Abstract
Water hammer (hydraulic shock) is a common yet often underestimated phenomenon in both industrial and municipal fluid systems. It can cause serious damage, including instrument failure, flange deformation, and pipeline rupture. This article explains the principles, mechanisms, case studies, international standards, engineering protection strategies, and future development directions for water hammer prevention and control.
1. Nature of Water Hammer
The essence of water hammer lies in the conflict between fluid inertia and system boundary conditions.
When a valve is closed too quickly, a pump suddenly stops, or fluid direction changes abruptly, the flowing liquid is blocked and cannot dissipate energy instantly.
Since liquids are nearly incompressible, this energy is released as a pressure wave, propagating at almost the speed of sound through the pipeline, reflecting and amplifying within the system.
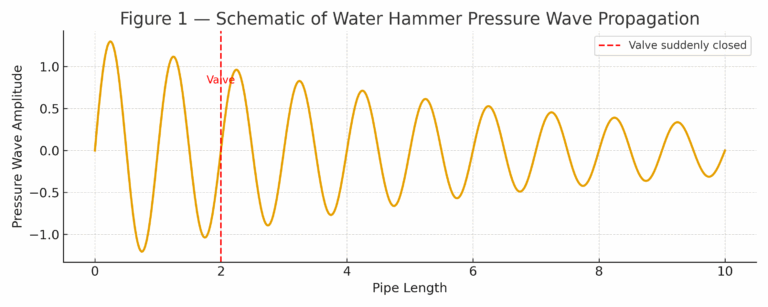
2. Multiple Destructive Mechanisms
Water hammer damage is not limited to a single pressure surge. Instead, it manifests through several mechanisms:
Positive Surge Impact: Sudden pressure rise exceeding material limits.
Negative Pressure Cavitation: Liquid column separation, vacuum formation, bubble collapse causing secondary shock.
Cyclic Fatigue: Alternating positive/negative pressure accelerates fatigue of metals and plastics.
Resonance Amplification: Reflected waves resonate with system natural frequency, magnifying destructive force.
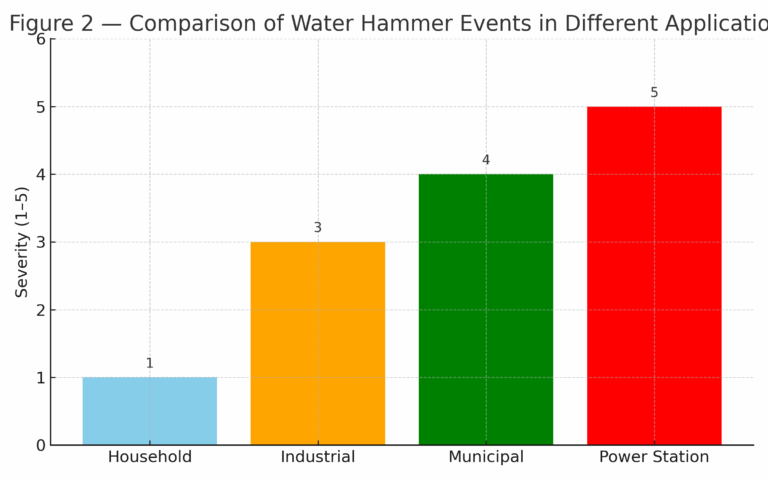
3. Case Studies
Household Networks: “Banging” noise when taps are shut off quickly; may lead to leakage or pipe rupture if joints are aged.
Industrial Pipelines: A chemical plant’s 300 mm cooling water elbow ruptured after sudden pump shutdown, causing 72 hours downtime and millions in losses.
Municipal Water Supply: In New York, a long-distance supply pipeline burst due to water hammer, cutting off supply to hundreds of thousands.
Power Stations: In high-pressure cooling systems, water hammer pressure exceeded the tensile strength of steel, resulting in total pipe failure.
4. International Standards and Codes
Water hammer protection is embedded in global engineering standards:
ISO Standards: Guidelines for hydraulic system surge protection.
ASME Piping Codes: Mandatory transient pressure checks.
EN 805 (Europe): Minimum valve closing time requirements for potable water networks.
API Standards (Oil & Gas): Strict limits on maximum flow velocity.
5. Engineering Protection Strategies
5.1 Design Stage
Control flow velocity to reduce momentum.
Select appropriate pipe diameters to distribute energy.
Optimize routing: avoid long straight runs, include flexible sections.
5.2 Equipment Configuration
Install surge suppressors (air chambers, bladder tanks).
Use buffer tanks to absorb energy via air compressibility.
Apply slow-closing valves and VFD-controlled pumps.
5.3 Operation & Maintenance
Install air-release valves to prevent air lock amplification.
Add pressure-reducing valves to control peak surges.
Conduct regular inspections and replace aging or loose components.

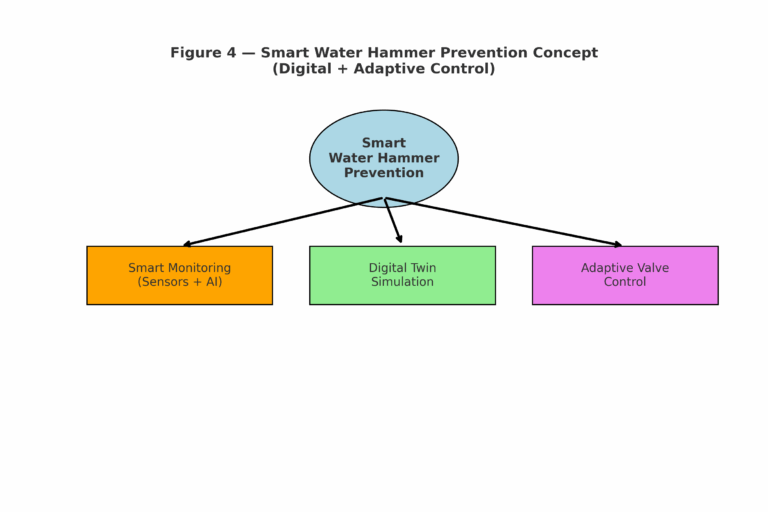
6. Future Development Directions
Smart Monitoring: Pressure sensors and algorithms for real-time detection.
Digital Twin Simulation: Virtual modeling to predict surge behavior.
Adaptive Valve Control: AI-driven valve modulation for dynamic protection.
7. Conclusion
Water hammer is a classic challenge in fluid mechanics and a persistent risk in engineering practice. Preventing it requires a three-pronged approach:
Slow — Gradual valve operation and pump transitions.
Soft — Buffer devices to absorb surge energy.
Stable — Robust design, equipment, and O&M practices.
Next time you hear pipes “bang” in your system, remember it is not just noise — it is the sound of a hidden force that combines fluid dynamics, structural mechanics, and engineering management.
