How they work
These meters operate on the same principle as turbine meters for liquids, as
described in section 5.3.1. Because of the relatively low kinetic energy of a
flowing gas, however, it is necessary to make a significant difference in shape.
A turbine meter for gases, as shown in Figure 5.11, always has a rotor with a
large central hub. This causes the flowing gas to accelerate through the meter,
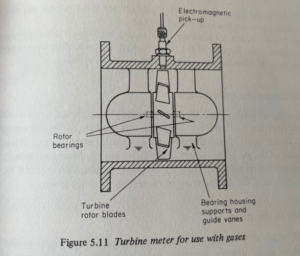
and to concentrate its impelling force on the blades near the perimeter, where
they will generate the maximum possible torque.
In addition, the bearings have to be designed to run for long periods in the air
with very little friction. Some meters are made with aerostatic bearings, but
conventional low-friction mechanical bearings appear to be more widely used at
present.
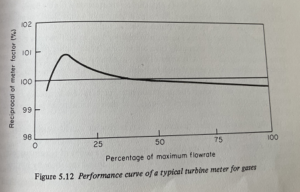
Because of the increased relative importance of bearing friction, turbine meters
for gases are rather less linear than liquid turbine meters, as is shown in Figure 5.12. In the larger sizes, they give highly repeatable readings and maintain their accuracy over quite a long period of time.
Some turbine meters for gases are fitted with a mechanical readout system, through a gear train. Because of the extra friction imposed, these do not have quite the same performance as those with an electrical pick-up.
Advantages and Disadvantages
They share the advantages and disadvantages already attributed to turbine meters for liquids, except that they are rather less sensitive to upstream disturbances, and that they are practically insensitive to changes in the viscosity of the gas being metered. The latter is a significant advantage since it means that they do not need the very frequent recalibration required by turbine meters used for the metering of oil at high accuracy levels.
When to use Them
Their main sphere of usefulness is in the accurate metering, for purposes of sale
or taxation, of large volumes of natural gas and gaseous chemicals at moderate of
high pressure. In this field, they are beginning to challenge the long-established
supremacy of the orifice plate, because, although more expensive, they offer
better accuracy and rangeability than the orifice plate.
