Terminal blocks are critical components in electrical and electronic systems, providing secure connections for transmitting voltage, current, or signals. However, various issues can arise during their use, impacting performance and reliability. This article discusses common terminal block failures, their causes, and preventive measures.
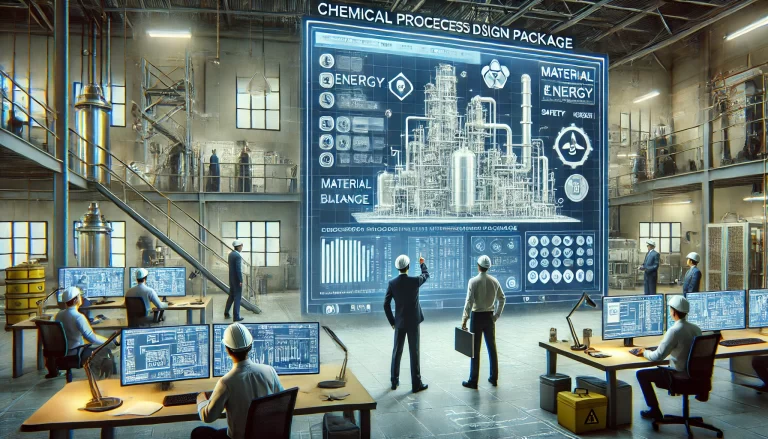

1. Contact Failure
The metallic conductor within a terminal block is the core component responsible for transmitting electricity or signals from an external wire to a connected contact. To ensure stable performance, contact parts must exhibit excellent structure, reliable retention, and good conductivity. However, contact failure can occur due to several factors:
Causes of Contact Failure:
- Poor Design: Inadequate structural design can lead to unstable connections.
- Material Issues: Incorrect choice of materials can result in high resistance or oxidation.
- Manufacturing Defects: Irregularities in mold stability, improper heat treatment, or inaccurate dimensions can impact contact quality.
- Surface Treatment: Faulty surface treatments, such as inadequate plating or rough finishing, can increase resistance.
- Environmental Factors: Storage or operational conditions, including high humidity or dust, may degrade contacts over time.
- Improper Handling: Incorrect installation or excessive force can damage the contacts.
Preventive Measures: To minimize contact failure:
- Design Optimization: Use reliable designs with secure contact points.
- Material Selection: Choose high-quality, corrosion-resistant materials.
- Quality Control: Ensure strict adherence to production standards for precise dimensions and surface treatments.
- Storage Conditions: Store terminal blocks in dry, clean environments.
- Proper Training: Train personnel on correct installation techniques to avoid improper handling.

2. Insulation Failure
The insulation within a terminal block plays a critical role in keeping contacts correctly aligned and ensuring separation between contacts or between the contact and housing. With the rise of high-density and miniaturized terminal blocks, insulation thickness has decreased, increasing demands on materials and manufacturing precision.
Causes of Insulation Failure:
- Contaminants: Metal debris, dust, or residual flux from soldering can compromise insulation.
- Moisture and Humidity: High humidity levels can form conductive paths on the insulation surface.
- Organic Material Deposits: Deposits from organic materials or adhesive gases can form conductive films.
- Aging: Over time, insulation materials may degrade, leading to cracking or shrinking.
Preventive Measures: To prevent insulation issues:
- Material Quality: Use high-performance insulation materials that can withstand environmental stress.
- Precision Molding: Employ precise molding techniques to maintain accurate dimensions.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean terminal blocks regularly to prevent dust and contaminant buildup.
- Environment Control: Ensure dry and controlled environments to prevent condensation or mold formation.
3. Fixation Failure
Beyond insulation, terminal block insulators are designed to maintain alignment, protect contacts, and secure the block onto equipment. Fixation issues can lead to disconnections, intermittent power supply, or, in severe cases, product disassembly.
Causes of Fixation Failure:
- Design Inconsistencies: Poorly designed locking or alignment features can lead to unreliable fixation.
- Material Weaknesses: Inappropriate material choices may reduce the durability of mounting components.
- Assembly Issues: Insufficient assembly quality, such as improper molding or welding, can affect the stability of the connection.
Preventive Measures: To prevent fixation failure:
- Robust Design: Implement reliable locking mechanisms and support structures.
- Durable Materials: Select strong, durable materials suited for structural applications.
- Assembly Accuracy: Ensure precise assembly with adequate quality checks.
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect fixation components to confirm integrity.
4. Other Issues (Aesthetic and Interchangeability)
Certain visual and functional issues may arise in terminal blocks, affecting performance, compatibility, or user experience.
Common Causes:
- Coating Peeling or Corrosion: Poor plating quality can lead to aesthetic and functional degradation.
- Misalignment: Deviations in dimensions may affect interchangeability between different parts.
- Damage During Handling: Improper handling can lead to cracks or deformation, impacting appearance and function.
Preventive Measures:
- High-Quality Coating: Use corrosion-resistant coatings to enhance durability.
- Dimensional Consistency: Maintain strict quality controls on dimensions for reliable interchangeability.
- Protective Handling: Train staff on handling techniques to avoid unnecessary damage.
Conclusion
Ensuring the reliability of terminal blocks involves a comprehensive approach covering design, material selection, manufacturing precision, and proper handling. By addressing these potential issues, companies can enhance the longevity, safety, and performance of their electrical connections. Regular inspections and preventive maintenance are essential in maintaining high-quality, durable terminal blocks.
