When it comes to flow measurement in industrial systems, two widely used technologies are vortex flow meters and differential pressure (DP) flow meters. Both have proven reliable across industries, especially for steam, gas, and liquid applications. However, they differ significantly in principle, performance, installation requirements, and cost.
This article compares vortex vs. differential pressure flow meters to help you make an informed selection.
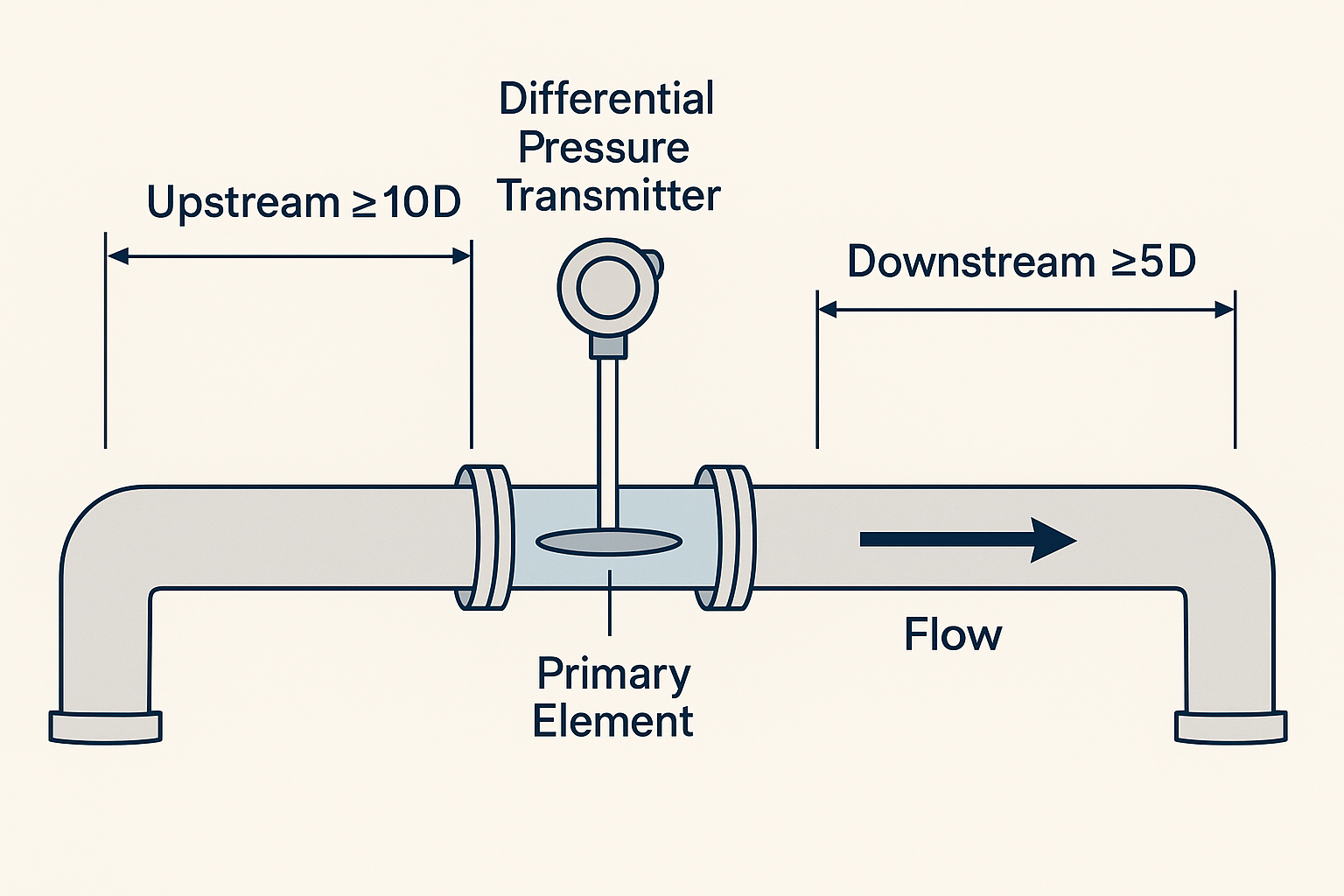
⚙️ 1. Working Principle
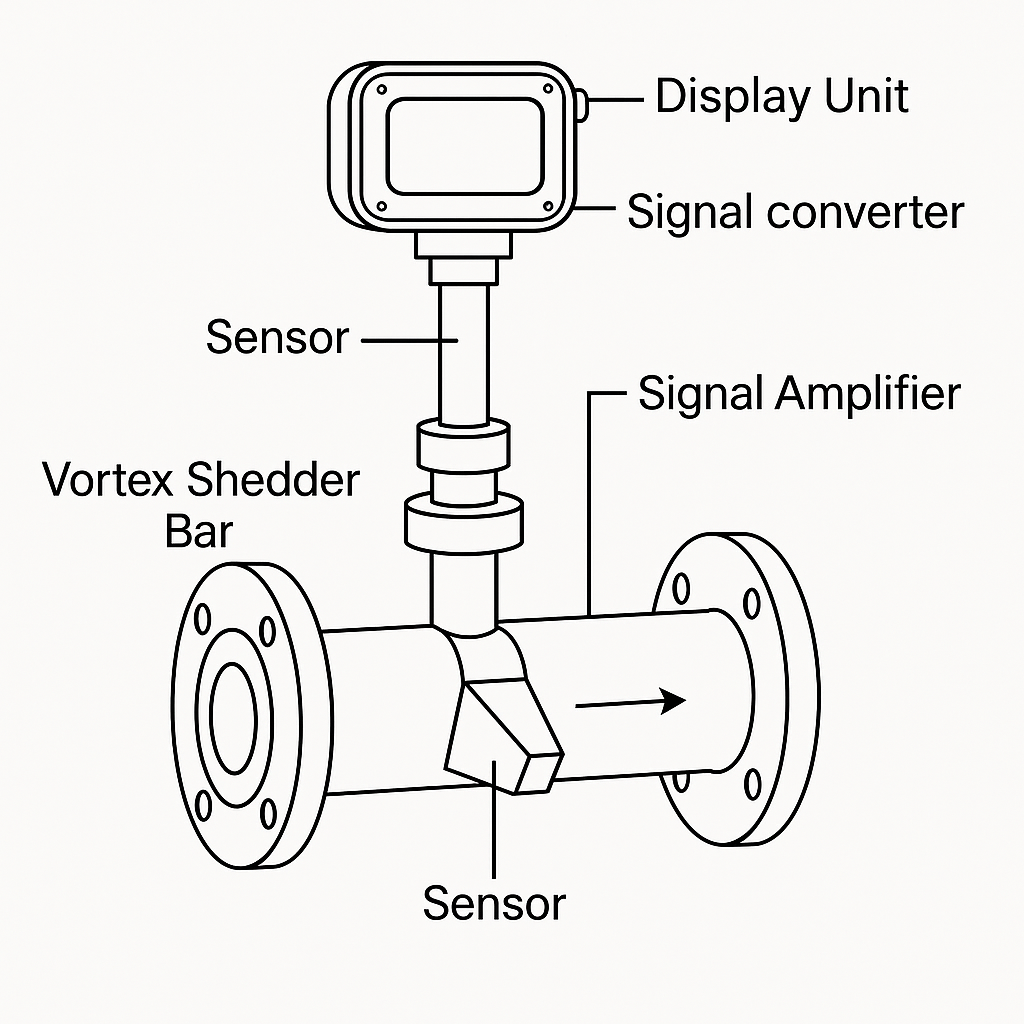
🔸 Vortex Flow Meter
Measures flow by detecting the frequency of vortices shed from a bluff body placed in the fluid stream.
Output: Frequency / 4–20 mA / Pulse
Best for: Steam, clean gases, liquids
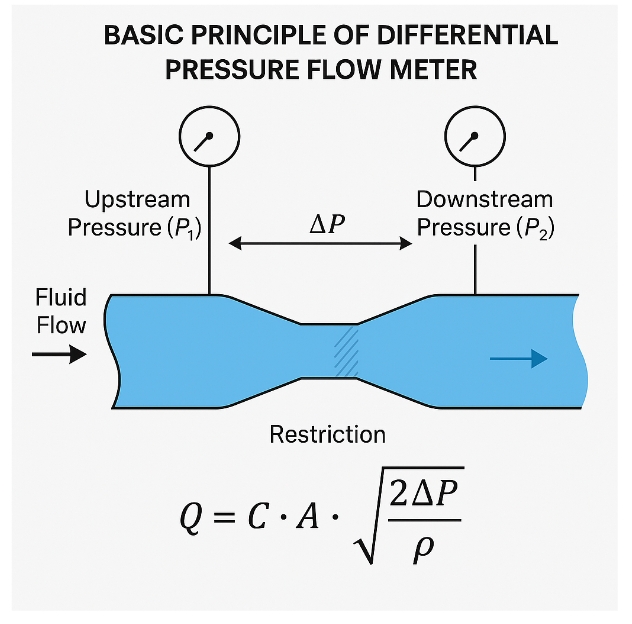
🔹 Differential Pressure Flow Meter
Measures flow rate by detecting the pressure drop across a restriction (e.g., orifice plate, venturi, or flow nozzle) in the pipeline.
Output: Pressure signal, often with transmitter
Best for: High-pressure systems, wide flow ranges
📊 2. Performance Comparison
| Feature | Vortex Flow Meter | Differential Pressure Flow Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | ±0.75% to ±1.0% | ±0.5% to ±2.0% (depends on type) |
| Repeatability | High | High |
| Response Time | Fast (1–2 seconds) | Moderate (depends on damping) |
| Rangeability (Turndown Ratio) | ~10:1 | Up to 3:1 (standard), 10:1 (with smart DP) |
| Sensitivity to Flow Profile | Medium | High (requires careful installation) |
🏭 3. Installation Requirements
| Factor | Vortex | Differential Pressure (Orifice Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Straight-run piping | 15–30 × DN (upstream) | 10–40 × DN (more for elbows/reducers) |
| Pressure Taps | Not needed | Required (2 or 3-point tapping) |
| Mounting Position | Horizontal or vertical | Must align with pressure port orientation |
| Maintenance | Low (no moving parts) | Medium (impulse lines prone to clogging) |
💡 DP meters with impulse tubes often require periodic purging, especially in dirty or wet media.
💸 4. Cost Consideration
| Item | Vortex Flow Meter | DP Flow Meter (Orifice + Transmitter) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Instrument Cost | $$ | $$$ (transmitter adds cost) |
| Installation Cost | Moderate | High (tapping, impulse tubing, manifolds) |
| Maintenance Cost | Low | Medium to High |

🔍 5. Suitable Media and Conditions
| Application Scenario | Recommended Type |
|---|---|
| Saturated or superheated steam | ✅ Vortex or ✅ DP |
| High-viscosity liquids | ❌ Vortex, ✅ DP (carefully) |
| Wet or dirty steam | ⚠️ Both need conditioning |
| Very low flow (low Reynolds number) | ❌ Vortex, ✅ DP with smart transmitter |
| Large pipelines | ✅ Vortex (insertion type) or ✅ DP with averaging pitot |
📌 6. Diagnostics and Smart Features
Vortex meters with digital electronics support self-diagnostics, Modbus/HART communication, and built-in temperature compensation.
DP flowmeters with smart transmitters can offer real-time diagnostics, square-root extraction, and integration into safety systems.
✅ Conclusion
| If you need… | Go with… |
|---|---|
| Easy installation + low maintenance | ✅ Vortex Flow Meter |
| Precise low-flow measurement + proven standard | ✅ Differential Pressure |
| Budget-friendly steam measurement in mid-range | ✅ Vortex Flow Meter |
| High-pressure system with strong engineering support | ✅ DP Flow Meter |
Both technologies are mature and reliable, but your choice should depend on process conditions, maintenance ability, and integration needs. When properly selected and installed, both can deliver accurate and stable flow measurement over many years.
