1. Introduction
In industrial automation and instrumentation control systems, the selection of relay contact types plays a critical role in system reliability and control flexibility. Two commonly used types are:
SPST (Single Pole Single Throw)
DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw)
This article compares the structural differences, wiring diagrams, and application scenarios of SPST and DPDT relays. A practical example using a Ring-11 tuning fork level switch is also included for reference.

2. SPST Relay Wiring
2.1 Structure and Function
An SPST relay includes:
One common terminal (COM)
One contact (normally open NO, or normally closed NC)
Its primary function is to switch a circuit ON or OFF, making it ideal for basic control tasks.
2.2 Wiring Diagram
(See left side of the comparison diagram)
When the relay coil is energized, the COM terminal closes with NO, powering the load (e.g., alarm or actuator).
When de-energized, the contact opens, interrupting the current.
2.3 Typical Applications
Simple alarm circuits
Basic start/stop operations
Low-cost, single-channel control requirements
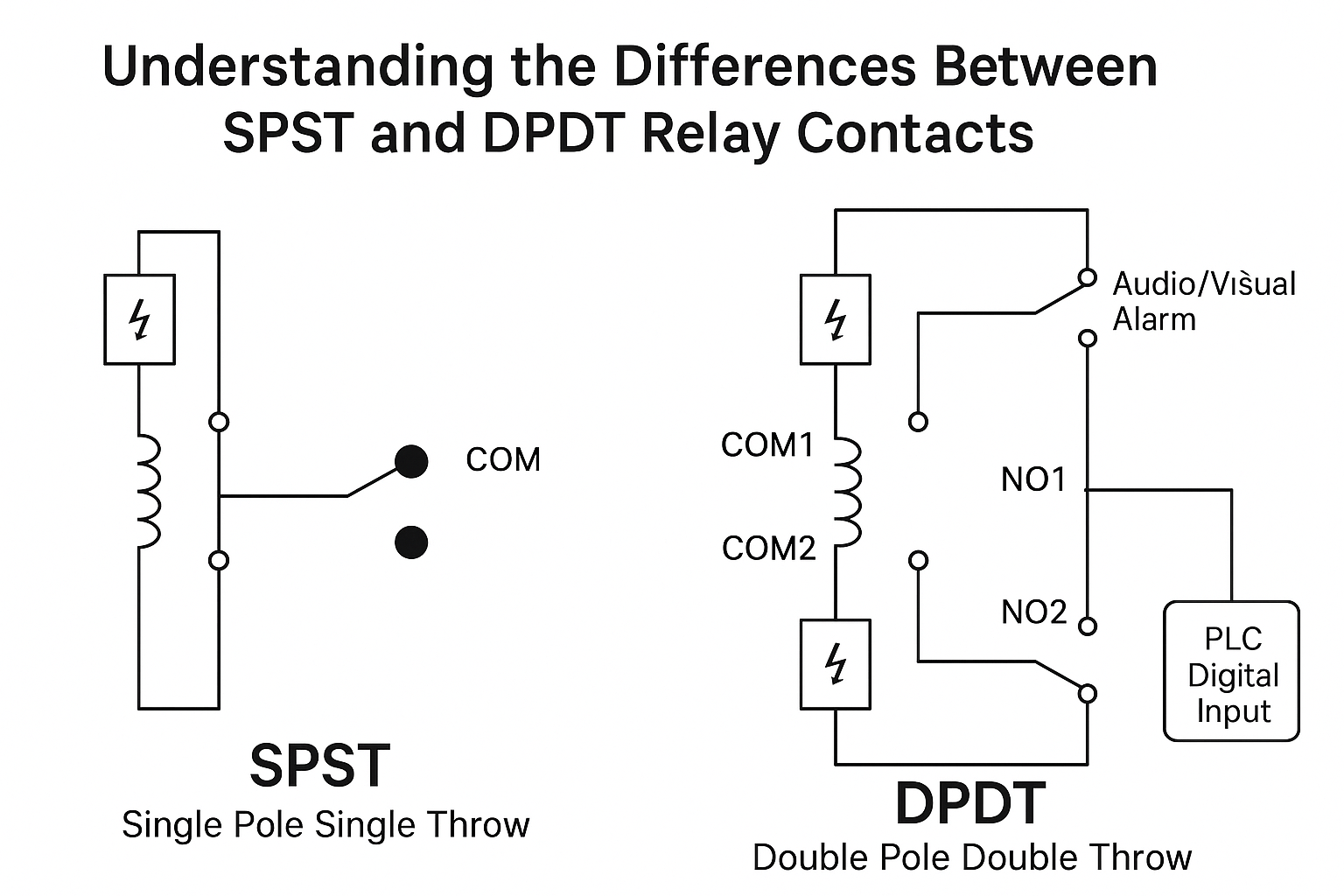
3. DPDT Relay Wiring
3.1 Structure and Function
A DPDT relay consists of two independent SPDT contact sets, each with:
One COM terminal
One NO terminal
One NC terminal
This structure enables simultaneous control of two independent circuits.
3.2 Wiring Diagram
(See right side of the comparison diagram)
When energized:
COM1 switches to NO1
COM2 switches to NO2
When de-energized:
COM1 connects to NC1
COM2 connects to NC2
3.3 Typical Applications
Multi-channel alarm systems
Simultaneous control of audio/visual alarms and PLC input signals
Systems requiring redundant or backup control

4. Case Study: DPDT in Tuning Fork Level Switch
4.1 Application Background
In liquid tank level measurement, the Ring-11 tuning fork level switch uses a DPDT relay output to offer enhanced safety and flexibility. The dual-contact design allows simultaneous signaling to alarm systems and PLC controls.
4.2 Wiring Example
Output Group 1 (COM1–NO1–NC1)
Connected to an audio/visual alarm
Triggers high-level alarm when liquid rises beyond a threshold
Output Group 2 (COM2–NO2–NC2)
Connected to a PLC digital input
Triggers automatic shut-off of inlet pump or valve when the tank is full
This dual-circuit configuration ensures redundancy: even if one system fails, the other can still function, significantly increasing system reliability.
4.3 Why Choose DPDT Output?
Offers flexibility for dual signaling
Enhances safety in critical applications (chemical, food, water treatment industries)
Provides fail-safe operation with redundancy logic
Allows separation of logic circuits for diagnostics or logging

5. Ring-11 Relay Wiring Diagram
This diagram illustrates how the two independent DPDT relay groups in Ring-11 enable multi-channel control for different output needs (e.g., alarms + PLC).
[COM1] → [NO1] → Audio/Visual Alarm
[COM2] → [NO2] → PLC Digital Input
Relay coil powered by control loop (e.g., 24VDC)
The user can choose between NO or NC terminals depending on control logic. Ring-11 also features IP66/IP67 protection and optional food-grade certification, making it suitable for sanitary applications like beverage or pharmaceutical tanks.

6. Summary & Selection Advice
| Feature | SPST Relay | DPDT Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Contact Sets | 1 | 2 |
| Channels Controlled | Single | Dual |
| Wiring Complexity | Low | Moderate |
| Redundancy Capability | No | Yes |
| Typical Use | Basic ON/OFF control | Alarm + PLC signal split |
| Cost | Lower | Slightly higher |
| Recommended For | Simple circuits | High-reliability applications |

Recommendation:
When designing control systems requiring higher reliability, multi-channel output, or redundancy (especially in fluid level control), DPDT relays offer significant advantages. Devices like the Ring-11 tuning fork level switch with DPDT output provide enhanced safety and control flexibility.
