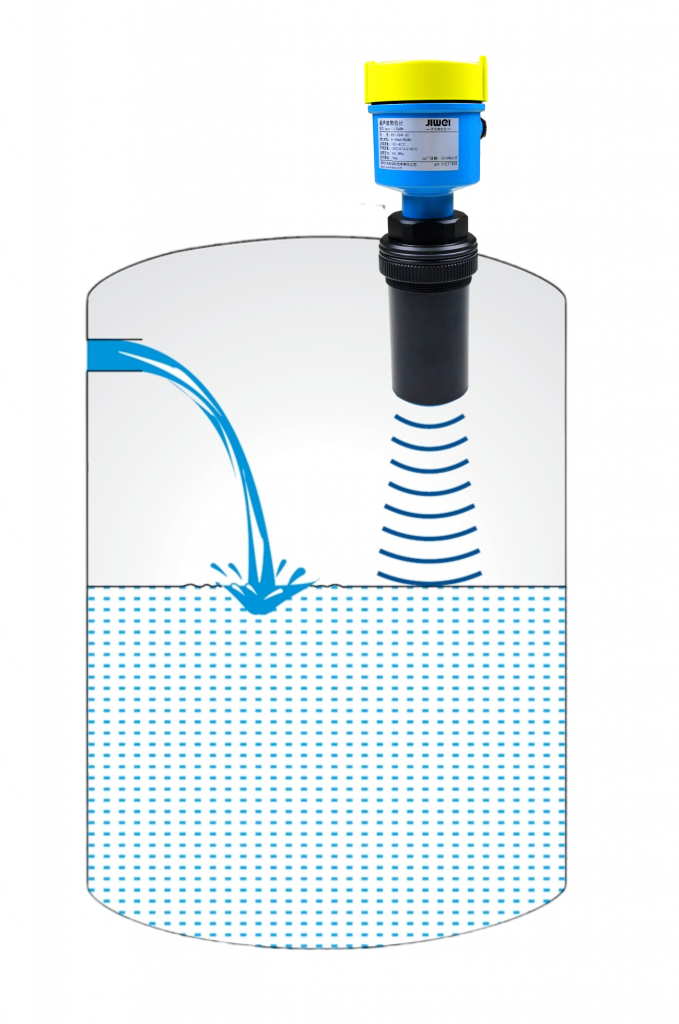
I. Working Principle
The ultrasonic level gauge is an instrument that measures the height of liquid by utilizing the reflection principle of ultrasonic waves. It is mainly composed of an ultrasonic transducer (probe), an electronic processing unit, and a display unit. When the instrument is in operation, the ultrasonic transducer emits ultrasonic waves of a certain frequency.
These ultrasonic waves propagate in the liquid and are reflected when they encounter the liquid surface. The reflected waves are received by the same transducer and converted into electrical signals.
By measuring the time required for the ultrasonic waves to travel from emission to reception (i.e., the transit time), combined with the propagation speed of ultrasonic waves in the liquid, the distance traveled by the ultrasonic waves can be calculated.
Then, the distance from the liquid surface to the transducer can be determined, thereby obtaining the liquid level height.
II. Causes of Faults
Ultrasonic level gauges may encounter various faults during use. The following are some common causes of faults and their troubleshooting methods:
1. No display or abnormal display Cause of fault: Power failure, damage to the display unit or problems with the connection lines. Troubleshooting method: Check whether the power supply is normal, whether the display unit is damaged, and whether the connection lines are firm.
2. Inaccurate measurement value Cause of fault: Contamination of the ultrasonic transducer, foam or gas layer on the liquid surface, incorrect setting of the ultrasonic wave propagation speed, and influence of liquid temperature changes on the ultrasonic wave speed.
Troubleshooting method: Clean the surface of the transducer to ensure there are no interfering factors on the liquid surface; Set the correct ultrasonic wave propagation speed according to the liquid type; Consider the influence of liquid temperature changes on the ultrasonic wave speed and make corresponding compensations.

3. Large fluctuations in measurement values Cause of fault: Large fluctuations on the liquid surface, presence of vibration sources or electromagnetic interference around.
Troubleshooting method: Reduce the fluctuations on the liquid surface; Stay away from vibration sources or electromagnetic interference sources; Consider installing a protective cover on the transducer to reduce external interference.
4. Insufficient measurement range Cause of fault: Improper selection of transducer, inappropriate installation position or significant attenuation of ultrasonic waves due to changes in liquid properties.
Troubleshooting method: Select the appropriate transducer based on the measurement range and liquid properties; Adjust the installation position to ensure the best propagation path of ultrasonic waves in the liquid; Consider the influence of changes in liquid properties on the propagation of ultrasonic waves and make corresponding adjustments.

5. Communication failure Cause of fault: Fault in communication lines, mismatch of communication protocols or incorrect instrument settings. Troubleshooting method: Check whether the communication lines are intact; Ensure that the communication protocol matches the host computer or control system; Check whether the instrument settings are correct.
6. Other faults Depending on the specific instrument model and the usage environment, there may be other causes of faults.
When troubleshooting faults, the instrument manual and relevant technical materials should be referred to, and possible causes should be gradually investigated.

In practical applications, when a fault occurs in the ultrasonic level gauge, the display status and indicator light status of the instrument should be observed first.
Based on the fault phenomenon, the possible causes of the fault can be preliminarily judged.
Then, troubleshoot one by one according to the above troubleshooting methods until the cause of the fault is found and the problem is solved.
