1. Introduction
Threads play a critical role in connection, sealing, and power transmission across mechanical manufacturing, piping systems, and equipment maintenance. Due to differences in standards, thread profiles, and application environments, engineers must carefully select the appropriate thread type.
This document provides a systematic comparison of NPT, PT (BSPT), G (BSPP), TR, S, M, ZG, and RC threads, highlighting their structure, sealing capability, and typical applications.
2. Thread Types
2.1 NPT — American National Pipe Taper Thread
Standard: ASME B1.20.1
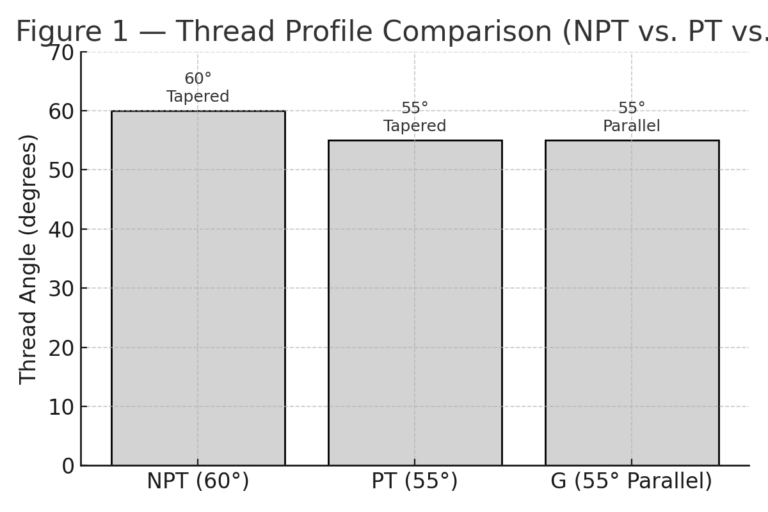
Thread Angle: 60°
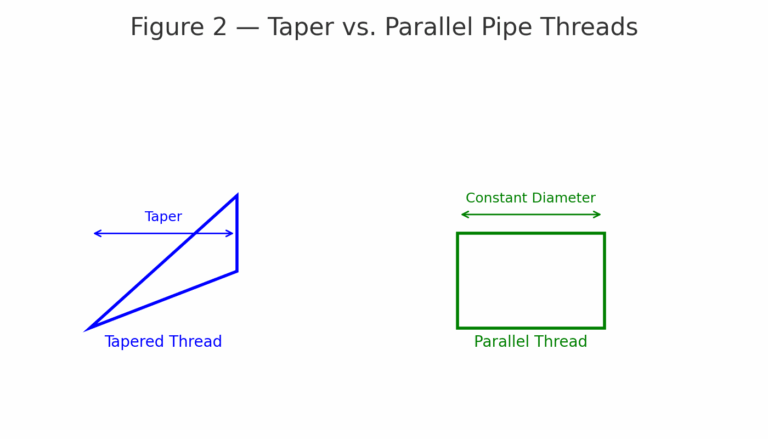
Structure: 1:16 taper, metal-to-metal sealing by interference fit
Applications: Widely used in oil, gas, and fluid pipelines in North America
Key Feature: High sealing reliability, suitable for high-pressure conditions
2.2 PT (BSPT) — British Standard Pipe Taper Thread
Standard: ISO 7-1 / JIS B 0203
Thread Angle: 55°
Structure: 1:16 taper, sealing by interference
Applications: Common in water, air, and low-to-medium pressure pipelines in Europe and Asia
Comparison with NPT: Similar sealing principle, but different thread angle → not interchangeable
2.3 G (BSPP) — British Standard Pipe Parallel Thread
Standard: ISO 228-1
Thread Angle: 55°
Structure: Parallel thread, requires sealing material (gasket, O-ring)
Applications: Building water supply, HVAC, fire protection systems
Key Feature: High universality, but sealing depends on auxiliary materials
2.4 TR — Trapezoidal Thread
Standard: ISO 2901, 2902, 2903
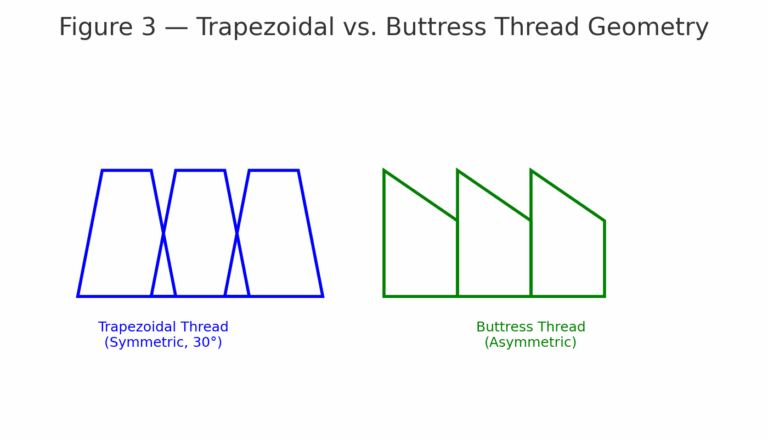
Thread Angle: 30° (sometimes 29°)
Structure: Symmetrical trapezoid, high load-bearing capacity, low friction
Applications: Machine tool lead screws, jacks, heavy-duty transmission
Key Feature: Designed for power transmission, not sealing
2.5 S — Buttress (Saw-Tooth) Thread
Standard: ISO 2903
Profile: Asymmetrical, one flank vertical, one inclined
Applications: Hydraulic presses, jacks, structures with one-directional loads
Key Feature: Optimized for unidirectional force transmission
2.6 M — Metric ISO Thread
Standard: ISO 68-1 / ISO 261
Thread Angle: 60°
Structure: Triangular profile, straight thread
Applications: General mechanical fastening, the most widely used thread type worldwide
Key Feature: Highly standardized, suitable for universal mechanical connections
2.7 ZG — Obsolete Chinese Pipe Taper Thread
Standard: GB 7306 (old standard, replaced by ISO 7/1 RC/RP)
Thread Angle: 55°
Note: Used in legacy equipment, gradually phased out
2.8 RC — ISO Tapered Internal Pipe Thread
Standard: ISO 7-1 (equivalent to BSPT internal)
Thread Angle: 55°
Structure: Tapered internal thread, sealing with matching external thread
Applications: Building, chemical, and mechanical low-to-medium pressure systems
Key Feature: Reliable sealing, widely adopted in international projects
3. Comparison Table
| Thread Type | Angle | Shape | Sealing Method | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPT | 60° | Taper | Self-sealing | Oil & gas pipelines (North America) |
| PT (BSPT) | 55° | Taper | Self-sealing | Water, air pipelines (Europe, Asia) |
| G (BSPP) | 55° | Parallel | Requires gasket/O-ring | Water supply, HVAC |
| TR | 30° | Trapezoidal | Non-sealing | Machine tools, jacks |
| S | Asymmetric | Buttress | Non-sealing | Presses, one-way load |
| M | 60° | Metric ISO | Non-sealing | General fasteners |
| ZG | 55° | Taper | Self-sealing | Legacy Chinese standard |
| RC | 55° | Taper | Self-sealing | Low-medium pressure pipelines |
4. Engineering Selection Guidelines
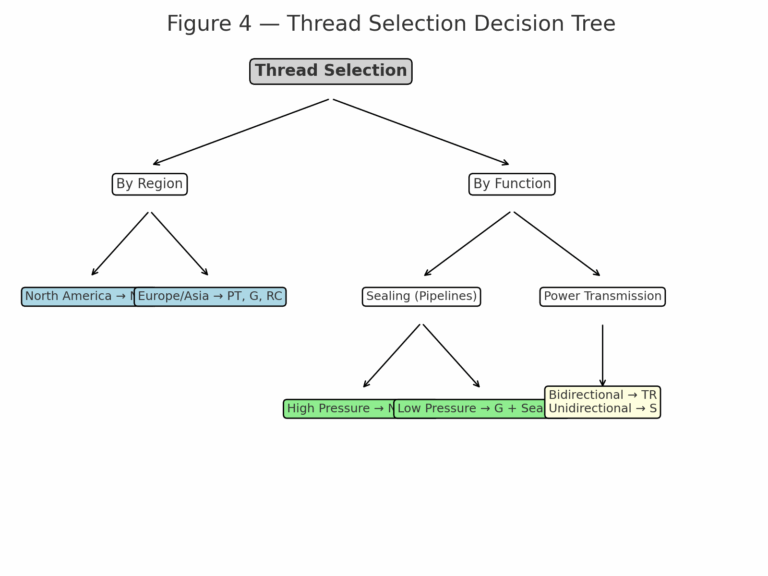
By Region:
North America → NPT
Europe & Asia → PT, G, RC
By Pressure & Medium:
High pressure & hazardous fluids → NPT, RC
Low pressure water/air → G with sealing material
By Mechanical Function:
Power transmission → TR (bidirectional), S (unidirectional)
5. Conclusion
Different thread types vary in angle, sealing performance, and applicable scenarios. Understanding these differences ensures pipeline sealing reliability, efficient power transmission, and safe equipment operation.
In practice, engineers should consider regional standards, medium characteristics, working pressure, and load type to select the most appropriate thread type.
