RS-485 is one of the most widely used industrial communication standards. It provides a robust, long-distance and noise-resistant method for data exchange between field devices, PLCs, controllers and sensors. Due to its differential transmission and multi-drop capability, RS-485 is considered a reliable backbone for distributed industrial control systems.
1. What Is RS-485?
RS-485 is a differential serial communication protocol defined by the EIA/TIA standard.
It uses a pair of balanced signal lines (A and B) to transmit data, which significantly improves noise immunity and allows long-distance communication.
Key advantages include:
Strong anti-interference capability due to differential signaling
Long transmission distance, typically up to 1200 m
Stable communication in harsh industrial environments
Supports multi-drop networks (up to 32 or more nodes depending on driver capability)
Cost-effective cabling and installation

2. How Many Cores Does an RS-485 Cable Need?
The number of cores depends on the device requirements, communication topology, and whether power or additional signals need to be transmitted through the same cable.
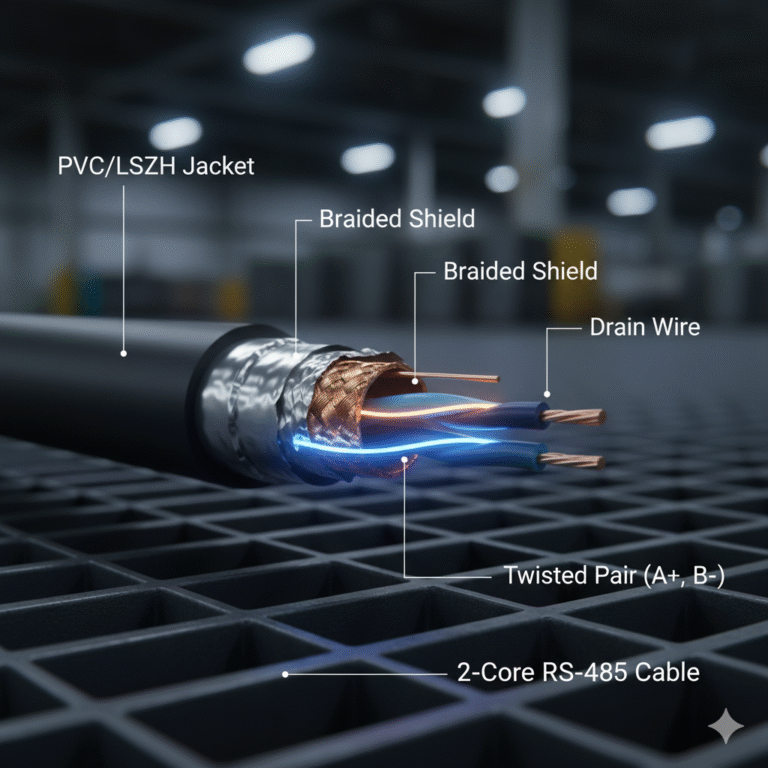
(1) 2-Core RS-485 Cable
Typical structure: One twisted pair (A+ and B–).
This is the minimum requirement for RS-485 differential communication.
Application scenarios:
Basic two-wire RS-485 networks (half-duplex)
Modbus-RTU communication
Long-distance sensor data transmission
Environments where only data communication is needed
Notes:
Although RS-485 can technically work without a ground wire, adding a reference ground is recommended to reduce common-mode noise.
(2) 3-Core RS-485 Cable
Includes:
A+
B–
GND (signal reference ground)
Advantages:
Improves communication stability, especially in high-noise environments
Reduces common-mode voltage differences between devices
Typical applications:
Industrial instruments
Flow/level/pressure transmitters
Modbus devices installed far from the control room
(3) 4-Core RS-485 Cable
Contains two twisted pairs.
One pair is used for data (A/B), and the additional pair may be used for:
Power supply (24 V / GND)
Auxiliary signals
Full-duplex RS-485 communication (less common)
Applications:
Sensors or transmitters requiring both communication and power in the same cable
Systems requiring higher noise immunity
RS-485 devices with full-duplex capability
(4) 6-Core or 8-Core RS-485 Cable
These cables provide more pairs and are used in more complex or multi-function systems.
Advantages:
Can transmit multiple signal types simultaneously
Supports redundant communication paths
Better shielding and noise isolation (more twisted pairs)
Typical usage:
Multi-parameter transmitters
Instruments requiring communication + power + control signals
Special automation systems with higher EMC requirements
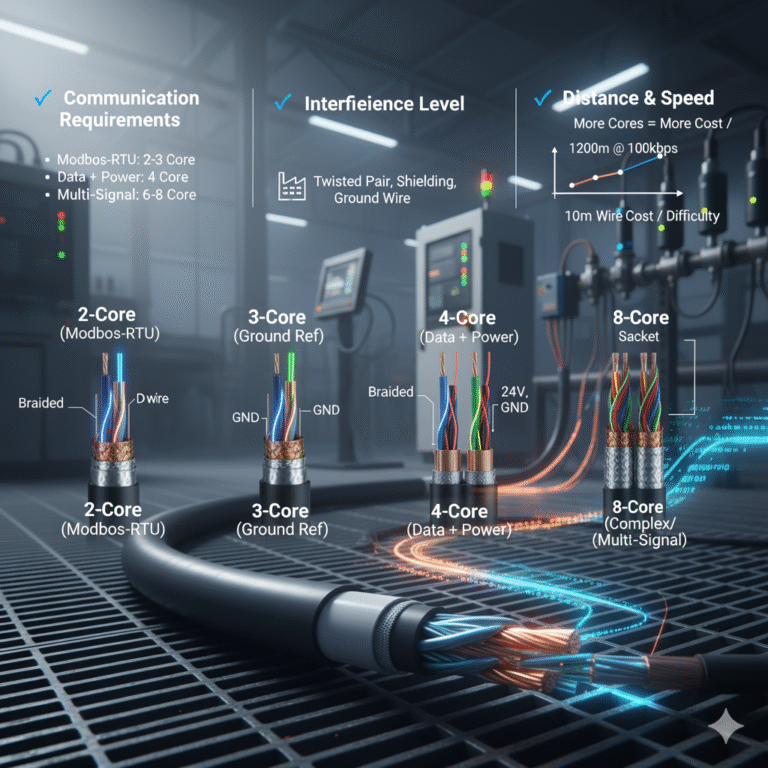
3. How to Select the Proper RS-485 Cable Core Count
When choosing a cable, consider:
✔ Communication requirements
Basic Modbus-RTU → 2 or 3 cores
Communication + power → 4 cores
High-performance or multi-signal applications → 6–8 cores
✔ Interference level
Noisy industrial environments should use:
Twisted pairs
Shielding (foil + braid)
Ground reference wire
✔ Transmission distance and speed
RS-485 supports:
100 kbps @ 1200 m
1 Mbps @ 100 m
Longer distances require better shielding and lower baud rates.
✔ Cost vs. functionality
More cores increase:
Cable diameter
Installation difficulty
Cost
Select “appropriate and sufficient”; more is not always better.
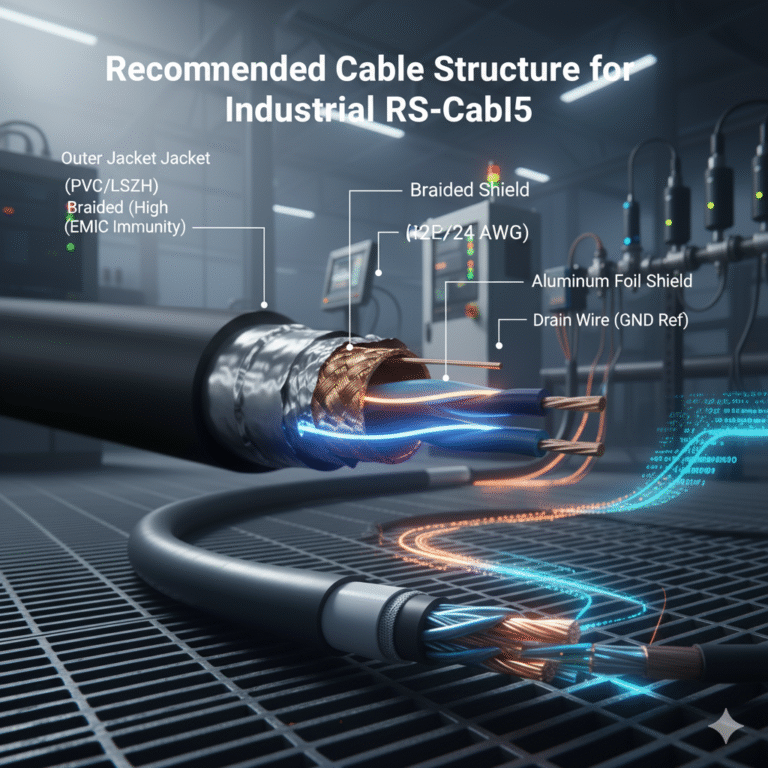
4. Recommended Cable Structure for Industrial RS-485
A professional RS-485 cable typically includes:
1–2 Twisted pairs (22–24 AWG)
Aluminum foil shielding
Optional braided shield (improves EMC immunity)
Drain wire / GND reference wire
PVC or LSZH jacket
This structure ensures stable communication even in high-noise environments such as plants, power stations, wastewater facilities and chemical industries.
Summary
RS-485 communication is reliable, economical and suitable for long-distance industrial data transmission. Selecting the correct cable depends on:
Required signals
Distance
EMC environment
Whether power needs to be included in the same cable
2-core cables are suitable for basic communication,
3-core and 4-core cables offer better stability or combined power supply,
while 6-core and 8-core cables are used for more complex applications.
