1. Classification and Properties of Common Chemical Media
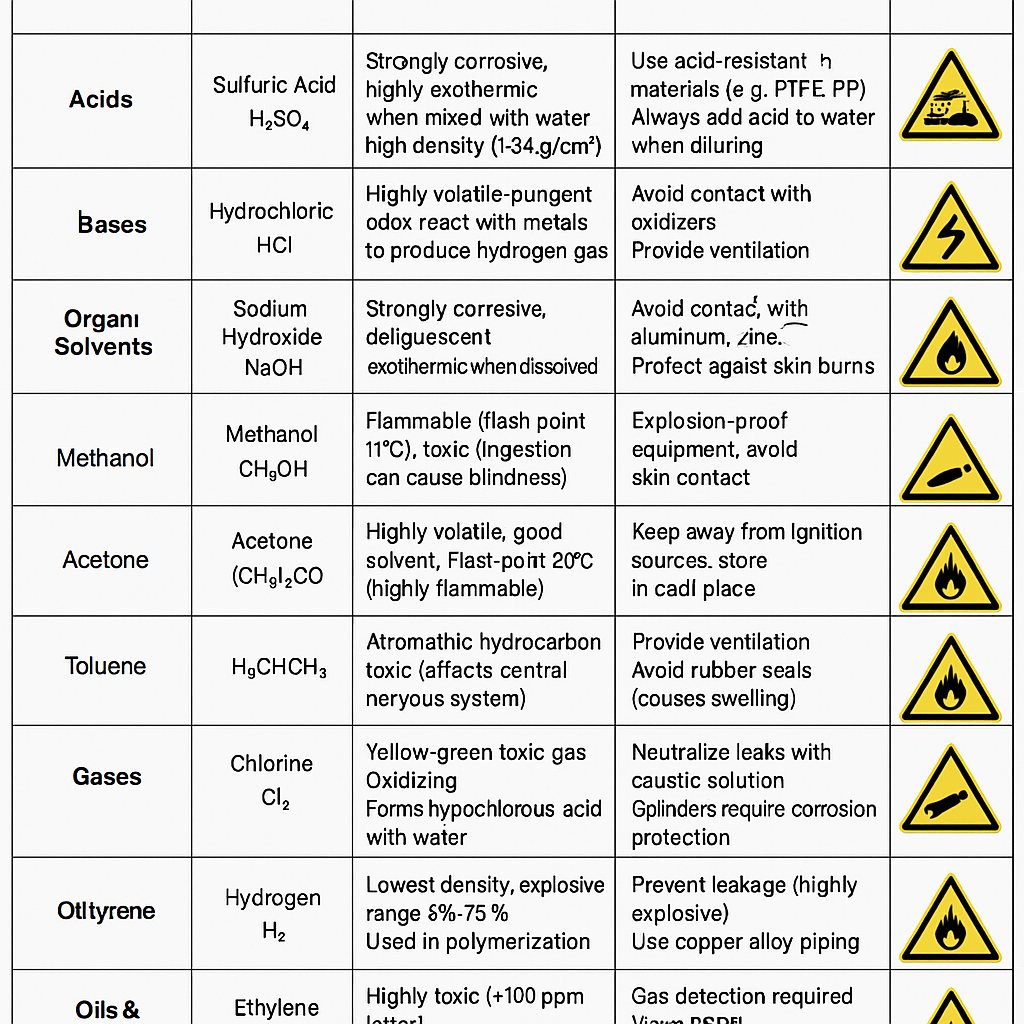
A. Acids
| Media | Chemical Formula | Characteristics | Safety Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfuric Acid | H₂SO₄ | Strongly corrosive, high density (1.84 g/cm³), highly exothermic when diluted | Use acid-resistant materials (e.g., PP, PTFE, lead); always add acid to water |
| Hydrochloric Acid | HCl | Strong volatility, pungent smell, reacts with metals to release hydrogen gas | Use in ventilated areas, avoid contact with oxidizers |
| Nitric Acid | HNO₃ | Strong oxidizer, reacts violently with organics, decomposes under light | Store in amber bottles; keep away from reducing agents |
B. Bases
| Media | Chemical Formula | Characteristics | Safety Precautions |
| Sodium Hydroxide | NaOH | Strongly corrosive, deliquescent, exothermic when dissolved | Avoid contact with amphoteric metals (e.g., Al, Zn); protect skin |
| Ammonia Solution | NH₄OH | Volatile, pungent smell, weak base | Ensure ventilation; avoid inhalation; reacts with acids to form ammonium salts |
C. Organic Solvents
| Media | Chemical Formula | Characteristics | Safety Precautions |
| Methanol | CH₃OH | Flammable (flash point 11°C), highly toxic (can cause blindness if ingested) | Use explosion-proof equipment; avoid skin contact |
| Acetone | (CH₃)₂CO | Volatile, strong solvency, highly flammable (flash point -20°C) | Store away from ignition sources; keep in cool places |
| Toluene | C₆H₅CH₃ | Aromatic hydrocarbon, neurotoxic, flammable | Ensure ventilation; incompatible with rubber seals |
D. Gases
| Media | Chemical Formula | Characteristics | Safety Precautions |
| Chlorine | Cl₂ | Toxic yellow-green gas, strong oxidizer, forms hypochlorous acid with water | Neutralize leaks with alkaline solution; store in corrosion-resistant cylinders |
| Hydrogen | H₂ | Lightest gas, explosive range 4%-75%, odorless and colorless | Prevent leakage; use copper alloy pipelines |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | H₂S | Highly toxic (>100 ppm is fatal), smells like rotten eggs | Use gas detectors; wear positive pressure respirators during maintenance |
E. Oils and Hydrocarbons
| Media | Formula / Type | Characteristics | Safety Precautions |
| Crude Oil | Mixture | May contain sulfur compounds (corrosive), viscosity varies with temperature | Use anti-static measures; desulfurize as needed |
| Ethylene | C₂H₄ | Flammable and explosive (2.7%-36%), used in polymerization | Store at low temperature (-104°C); avoid oxidizers |
2. Key Property Parameters
Physical Properties:
Density: Affects pump selection (e.g., sulfuric acid requires high-head pumps)
Viscosity: High-viscosity media (e.g., heavy oil) may require heating or screw pumps
Boiling/Melting Point: Cryogenic media (e.g., liquid nitrogen) require insulation; high-temp media (e.g., molten salts) need heat-resistant materials
Chemical Properties:
Corrosiveness: Hydrochloric acid requires Hastelloy or PTFE-lined equipment
Reactivity: Ethylene oxide is highly reactive; avoid mixing with air due to explosion risk
Safety Characteristics:
Flash Point: Acetone (-20°C) is a Class A flammable liquid
Toxicity: Benzene TLV is 0.5 ppm; strict protection measures are essential
3. Material Selection and Safety Measures
Material Recommendations:
Hydrochloric Acid: PVDF, FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic)
Hydrofluoric Acid: Monel alloy (Ni-Cu alloy)
Safety Strategies:
Flammable Media: Inert gas blanketing, explosion-proof zoning
Toxic Gases: Gas alarms (e.g., H₂S detectors), emergency response kits
4. Typical Application Scenarios
| Media | Common Uses |
| Sulfuric Acid | Fertilizer production, battery electrolyte |
| Anhydrous Ammonia | Refrigerant, urea synthesis |
| Xylene | Paint thinner, PTA raw material |
