When selecting a vortex flow meter, choosing the right output signal is as important as choosing the right size or material. Output signals determine how the flow data is transmitted, how easily it integrates into control systems, and what diagnostics or advanced functions are possible.
This article compares the most common output types used in vortex flow meters: 4–20mA analog, pulse output, Modbus RTU, and HART protocol.

🔌 1. 4–20mA Analog Output
Overview:
A current signal proportional to the measured flow rate, widely used in industrial automation.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Signal Range | 4 mA (zero) to 20 mA (full scale) |
| Compatibility | PLCs, DCS, analog controllers |
| Cable Type | Shielded twisted-pair |
| Power Requirement | Loop-powered or external |
Advantages:
Universally accepted and easy to integrate.
Immune to signal loss over long distances.
Simple to scale and configure.
Limitations:
No built-in diagnostics.
One-way communication only.
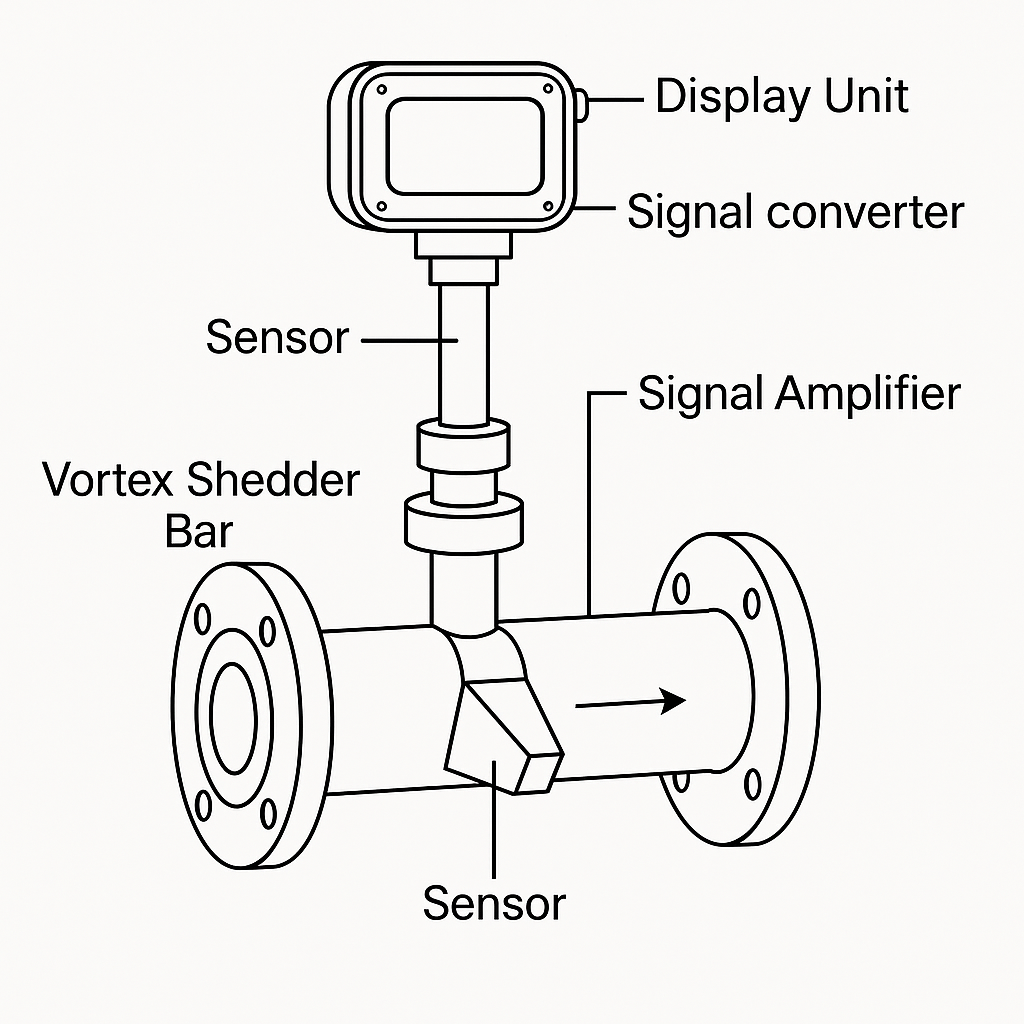
⚡ 2. Pulse Output
Overview:
Digital square-wave signal representing flow totalization. Each pulse = fixed volume.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Typical Signal | Open collector, 5–24V |
| Output Mode | Passive or active |
| Use Case | Flow totalizers, batch control |
Advantages:
Ideal for integrating with counters or batch systems.
High-resolution for accurate total flow.
Limitations:
No real-time flow rate unless externally converted.
Shorter cable runs recommended to prevent signal loss.
🔄 3. Modbus RTU (RS485)
Overview:
A serial digital communication protocol that transmits data via RS485 over twisted-pair wiring.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Modbus RTU (slave mode) |
| Bus Type | RS485, half-duplex |
| Max Devices | Up to 32 per bus |
Advantages:
Transmits multiple parameters: flow, temp, diagnostics.
Cost-effective and widely supported.
Long-distance transmission possible (up to 1200m).
Limitations:
Requires protocol configuration (baud rate, ID, etc.).
Not plug-and-play like 4–20mA.
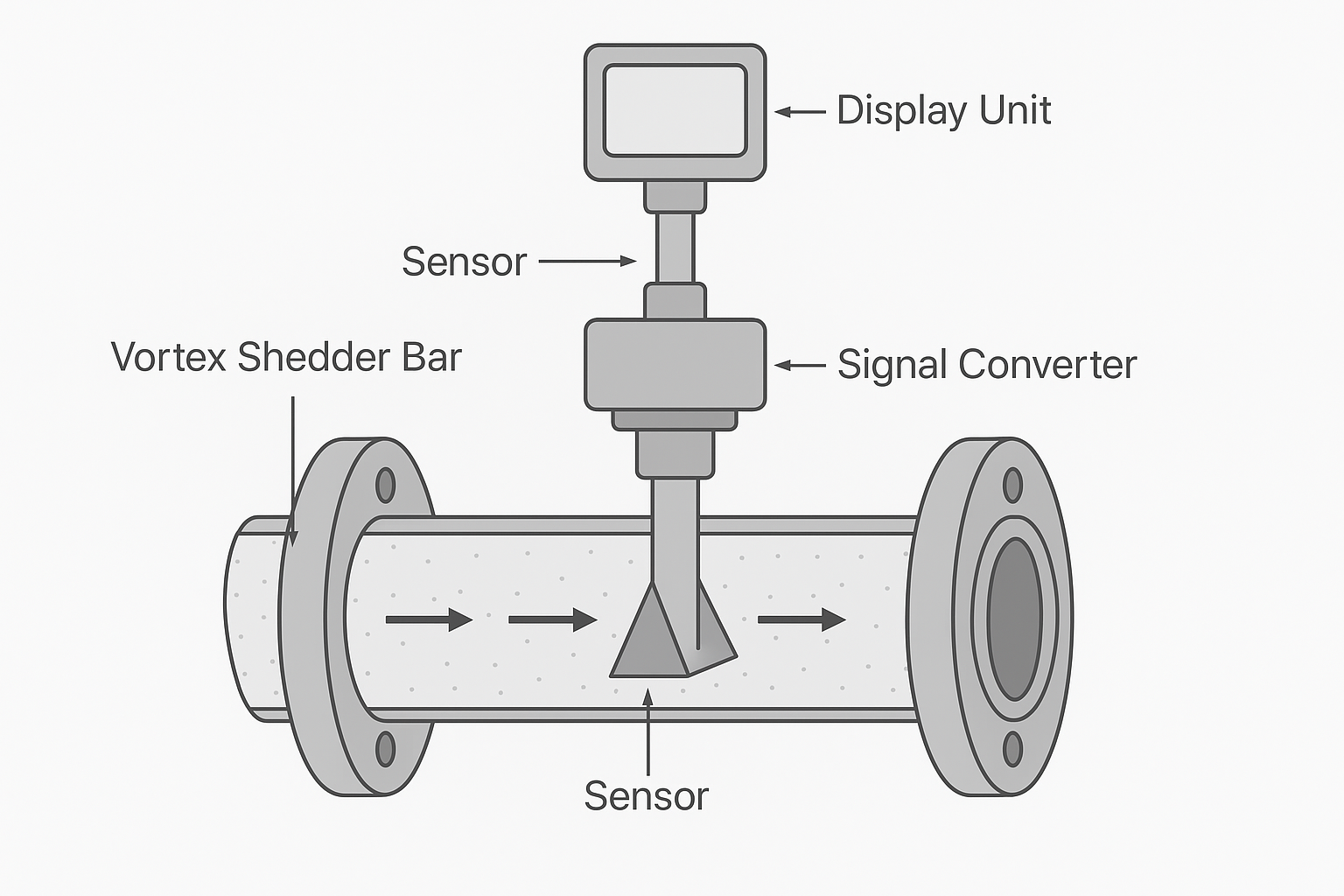
📡 4. HART Protocol
Overview:
Hybrid protocol combining analog 4–20mA signal with a digital communication overlay.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Signal Layer | Analog (4–20mA) + digital FSK |
| Tool Compatibility | HART communicators, handhelds |
| Data Access | Parameters + diagnostics + config |
Advantages:
Enables remote configuration and status monitoring.
Allows advanced diagnostics without separate wiring.
Backward compatible with analog systems.
Limitations:
Slightly more expensive.
Slower data rate than full-digital protocols.
📊 Output Signal Comparison Table
| Feature / Signal | 4–20mA | Pulse | Modbus RTU | HART |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Rate Output | ✅ | ❌ (total only) | ✅ | ✅ |
| Total Flow Output | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Diagnostic Data | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Remote Configuration | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Ease of Integration | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ Medium | ⚠️ Medium |
| Max Cable Length | >500m | <100m | >1200m | ~1000m |
✅ Application Recommendations
| Application Scenario | Recommended Output Type |
|---|---|
| Standard process control | 4–20mA |
| Batch control with flow totalizer | Pulse |
| SCADA system with multi-variable input | Modbus RTU |
| Smart plant or remote diagnostics needed | HART Protocol |
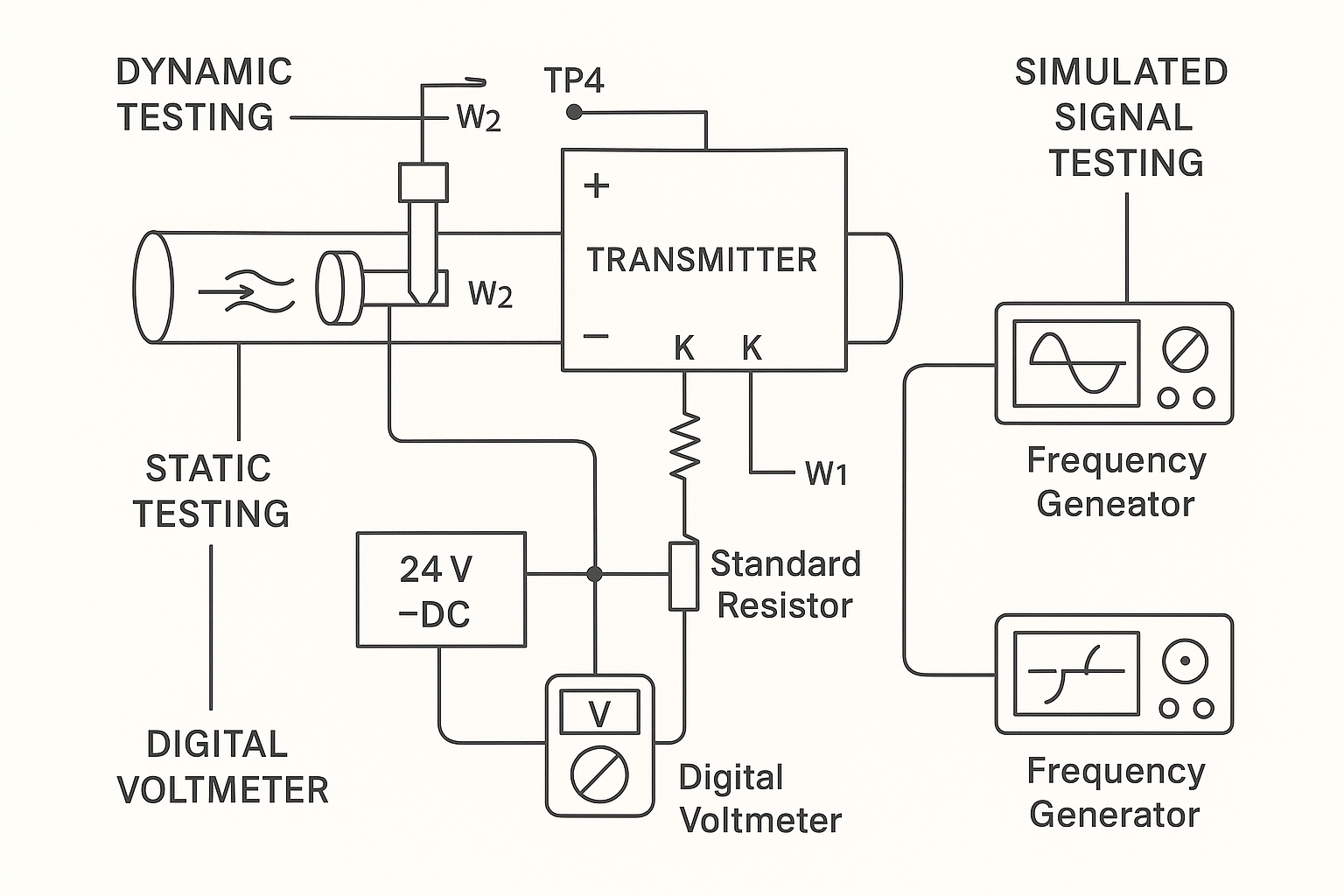
📌 Conclusion
Each vortex flow meter output signal has its unique advantages depending on your system requirements, communication protocols, and budget. For traditional control systems, 4–20mA or pulse outputs work well. For smart automation and diagnostics, Modbus RTU or HART offer added functionality and remote access.
