When it comes to British Standard Pipe (BSP) threads, two types stand out: BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) and BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel). These thread types are common in pipe fittings and other industrial applications, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. Understanding their differences is essential for selecting the right thread type for a specific application, especially when factors such as pressure resistance and sealing are critical.
1. Basic Thread Types: BSPT vs. BSPP
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) and BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) refer to two types of threads under the BSP standard. Although they may appear similar at first glance, there are key structural differences between them:
- BSPT: BSPT threads are tapered, meaning they have a conical form with a gradually decreasing diameter along the length of the thread. This tapering allows for tight engagement, leading to self-sealing properties.
- BSPP: BSPP threads, on the other hand, are parallel (or straight). The diameter of BSPP threads remains constant along the entire length of the thread. Because of this, they require additional sealing measures for applications involving pressurized fluids.
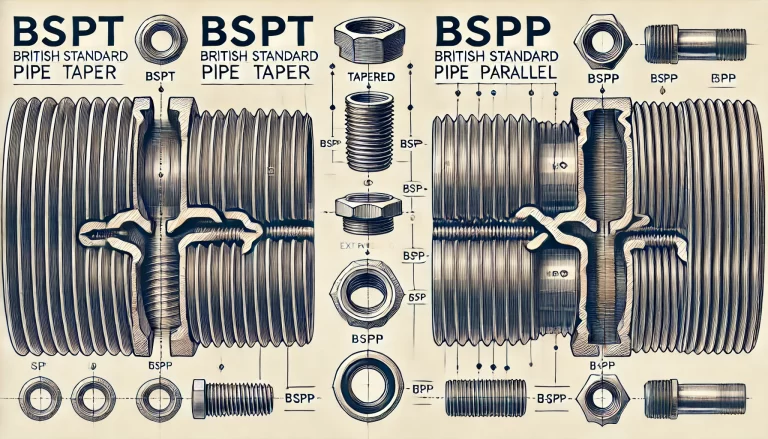
2. Sealing Mechanisms
The sealing mechanisms of BSPT and BSPP threads are among the most significant differences:
BSPT (Tapered Threads): With BSPT threads, the conical shape enables a tight, wedge-like fit when two threads are engaged. As the male and female threads are tightened, the taper creates pressure at the point of contact, achieving a self-sealing effect. This makes BSPT threads ideal for applications requiring a high-pressure seal without additional sealing materials, such as certain hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
BSPP (Parallel Threads): BSPP threads do not self-seal because they are parallel and have a constant diameter. To create an effective seal, BSPP threads generally require the use of a soft sealing component, such as an O-ring, gasket, or bonded washer. This extra sealing element fills any gaps and provides the necessary seal for fluid containment. BSPP threads are widely used in systems where pressure is moderate and where a leak-proof connection is necessary but does not rely on the thread profile alone.
3. Applications and Usage
The differences in design and sealing methods mean BSPT and BSPP threads are suited to different types of applications:
BSPT Applications:
- BSPT threads are ideal for applications that require high sealing reliability under pressure without external seals. Examples include hydraulic systems, air compressors, gas fittings, and pressurized fluid transport lines.
- The self-sealing property of BSPT threads makes them particularly useful for applications where external seals might wear out or where maintaining a perfect seal is critical for safety.
BSPP Applications:
- BSPP threads are commonly used in water supply systems, plumbing, and connections where pressures are not extreme or where the system is not directly pressurized.
- Because BSPP threads rely on O-rings, gaskets, or washers for sealing, they are often chosen for systems that need a reliable seal at lower pressures or where the use of external seals is acceptable.
4. Installation and Compatibility
Despite sharing the BSP standard, BSPT and BSPP threads are not interchangeable due to their differing thread profiles.
BSPT Installation: The tapered design of BSPT threads means they create a seal through the wedging effect as they are tightened. It is important to avoid over-tightening, as excessive force can damage the threads and compromise the seal.
BSPP Installation: Because BSPP threads are parallel, they must use a secondary sealing mechanism. O-rings, washers, or other seals should be placed between the mating surfaces during installation. Unlike BSPT threads, BSPP threads do not require special attention to the thread engagement angle during installation, but care should be taken to ensure that the sealing element is correctly positioned.
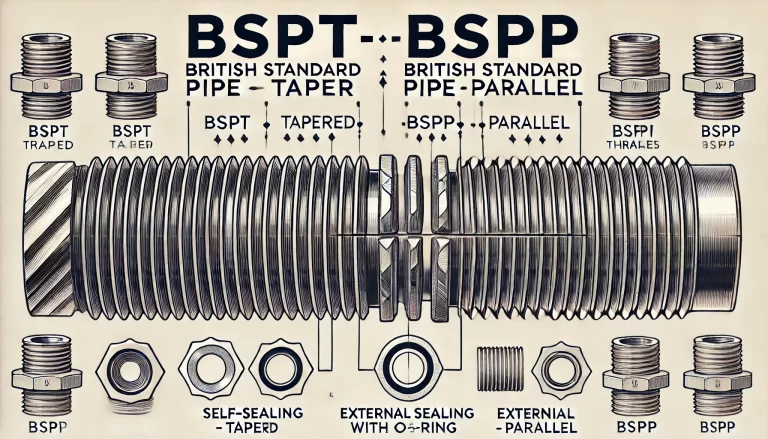
5. Compatibility and Conversion
Though BSPT and BSPP are both based on the British Standard, they are generally not directly compatible due to the different thread angles and sealing requirements. There are specialized adapters that allow for connections between BSPT and BSPP fittings, but this is typically only necessary when working with pre-existing components in a system where both types are present.
Summary of Key Differences Between BSPT and BSPP Threads:
| Feature | BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) | BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Shape | Tapered (conical) | Parallel (straight) |
| Sealing Mechanism | Self-sealing by taper fit | Requires an O-ring, gasket, or washer |
| Applications | High-pressure systems | Moderate-pressure systems |
| Installation | Tightened to create a wedge seal | Seals using external components |
| Compatibility | Not interchangeable with BSPP | Not interchangeable with BSPT |
Conclusion
BSPT and BSPP threads serve unique purposes based on their structural and sealing characteristics. BSPT threads, with their tapered design, provide a reliable seal in high-pressure environments without the need for additional sealing materials. BSPP threads, with a parallel structure, rely on external sealing components, making them ideal for applications with moderate pressure requirements. Proper understanding of these differences is crucial for selecting the correct thread type for your specific application, ensuring both efficiency and safety in fluid systems.
By choosing the appropriate thread type, you can prevent leaks, ensure reliable connections, and maintain the integrity of your system over time.
