During a recent device debugging session, I encountered an unstable RS485 communication issue. It reminded me of a fundamental yet crucial point: why must the voltage of an RS485 signal be confined within the -7V to +7V range? Many people may know this as a requirement but may not fully understand the reasoning behind it. Today, I’ll break it down in simple terms and share how this design came to be, and what benefits it brings.
The Foundation: Differential Signals
RS485 communication relies on differential signals. In simple terms, it uses two wires, A and B, to carry inverted signals. The receiving end doesn’t measure the voltage of each wire individually but rather compares the difference between them. If the A line is higher than the B line, it represents a ‘1’; if B is higher than A, it represents a ‘0’. Since external interference usually affects both lines equally, the differential method makes it more resistant to noise.
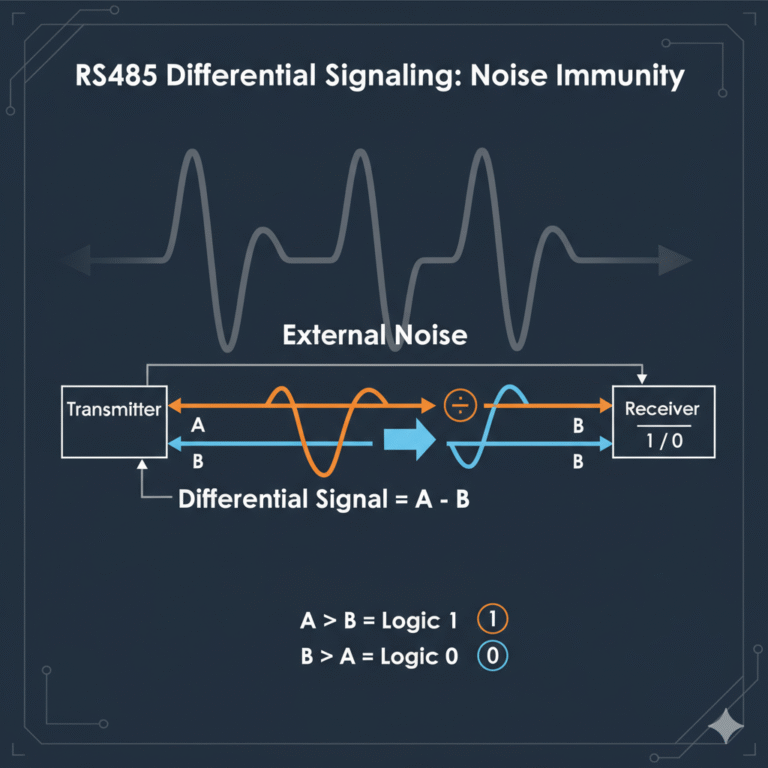
Why the Range of -7V to +7V?
The -7V to +7V range is not arbitrary; it provides an optimal range for the differential voltage. As long as the voltage stays within this range, the receiving chip can reliably identify ‘1’ and ‘0’. If the range is too small, it becomes more susceptible to interference, and if it’s too large, it’s unnecessary.
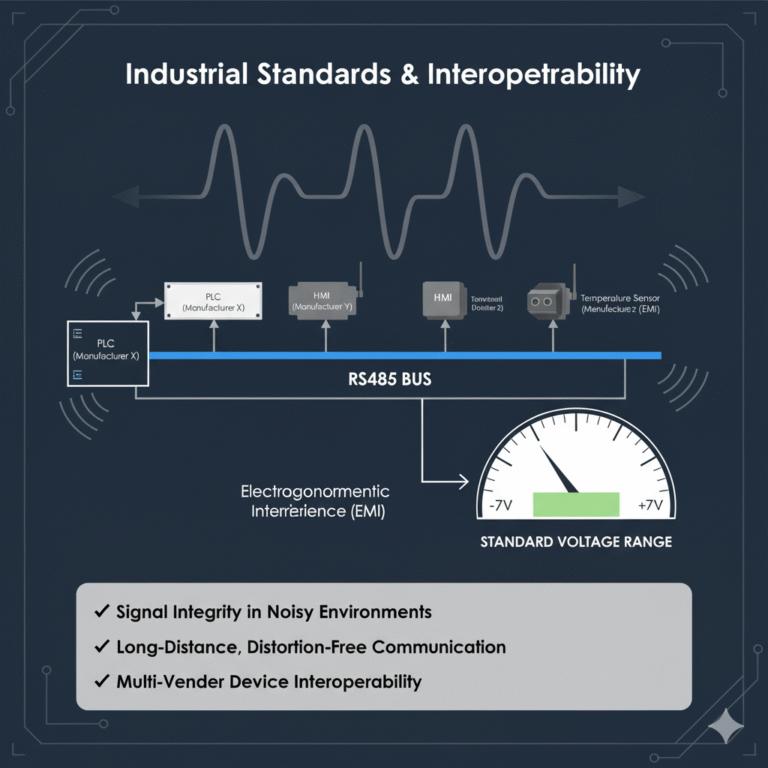
Compliance with Industrial Standards
This voltage range aligns with international industrial communication standards and has been validated through years of practical use. In industrial environments, where electromagnetic interference is common, this voltage range helps maintain signal integrity, ensuring that communication is both long-distance and distortion-free.
Furthermore, multiple devices are often connected to an RS485 bus. A standardized voltage range ensures that devices from different manufacturers can communicate reliably without issues like voltage mismatches.
Balancing Safety and Cost
If the voltage is too high, it can damage the chips. The -7V to +7V range strikes a balance between safety and performance. It’s low enough to prevent over-voltage damage to components and keeps the power consumption lower, which is beneficial for hardware design. Additionally, this range accommodates slight voltage differences in the ground line, ensuring that communication remains stable even in the presence of common-mode voltage fluctuations.
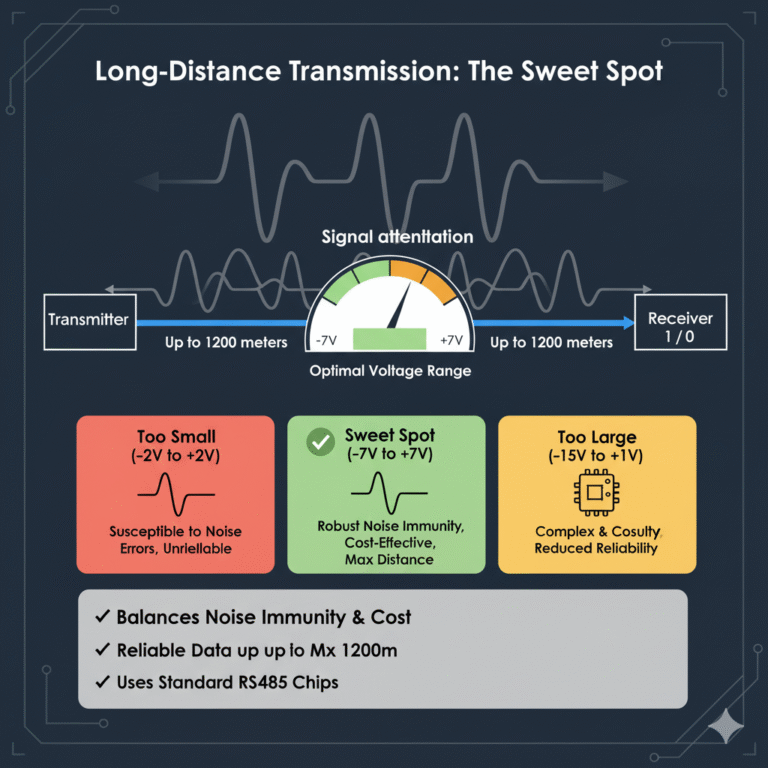
The Sweet Spot for Long-Distance Transmission
RS485 is frequently used for long-distance communication, sometimes over one or two kilometers. As the distance increases, signal attenuation and interference become more significant. A smaller voltage range would lead to signal errors due to noise, while a larger range would require more complex and costly receiver circuits, potentially reducing reliability.
The -7V to +7V range is the perfect compromise, offering a balance between noise immunity and implementation cost. It ensures that signals can travel up to 1200 meters reliably while allowing standard chips to handle the communication effectively.
Practical Tips for Reliable Communication
To maintain proper voltage levels, always make sure to connect the A and B lines correctly, avoiding reverse connections or short circuits. For long-distance transmission, place 120-ohm termination resistors at both ends of the bus to prevent signal reflection. When connecting multiple devices, ensure they share a common ground to minimize voltage differences. Additionally, always choose chips that are fully compliant with RS485 standards.
In my experience, the -7V to +7V voltage range is crucial to the reliable operation of RS485 communication. It’s not just an arbitrary standard—it’s the result of years of engineering wisdom, carefully balancing signal integrity, hardware safety, and cost. Every time I use RS485, I’m reminded of how well this design works.
