1. Importance of Cable Interfaces in Industrial Instruments
Cable interfaces are critical components in industrial automation systems, ensuring reliable power supply and signal transmission between field devices and control systems. Their proper selection directly impacts:
Mechanical stability (preventing cable loosening due to vibration or pull),
Ingress protection (IP65/IP67) against dust, moisture, and corrosive gases,
Electrical safety in harsh environments with high temperature, pressure, or explosive dust,
Measurement stability and device longevity.
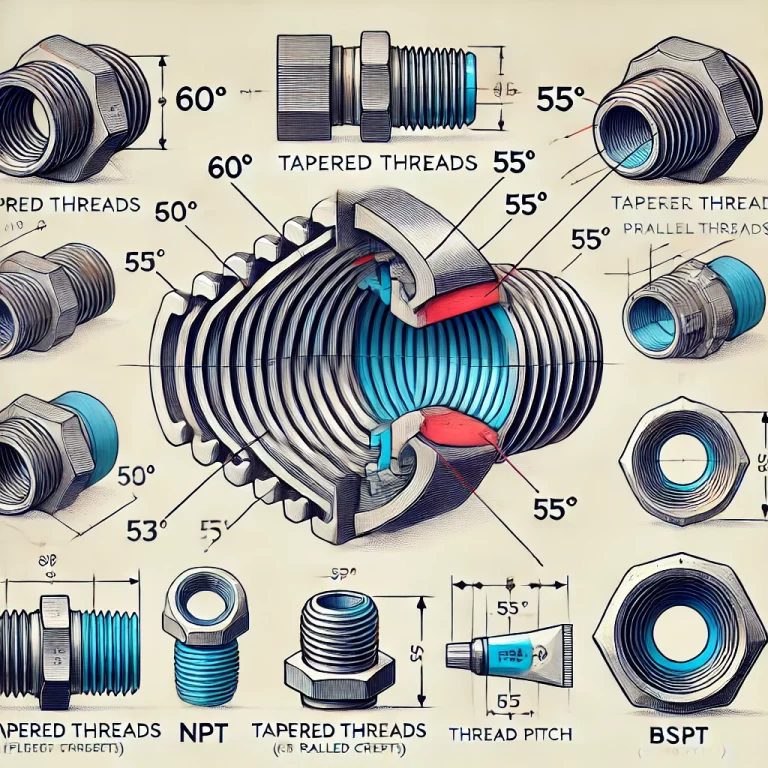
2. Common Cable Gland Thread Types and Matching Cable Diameters
A) Metric Thread (M)
Widely used in pressure transmitters, radar level sensors, and temperature probes.
| Thread Size | Suitable Cable OD | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| M16×1.5 | 4–8 mm | Small sensors, signal lines |
| M20×1.5 | 6–12 mm | Standard for level switches and pressure transmitters |
| M25×1.5 | 10–16 mm | Larger power cables or multi-core instrumentation cables |
💡 Technical Tip: Always ensure proper gasket placement and thread length to maintain sealing and IP rating.

B) American Thread Standards (NPT / BSPP / G)
Common in North American instruments or ANSI-standard devices.
| Thread Size | Suitable Cable OD | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| 1/4″ NPT | 3–6 mm | Signal lines for compact sensors |
| 3/8″ NPT | 4–8 mm | Medium-sized device interface |
| 1/2″ NPT | 6–12 mm | Liquid level switches, pressure transmitters |
| 3/4″ NPT | 10–16 mm | Heavy-duty or multi-core cable connections |
⚠️ Note: NPT threads require PTFE sealant or gaskets to ensure proper sealing, especially in dusty or moist environments.

C) PG Thread (Panzer-Gewinde, German Standard)
Still common in European instruments, with a wide range of sizes.
| PG Thread | Cable OD (mm) | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| PG7 | 3–5 mm | Compact sensor or control lines |
| PG9 | 4–6 mm | Switches and control modules |
| PG11 | 5–8 mm | Medium-sized devices |
| PG13.5 | 6–10 mm | Transmitters and actuators |
| PG16 | 8–12 mm | Most level or pressure sensors |
| PG21 | 12–14 mm | Larger power or signal cables |
🔄 PG threads can often be used interchangeably with M20×1.5, but sealing and dimensional fit should be verified.
3. Key Factors in Cable Gland Selection
Cable Outer Diameter Compatibility
Ensure snug fit for proper strain relief and sealing.
Ingress Protection (IP Rating)
IP65 or IP67 is standard for outdoor or harsh environments.
Material and Corrosion Resistance
For corrosive or high-temperature areas, use stainless steel or high-grade plastics with chemical-resistant seals.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Match thread type with existing panel cutouts or gland plates to reduce on-site rework.
4. Case Example: Selecting a Cable Interface for Level Switches
For an industrial level switch using a 6–12 mm diameter cable, appropriate thread types include:
M20×1.5 (metric)
PG16 (European)
1/2″ NPT (American)
Among these:
M20×1.5 and PG16 offer quick sealing with common glands and better integration with IP-rated enclosures.
1/2″ NPT provides rugged thread but often requires additional sealing materials.

5. Summary
Selecting the correct cable gland thread type and size is vital for ensuring:
Long-term device stability,
Resistance to environmental hazards,
Safe and accurate process measurement.
A clear understanding of metric, NPT, and PG threads—along with cable outer diameter and IP rating considerations—allows engineers and procurement professionals to make informed, safe, and cost-effective decisions for industrial sensor installations.
