In chemical production, the method of connecting pipelines to storage tanks is often seen as a small detail, but it directly impacts the fundamental safety of the facility. This is especially true for hazardous and highly flammable substances like liquid ammonia. A leak caused by unreliable connections can have catastrophic consequences. This article examines the circumstances under which flexible connections are required for storage tanks, how to implement them, and why flexible hose connections are prohibited for liquid ammonia storage tanks. Additionally, we will explore the compliant methods for flexible connections.
Why Flexible Connections are Necessary for Storage Tanks
Flexible connections are required in tank designs to prevent damage caused by uneven settlement or other mechanical stresses. This is addressed by several industry standards:
Petrochemical Enterprise Fire Prevention Design Standard (2018 version) – GB 50160-2008
Clause 6.2.25: The inlet and outlet pipelines of storage tanks should be equipped with flexible connections to prevent damage caused by uneven settlement between the tank and pipeline.
Clause 7.2.18: Pipelines for liquefied hydrocarbons, liquid chlorine, and liquid ammonia must not use flexible hoses due to safety risks, as these hoses can degrade over time or suffer from pressure fluctuations, leading to leaks.
Petroleum Storage Tank Design Code – GB 50074-2014
Clause 9.1.10: Pipelines connected to storage tanks must have sufficient flexibility to meet the stress and load-bearing requirements of the tank.
Tank Area Design Specifications for Petrochemical Storage Systems – SH/T 3007-2014
Clause 5.3.10: The main inlet and outlet pipelines of storage tanks should use flexible connections, and must meet the foundation settlement and seismic resistance requirements.
The purpose of these standards is clear: to prevent accidents caused by settlement-related stress on tank connections.
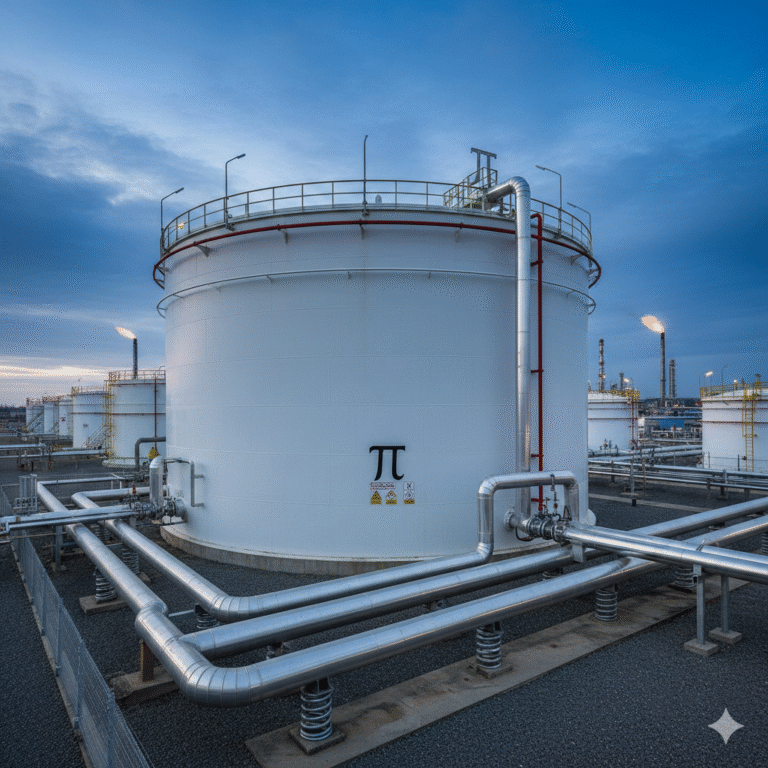

Why Flexible Hose Connections Are Prohibited for Liquid Ammonia
Liquid ammonia is a toxic and highly flammable substance. Using flexible hose connections in its storage and transportation pipelines is explicitly prohibited by the following standards:
Petrochemical Enterprise Fire Prevention Design Standard (GB 50160-2008)
Clause 7.2.18: Flexible hoses are not permitted for the inlet and outlet pipelines of liquid ammonia storage tanks, as these hoses can wear out over time or suffer from pressure changes, leading to potentially catastrophic leaks.
Dangerous Chemicals Safety Production Guidelines (2008)
The guidelines highlight that flexible hoses used for filling dangerous chemicals like liquid ammonia are considered unsafe due to their lack of durability and testing requirements.
Using soft hoses in liquid ammonia systems violates safety regulations and creates significant risks, including toxic exposure, fires, or explosions if the hose deteriorates or fails.
Compliant Methods for Flexible Connections in Hazardous Material Storage
For hazardous materials like liquid ammonia, other compliant flexible connection methods must be employed. These methods ensure safety while maintaining the necessary flexibility to accommodate tank settlement or other mechanical movements:
Pipe Natural Bending Compensation
This method involves designing the pipeline with natural bends (such as π-shaped bends or multi-bend structures) to absorb movements caused by settlement or thermal expansion. This solution is both cost-effective and reliable.
Spring Supports
Spring supports are elastic devices that allow controlled movement of the pipeline while absorbing stress. These are especially useful for maintaining flexibility in systems with significant mechanical forces.
Metal Hose
Metal hoses may be used for some applications, but only when they meet strict pressure and material requirements to prevent failure. They should not be used for highly hazardous chemicals like liquid ammonia or liquid chlorine.
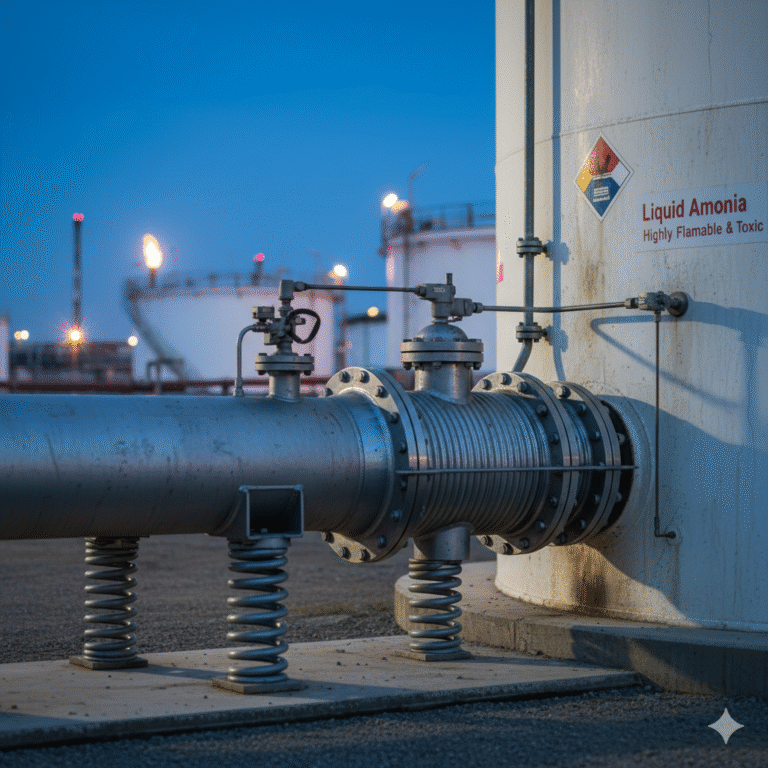
Compliance with Safety Standards
In the case of liquid ammonia storage tanks, flexible hose connections are strictly prohibited. Instead, methods such as pipe natural bending compensation or spring supports must be used to ensure safety and prevent leaks. On the other hand, for other flammable liquids like epoxy chloropropane, compliant methods such as metal hoses, natural bends, or spring supports may be used, provided they meet the necessary safety, seismic, and foundation settlement requirements.
Conclusion
The use of flexible connections in storage tanks is crucial to prevent accidents caused by uneven settlement and other mechanical stresses. For highly hazardous substances like liquid ammonia, the use of flexible hose connections is explicitly prohibited due to safety concerns. Instead, methods like natural pipe bends and spring supports offer compliant, safer alternatives. Always ensure that the selected flexible connection method complies with the relevant safety standards to protect personnel and equipment.
