In modern industrial boilers, there is an often overlooked yet crucial component — the water-cooled wall. While many are familiar with the term, do you know its exact function and significance? In fact, the water-cooled wall not only serves as the boiler’s “protective barrier” but also plays a vital role in steam generation.
1. The First Role of a Water-Cooled Wall
Back in the 1920s, in an effort to reduce combustion losses, the pulverized coal furnace was invented. This furnace, using the “furnace chamber combustion” method, offered high efficiency and complete combustion. However, it introduced a new challenge — excessively high furnace temperatures, which caused the furnace walls to easily accumulate ash.
At high temperatures, the ash in the fuel turns into a liquid or softens, easily adhering to the furnace walls. When the ash builds up, it requires the boiler to be shut down for cleaning, which not only impacts efficiency but may also damage the furnace walls. Traditional refractory bricks had a short lifespan under the high temperature and ash corrosion.
Thus, the water-cooled wall came into play. It effectively cools the furnace walls, significantly reducing the risk of ash buildup, keeping the furnace “cooler” and extending the service life of the boiler. This solution significantly prolongs the operational cycle of the boiler.
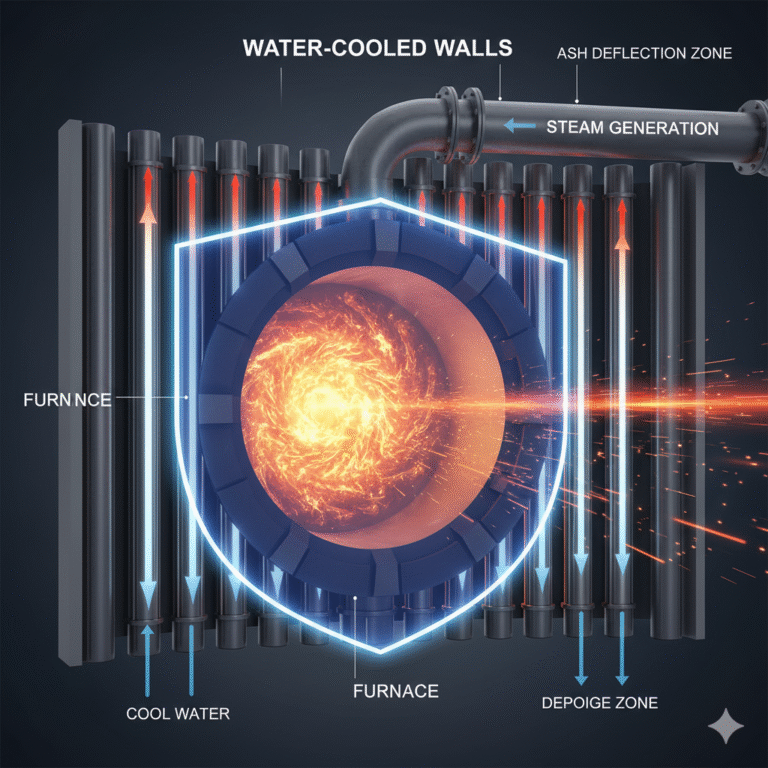
2. The Second Role of a Water-Cooled Wall
Beyond protecting the furnace walls, the water-cooled wall serves an even more critical function — steam generation.
It is the primary evaporative heat surface in a boiler, contributing up to 80%-90% of the total steam output. Due to the intense heat within the furnace, radiative heat transfer is very strong. The heat absorbed by the water-cooled wall is significantly higher than that absorbed by other heat exchange components (such as the convection tubes or economizers), making it a key factor in improving boiler thermal efficiency.
With the introduction of the water-cooled wall, steam production efficiency improves while also saving a large amount of metal material, making the boiler lighter and more cost-effective.
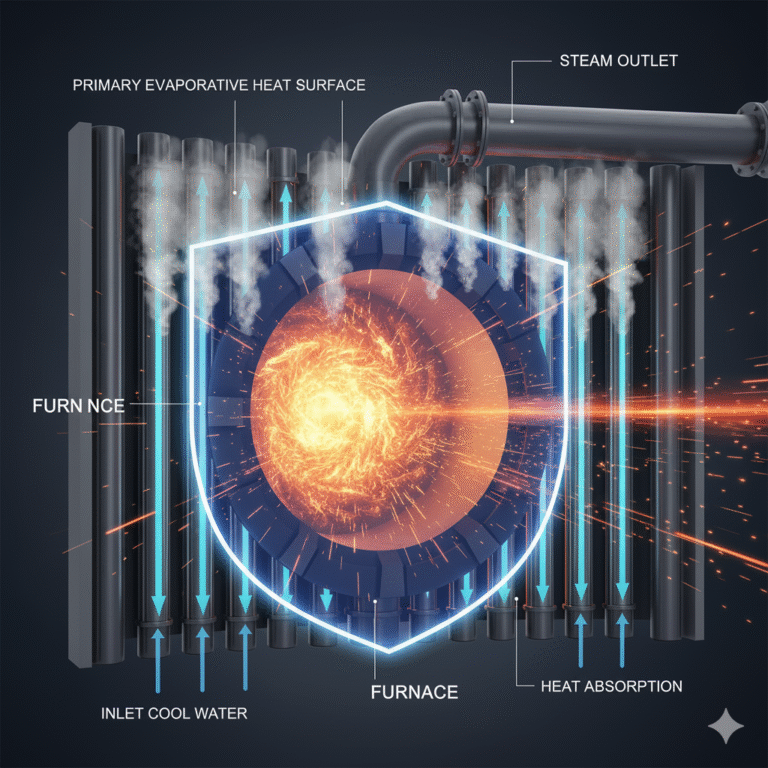
3. Summary
The water-cooled wall is the boiler’s protective shield and steam engine. It not only shields the furnace walls from high-temperature erosion but also efficiently absorbs heat and generates steam. As a core component of modern boilers, it is indispensable for ensuring both the protection and efficiency of the boiler system.
