bore to improve fluid flow.
5. Threaded Flange (RF – Raised Face)
- Description: Threaded flanges are designed with internal threads that match the external threads of the pipe. They are typically used in applications where welding is not feasible.
- Designation: RF
- Applications:
- Ideal for systems requiring frequent maintenance.
- Common in explosive or flammable environments.
- Advantages:
- Easy to assemble and disassemble.
- No welding required, which minimizes fire hazards.
6. Lap Joint Flange (LJ)
- Description: This flange is used with a stub end, allowing the flange to rotate freely around the pipe. It provides flexibility in alignment.
- Designation: LJ
- Applications:
- Piping systems that require frequent disassembly.
- Ideal for systems with corrosion-resistant lining.
- Advantages:
- Easy to install and adjust.
- Suitable for non-critical pressure applications.

7. Flat Face Flange (FF)
- Description: Flat face flanges have a flat sealing surface and are used with flat gaskets.
- Designation: FF
- Applications:
- Low-pressure and non-critical connections.
- Used in systems where flange alignment is not stringent.
- Advantages:
- Simplifies installation.
- Cost-effective for low-pressure connections.
8. Male and Female Flange (MFM)
- Description: This type consists of one flange with a raised male surface and another with a recessed female surface, which fit together to create a seal.
- Designation: MFM
- Applications:
- High-sealing applications, such as steam systems.
- Suitable for systems with elevated temperatures and pressures.
- Advantages:
- Provides a tight seal.
- Reduces gasket movement and blowouts.
9. Tongue and Groove Flange (TG)
- Description: Similar to the male and female flange, the tongue and groove design ensures a tight fit. The tongue flange has a raised surface, while the groove flange has a matching depression.
- Designation: TG
- Applications:
- High-pressure, high-temperature systems.
- Used in applications requiring leak-proof seals.
- Advantages:
- Enhanced sealing capabilities.
- Reduces risk of misalignment.

10. Ring-Type Joint Flange (RTJ)
- Description: These flanges have a groove cut into their sealing face to accommodate a metal ring gasket, ensuring a leak-proof connection.
- Designation: RTJ
- Applications:
- Commonly used in high-pressure and high-temperature environments, such as oil and gas pipelines.
- Advantages:
- Excellent sealing performance under extreme conditions.
- Resistant to vibrations and stress.
Conclusion
Flanges play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of piping systems. Selecting the right flange type depends on factors such as operating pressure, temperature, application requirements, and ease of maintenance. Understanding the different types and their specific applications helps engineers and technicians make informed decisions, ensuring the durability and reliability of the piping system.
