1. Introduction
In modern industrial production, transmitters have become an indispensable category of measuring instruments. By integrating transmitters into traditional equipment, operators can achieve easier operation and maintenance, enhanced accuracy, and improved safety performance.
In automated control systems, transmitters are considered a critical component, ensuring the stable and efficient operation of the entire system.
Temperature is one of the most fundamental parameters in industrial monitoring and control. As industries demand higher reliability and accuracy in temperature measurement, temperature transmitters play an increasingly vital role.
2. Industrial Applications
Temperature transmitters are widely used across multiple industries, including:
Petroleum and petrochemicals
Chemical plants
Metallurgy and steelmaking
Mechanical and electrical manufacturing
Ceramics and glass production
Power generation
Aerospace and aviation
Food processing
Medical engineering
In these fields, temperature transmitters enable precise temperature monitoring and process control, and they can also be integrated with other instruments for comprehensive process automation.
3. Key Advantages of Temperature Transmitters
The importance of temperature transmitters is closely tied to their performance advantages:
Reliable Signal Transmission
Strong resistance to electromagnetic and radio-frequency interference, ensuring stable data transfer.Configurable Measuring Range
Adjustable span settings to fit specific applications, allowing higher measurement accuracy.Standardized Output Signals
Support for industry-standard outputs (e.g., 4–20 mA, 0–10 V, HART, RS485), enabling seamless integration into distributed control systems (DCS) or programmable logic controllers (PLC).Integrated Design
Compact transmitter head combined with probe, enabling flexible installation.Display Functionality
On-site LCD or LED display for real-time temperature readings, trends, and diagnostics.

4. Case Example: Food Industry
In food production processes, strict temperature control is a fundamental requirement. Even slight deviations in temperature accuracy can directly affect product quality and safety.
By deploying temperature transmitters, production lines can achieve:
Real-time monitoring of process temperature
Reliable feedback to automation systems
Enhanced consistency in product quality
Compliance with food safety regulations
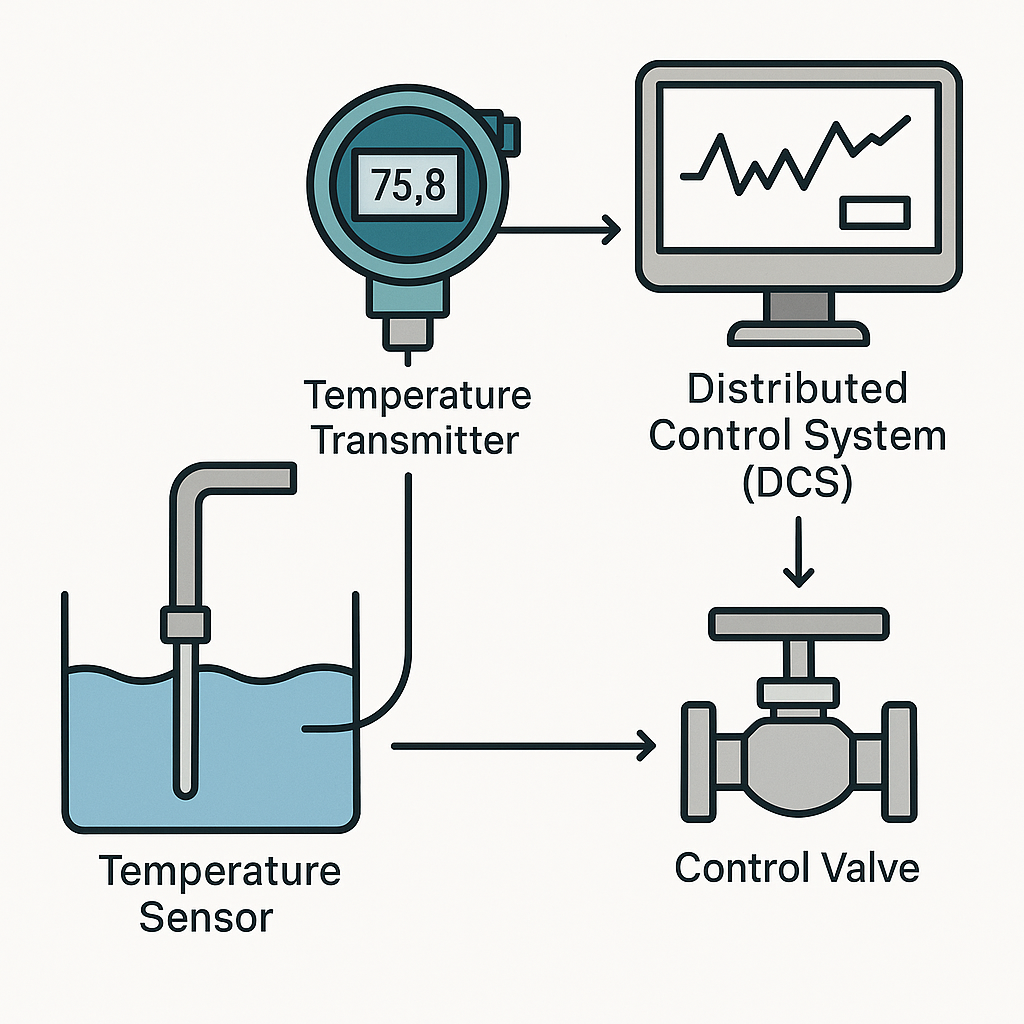
5. Conclusion
Temperature transmitters are more than just measuring devices — they are the foundation of industrial process reliability, automation, and quality assurance. From energy-intensive industries such as steelmaking and petrochemicals to high-precision fields such as food and medical engineering, temperature transmitters serve as the cornerstone for stable and efficient production.
