Introduction
Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) define various thread types for different industrial applications. These threads are widely used in mechanical components, piping systems, and precision instruments. This article provides an overview of the most common JIS thread types, their characteristics, applications, and examples.
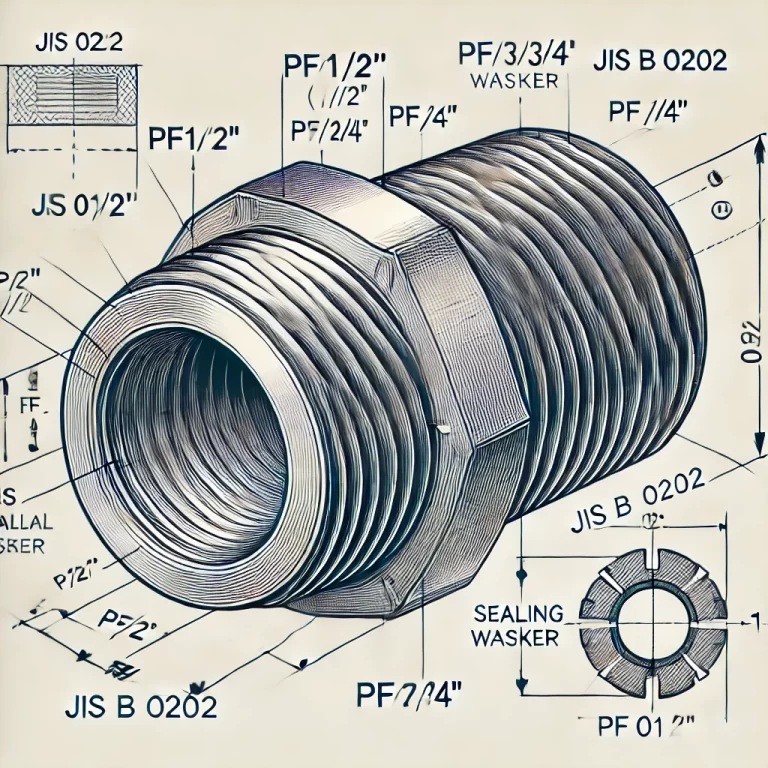
1. JIS Parallel Pipe Thread (JIS B 0202)
Designation: PF (Equivalent to BSPP)
Type: Parallel (non-tapered) thread
Characteristics:
Used for low-pressure sealing connections
Requires a sealing washer for proper sealing
Provides good mechanical stability
Applications: Commonly found in water, gas, and hydraulic systems
Examples: PF1/2″, PF3/4″, PF1″
Visual Representation:
2. JIS Tapered Pipe Thread (JIS B 0203)
Designation: PT (Equivalent to BSPT)
Type: Tapered thread
Characteristics:
Self-sealing without the need for additional sealing materials
Designed for fluid and gas connections
Provides a secure and leak-free joint when tightened
Applications: Used in pneumatic, hydraulic, and high-pressure fluid transport systems
Examples: PT1/2″, PT3/4″, PT1″
Thread Size Chart:
| Dash Size | Nominal Size (in.) | Thread Size | Male Thread OD | Female Thread ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -2 | 1/8″ | 1/8-28 | 3/8″ | 11/32″ |
| -4 | 1/4″ | 1/4-19 | 17/32″ | 7/16″ |
| -6 | 3/8″ | 3/8-19 | 21/32″ | 19/32″ |
| -8 | 1/2″ | 1/2-14 | 3/4″ | 11/16″ |
| -12 | 3/4″ | 3/4-14 | 15/16″ | 7/8″ |
| -16 | 1″ | 1-11 | 1 5/32″ | 1 3/16″ |
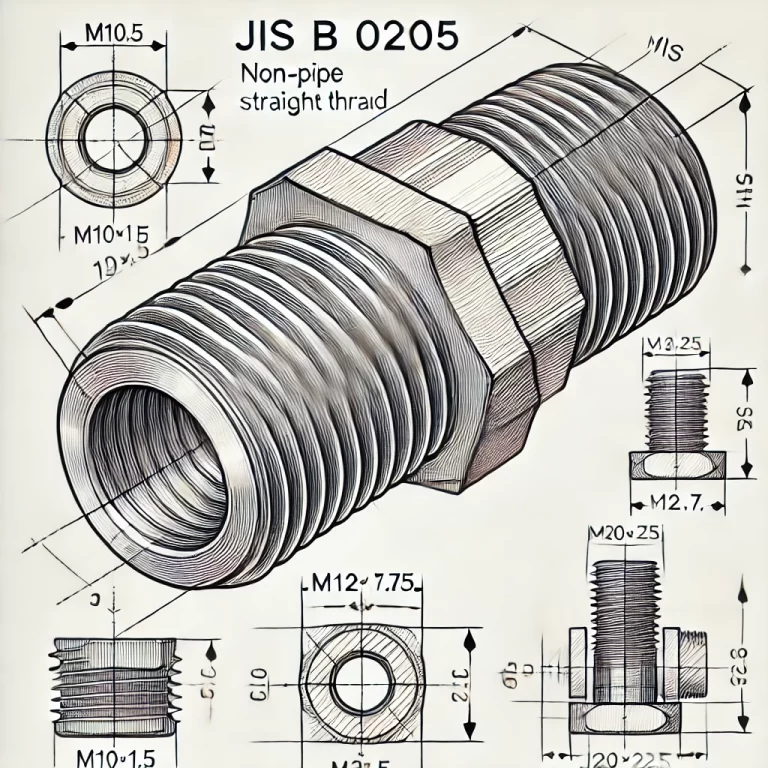
3. JIS Metric Thread (JIS B 0205)
Designation: M (Metric thread)
Type: Non-pipe straight thread
Characteristics:
Standard metric pitch and diameter
Used in mechanical fasteners such as bolts and nuts
Offers high precision and strength
Applications: Widely applied in machinery, automotive, and construction industries
Examples: M10×1.5, M12×1.75, M20×2.5
4. JIS Unified Thread (JIS B 0206)
Designation: UNC/UNF (Equivalent to ANSI/ASME B1.1)
Type: Unified National Thread (Coarse and Fine pitch)
Characteristics:
UNC (Unified National Coarse) threads are used for structural components
UNF (Unified National Fine) threads are used for precision parts
Commonly used in both general and aerospace industries
Applications: Engineering, automotive, precision instruments
Examples: 1/4-20 UNC, 3/8-24 UNF
Comparison Table:
| Type | Standard | Usage |
| UNC (Coarse) | ANSI B1.1 | Structural and general applications |
| UNF (Fine) | ANSI B1.1 | Precision and aerospace applications |
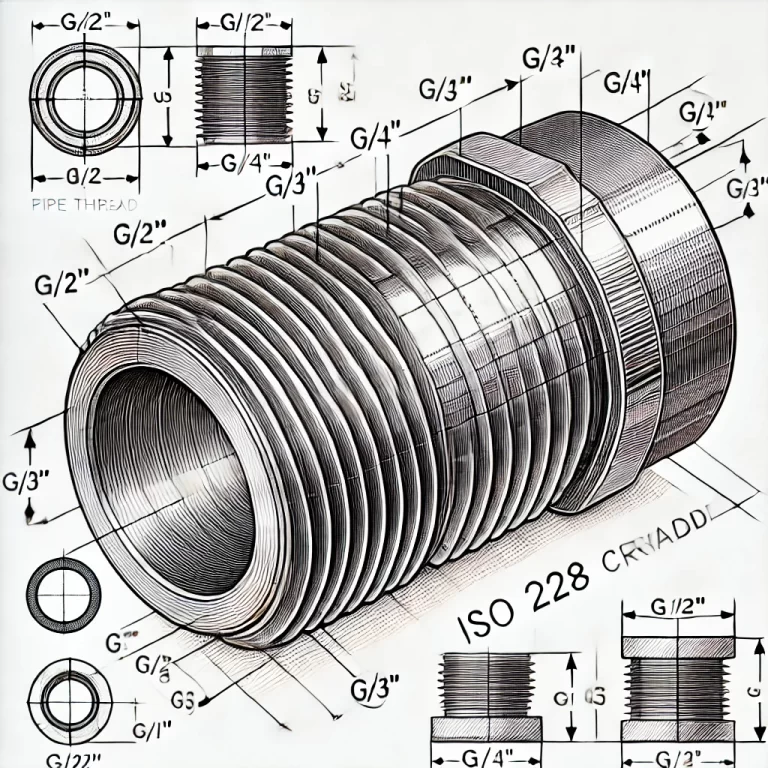
5. JIS Parallel Pipe Thread (ISO 228 Compliant)
Designation: G (Equivalent to ISO 228 BSPP)
Type: Parallel pipe thread
Characteristics:
Designed for mechanical joints with sealing washers
Used in applications where sealing with an O-ring or gasket is required
Compatible with ISO 228 standards
Applications: Plumbing, fluid control systems, gas pipelines
Examples: G1/2″, G3/4″, G1″
6. JIS NPT Thread (JIS B 0203, Equivalent to ANSI B1.20.1)
Designation: NPT
Type: Tapered thread (American standard)
Characteristics:
Provides a reliable seal without additional sealing components
Suitable for high-pressure liquid and gas pipelines
Standardized in North America and used in various industries worldwide
Applications: Oil & gas industry, plumbing, high-pressure fluid transport
Examples: NPT1/4, NPT1/2, NPT3/4
Summary Table: Common JIS Thread Types
| Thread Type | Standard | Type | Applications |
| PF (BSPP) | JIS B 0202 | Parallel | Low-pressure sealing |
| PT (BSPT) | JIS B 0203 | Tapered | Fluid, gas connections |
| M (Metric) | JIS B 0205 | Straight | Fasteners, machinery |
| UNC/UNF | JIS B 0206 | Straight | Structural, precision |
| G (ISO 228) | ISO 228 | Parallel | Sealed mechanical joints |
| NPT | ANSI B1.20.1 | Tapered | High-pressure piping |
Conclusion
The Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) define various thread types, each designed for specific industrial applications. Choosing the appropriate thread type depends on the operating conditions, required sealing performance, and the compatibility with international standards. Understanding these differences ensures proper selection and application in engineering and manufacturing processes.
For engineers and manufacturers, having a solid grasp of these thread types helps in selecting the right components for different industrial needs, ultimately ensuring reliability, safety, and efficiency.
