1. Working Principle of a Torque Sensor
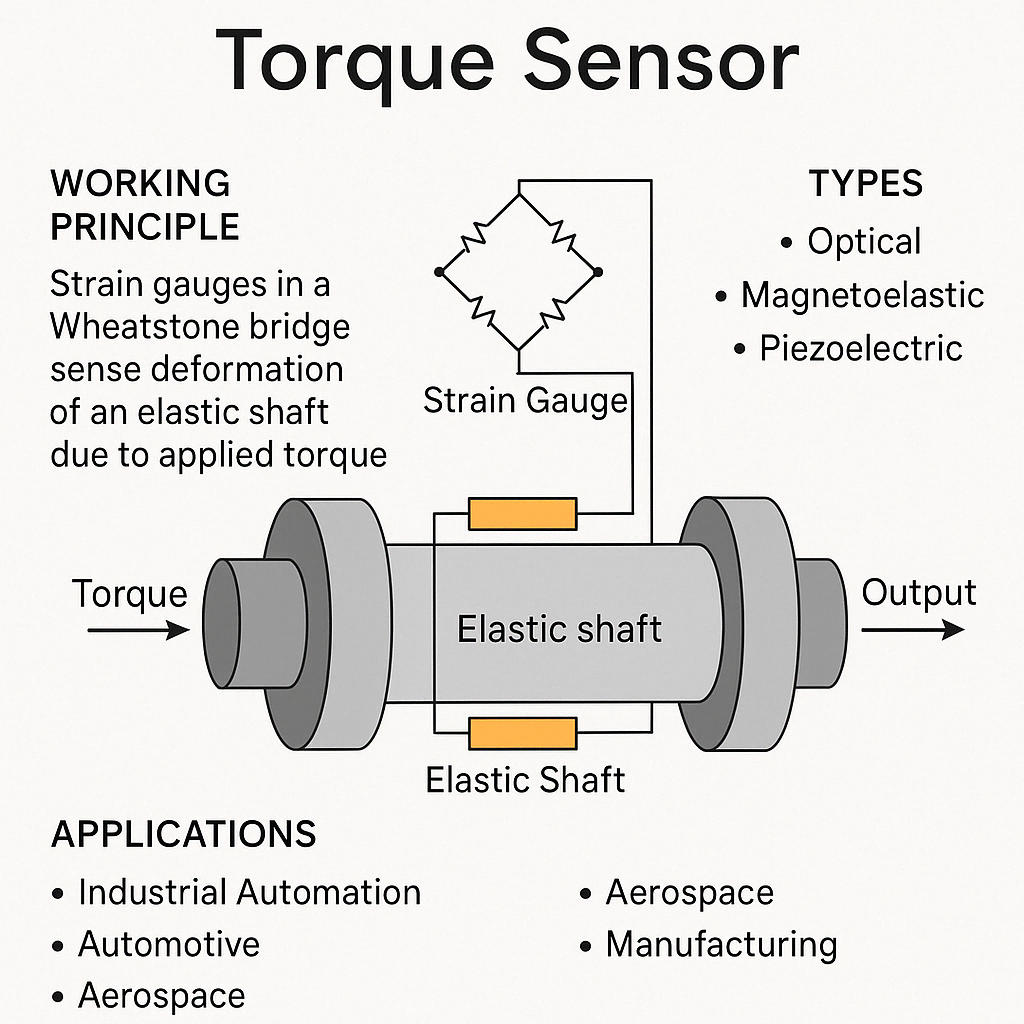
A torque sensor, also known as a torque transducer, is a device that converts the mechanical torque applied to it into a measurable electrical signal. The most common type is the strain gauge torque sensor, which operates based on the Wheatstone bridge principle.
In this design, strain gauges are bonded to a torsionally elastic shaft. When torque is applied to the shaft, it deforms slightly, causing the strain gauges to stretch or compress. This results in a change in their resistance. The strain gauges are configured in a Wheatstone bridge circuit, which outputs a voltage proportional to the applied torque. This voltage signal is then processed and displayed as a torque value.
Other Sensing Technologies:
Besides strain gauge types, there are several other torque sensor technologies:
Optical Torque Sensors: Use light transmission changes through a rotating disc or grating to measure angular deformation.
Magnetoelastic Torque Sensors: Detect changes in magnetic properties of a shaft under torque via electromagnetic induction.
Piezoelectric Torque Sensors: Generate a charge in response to mechanical stress, suitable for dynamic torque measurement.
Each technology is selected based on factors such as required sensitivity, environmental conditions, response time, and cost.

2. Structure and Types of Torque Sensors
Torque sensors are generally composed of two key parts:
Sensing Element: The component that directly detects mechanical deformation due to torque.
Signal Conditioning Circuit: Amplifies, filters, and converts the analog signal into a digital or analog output.
Common types of torque sensors include:
● Strain Gauge Torque Sensors
These are the most widely used types due to their high accuracy, stable output, and mature technology. Ideal for both static and dynamic torque measurement.
● Optical Torque Sensors
Rely on non-contact measurement and are suitable for applications requiring high-speed data transmission or electrical isolation.
● Inductive (Electromagnetic) Torque Sensors
Use changes in inductance caused by shaft deformation to measure torque. Often used in rugged environments and for rotational torque applications.
3. Applications of Torque Sensors
Torque sensors are widely used across many industries, playing a crucial role in process optimization, performance testing, and quality control. Key application areas include:
● Industrial Automation
Used in motors, gearboxes, and transmission systems to monitor torque during operation, ensuring equipment safety and energy efficiency.
● Automotive Industry
Critical in engine testing, transmission analysis, and electric power steering systems. Torque sensors help optimize performance, improve fuel efficiency, and ensure safety.
● Aerospace
Used to measure torque on aircraft engine components, control systems, and rotating machinery to maintain precise control and safety under demanding conditions.
● Manufacturing & Assembly
Integrated into tools such as digital torque wrenches and viscometers, improving accuracy and product quality on production lines.
● Medical Equipment
Torque sensors are used in robotic surgery systems, prosthetic devices, and diagnostic machines where precise force control is necessary.
4. Global Market Overview
According to industry data from Qianzhan Research Institute, the global torque sensor market has been on a steady growth path.
In 2021, the global market size reached USD 6.8 billion.
By 2023, it grew to USD 7.6 billion, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.7%.
● Regional Trends
Asia-Pacific leads the global market, with China, Japan, and South Korea as major contributors. The automotive and robotics industries drive strong demand.
Europe and North America also show stable growth, particularly in aerospace, renewable energy, and precision manufacturing.
● Key Market Players
Global torque sensor manufacturers can be broadly categorized into three major groups:
Europe & US: Companies like ATI Industrial Automation, Kistler, and Bota Systems dominate the high-precision segment.
Japan & South Korea: Brands such as Wacoh-Tech and Robo Tous are strong in robotics and automotive applications.
China: Local manufacturers such as Zero Instrument are emerging players competing in price-sensitive and customized solutions markets.
5. Future Outlook
Torque sensors are becoming increasingly vital in the context of Industry 4.0, smart manufacturing, and electric vehicles. As technologies evolve, future torque sensors will:
Offer higher precision and real-time data acquisition
Feature wireless communication and IoT integration
Support miniaturization for embedded applications
With expanding demand and continuous innovation, torque sensors are poised to become foundational components in next-generation automation and intelligent control systems.
