Modbus is one of the most widely used communication protocols in industrial automation and control systems. Among its various implementations, Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) and Modbus TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) are two prominent options. While they serve similar purposes, they differ in their communication mechanisms, application scenarios, and performance characteristics. This article explores these differences in detail to help you understand which implementation might be the best fit for your needs.
1. Communication Mechanism
Modbus RTU Modbus RTU uses serial communication over RS-232, RS-485, or RS-422 interfaces. Data is transmitted in binary format, making it compact and efficient. Communication is synchronous, with devices communicating in a master-slave architecture where only one device can transmit data at a time.
Modbus TCP Modbus TCP operates over Ethernet networks, leveraging the TCP/IP protocol stack. It encapsulates Modbus frames within TCP packets, enabling communication between devices over a local area network (LAN) or even across the internet. This implementation supports simultaneous communication between multiple devices.
2. Transmission Medium
Modbus RTU The protocol relies on physical serial communication mediums, typically using twisted-pair cables for RS-485 connections. It is suited for shorter distances, with a maximum range of about 1200 meters under ideal conditions.
Modbus TCP Modbus TCP utilizes Ethernet cables, wireless networks, or fiber optics. Its range is theoretically unlimited since it depends on the capabilities of the network infrastructure, such as routers and switches.
3. Network Topology
Modbus RTU Modbus RTU supports a master-slave configuration. A single master device communicates with multiple slave devices, usually in a daisy-chain or bus topology. The communication is sequential, meaning the master must poll each slave in turn.
Modbus TCP Modbus TCP uses a client-server model, allowing multiple clients to communicate with a single server or multiple servers simultaneously. This flexibility is particularly useful in modern industrial setups that require real-time data monitoring and control.
4. Speed and Performance
Modbus RTU The speed of Modbus RTU is limited by the baud rate, which typically ranges from 1200 to 115200 bits per second (bps). The sequential nature of the protocol can result in communication delays when multiple devices are connected.
Modbus TCP Ethernet networks offer significantly higher speeds, starting at 10 Mbps and often reaching 1 Gbps or more. Additionally, the ability to handle multiple simultaneous connections reduces latency and enhances system responsiveness.
5. Data Frame Format
Modbus RTU Data in Modbus RTU is transmitted in compact binary frames, which include a start bit, address field, function code, data, and cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for error detection. Precise timing between frames is crucial to avoid communication errors.
Modbus TCP Modbus TCP embeds Modbus frames into TCP packets. Since TCP/IP inherently ensures reliable delivery and error checking, additional CRC fields are unnecessary. This simplifies the protocol at the cost of slightly larger data packets.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
Modbus RTU Modbus RTU is limited to 247 slave devices due to address constraints. Expanding the network requires careful planning to avoid signal degradation and address conflicts.
Modbus TCP Modbus TCP networks can accommodate significantly more devices, as Ethernet networks support larger address spaces and more robust routing capabilities. The ability to integrate with IT systems and cloud platforms further enhances its scalability.
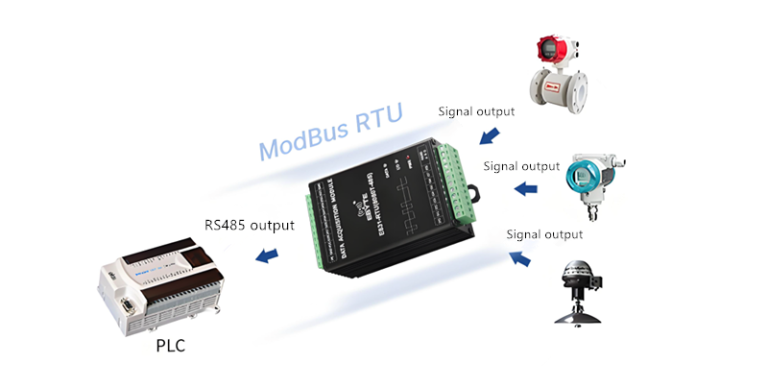
7. Applications
Modbus RTU This implementation is ideal for traditional industrial environments where devices are located relatively close to each other, such as PLCs, sensors, and actuators. It is also cost-effective for small-scale systems that do not require high-speed communication or extensive networking.
Modbus TCP Modbus TCP is better suited for modern industrial systems that require high-speed data exchange, integration with SCADA systems, and remote monitoring. It is particularly effective in applications that span large distances or involve multiple control layers.
8. Hardware Requirements
Modbus RTU Devices must be equipped with serial communication ports, such as RS-485 interfaces. External converters may be needed for compatibility with non-serial systems.
Modbus TCP Ethernet connectivity is required. Most modern industrial devices come with built-in Ethernet ports, and existing Modbus RTU devices can be integrated into Ethernet networks using Modbus gateways.
Summary Table
| Feature | Modbus RTU | Modbus TCP |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Type | Serial (RS-232/RS-485) | Ethernet (TCP/IP) |
| Speed | 1200 to 115200 bps | 10 Mbps or higher |
| Network Topology | Master-Slave | Client-Server |
| Maximum Distance | 1200 meters (RS-485) | Unlimited (network-based) |
| Scalability | Limited to 247 devices | Highly scalable |
| Error Checking | CRC | TCP/IP built-in |
| Applications | Local industrial systems | Large-scale, modern systems |
Choosing the Right Protocol
When deciding between Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP, consider the following factors:
Distance and Speed: For short distances and low-speed requirements, Modbus RTU is sufficient. For faster communication over longer distances, Modbus TCP is the better choice.
Network Complexity: If your system involves multiple control layers and extensive networking, Modbus TCP offers greater flexibility and scalability.
Legacy Systems: Modbus RTU is often the default choice for legacy equipment, but it can be integrated with Ethernet networks using gateways.
Cost: Modbus RTU implementations are typically more cost-effective for small-scale systems.
Understanding these differences will help you select the protocol that aligns with your system’s requirements, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
