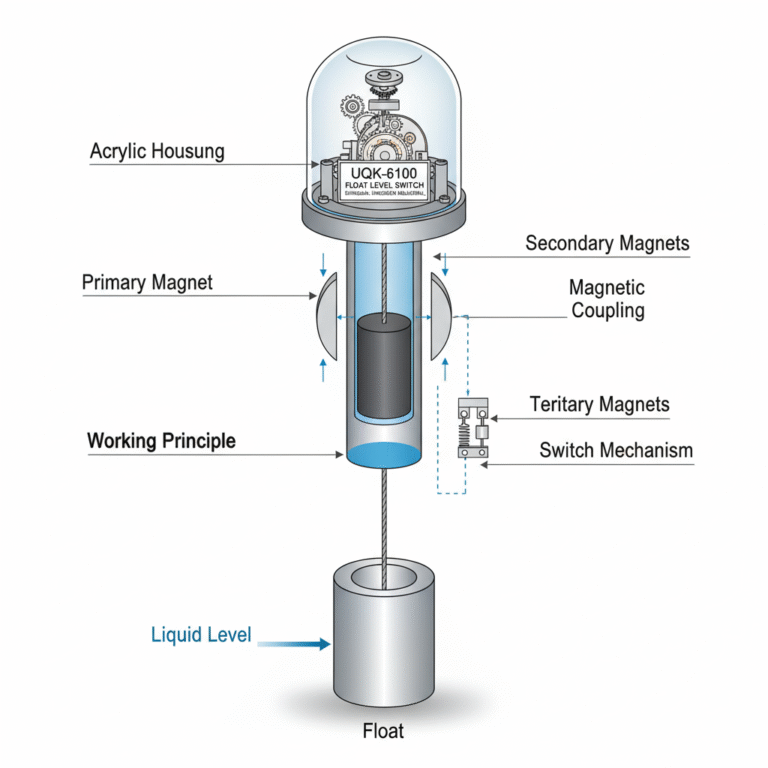
The UQK-6100 series float level switch operates by utilizing the buoyancy principle of Archimedes. As the float moves with the liquid level, the primary magnet inside the pressure tube moves vertically. The mechanical switch, which is adjustable, is located outside the pressure tube in the housing. The movement of the primary magnet triggers a secondary magnet, which in turn drives a tertiary magnet to activate the switch mechanism. This switch will remain triggered until the liquid level falls, at which point the switch returns to its original state.
Working Principle
The float level switch operates on the Archimedes’ principle of buoyancy. As the float rises or falls with the liquid level, a primary magnet moves vertically inside the pressure tube. Outside the pressure tube, a mechanical switch can be adjusted up or down. The movement of the primary magnet triggers a secondary magnet via magnetic coupling, and this magnetic drive activates the tertiary magnet, which in turn operates the switching mechanism. The mechanical switch will stay triggered until the liquid level drops, at which point it returns to its initial state.
Common Models
The UQK-6100 series float level switch includes the Shanghai XingShen UQK61 series, which follows the same working principle described above. The product’s construction and design are robust, ensuring reliable operation in various liquid levels.
Installation and Usage Notes
Top Mount Installation:
Ensure the float and steel cable naturally hang vertically during installation.
Wiring Instructions:
Use a single wire for the ground connection or shield ground.
Routine Maintenance:
Regularly clean the liquid contact parts of the switch to prevent the accumulation of dirt or other debris, which could interfere with the float’s movement.
Common Failures and Troubleshooting
Mechanical Obstruction:
The float may get stuck due to mechanical interference from the container wall or pipe.
Increased Friction:
Impurities, oil, or other substances can stick to the float or guide rod, increasing resistance and preventing smooth movement.
Damage to the Float:
Cracks, water ingress, or imbalance in weight distribution can cause the float to lose buoyancy or become less responsive.
Troubleshooting Steps
Test with a Magnet:
Use a strong external magnet to check if the switch responds. If the switch doesn’t activate, it could indicate a failure of the internal magnet. In this case, the magnetic components or the entire switch module may need to be replaced.
Contact Cleaning:
Open the switch housing and gently sand the contact points to remove oxidation. Check the spring’s elasticity, and if it is loose or if the contacts are worn, replace them immediately.
Recalibration:
Recalibrate the switch’s triggering position to align with the liquid level setpoint. Ensure the guide rod is vertically aligned to guarantee accurate positioning of the magnet during operation.
Product Specifications
Pressure Ratings:
Available in various pressure ratings such as PN2.5MPa, PN6.4MPa, and PN32MPa, suited for different applications.
Material Options:
Materials such as SUS304, SUS316, and SUS316L are available to ensure corrosion resistance in various environments.
Temperature Range:
The float level switch can operate in a temperature range from -46°C to +150°C, with some models capable of higher temperatures up to +260°C depending on materials used.
Installation Sizes:
Available in multiple sizes, including DN20, DN40, DN50, and other configurations, to fit various industrial applications.
