Introduction Diaphragm gas meters, also known as membrane gas meters, are widely used instruments for measuring gas flow. With the acceleration of urbanization and the widespread adoption of gas supply systems, accurate gas measurement has become crucial for both residential and commercial users. Diaphragm gas meters are favored for their simple structure, affordability, high accuracy, and ease of installation and maintenance.
This article provides an in-depth overview of diaphragm gas meters, including their working principle, key features, application scenarios, and factors to consider when selecting a meter.
1. Definition and Working Principle of Diaphragm Gas Meters
Definition: A diaphragm gas meter is a volumetric gas measuring device that uses a diaphragm (or membrane) to measure the flow of gas by counting the number of times the gas fills and empties the measuring chambers.
Working Principle:
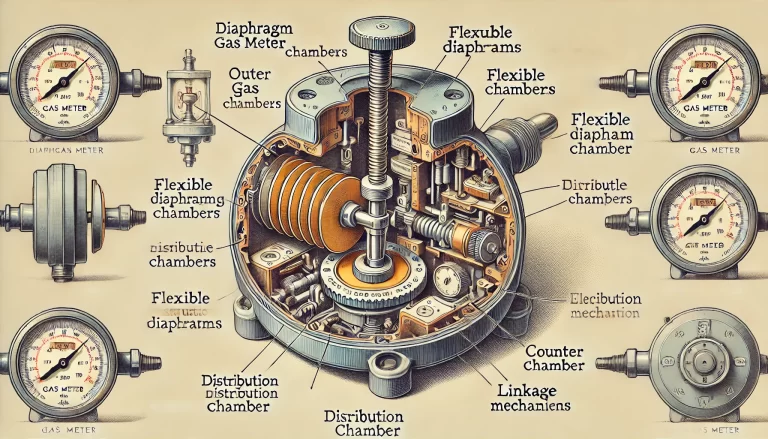
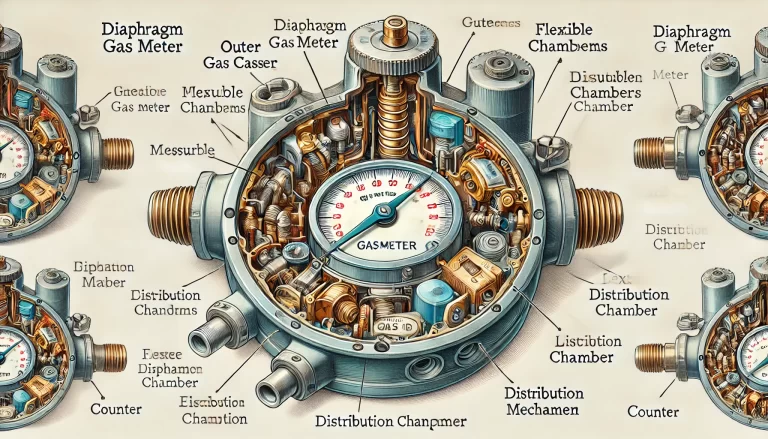
A diaphragm gas meter typically consists of an outer casing, measuring chambers, a distribution chamber, linkage mechanisms, and a counter.
Inside the meter are two measuring chambers, each divided into two sections by flexible diaphragms made of synthetic rubber.
When gas enters the meter through an inlet valve, it fills one chamber while the other empties.
The movement of the diaphragms drives a mechanical linkage, which in turn rotates a gear mechanism connected to the counter.
This repetitive filling and emptying cycle accurately records the volume of gas passing through the meter.
Visual Aid Suggestion: Including a labeled diagram showing the diaphragm movement and gas flow paths would significantly aid in explaining this principle.
2. Key Features of Diaphragm Gas Meters
High Accuracy:
The measuring accuracy depends on the diaphragm’s precise movement, making diaphragm gas meters ideal for residential and small commercial applications.
Wide Applicability:
Suitable for low-pressure gas systems, including natural gas and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
Easy Installation and Maintenance:
Their simple mechanical structure ensures easy installation and minimal maintenance requirements.
Cost-Effective:
Compared to other types of gas meters, diaphragm meters are relatively inexpensive, offering excellent value for money.
Stability in Low Flow Conditions:
Diaphragm meters perform reliably even in low gas flow conditions, maintaining consistent accuracy.
3. Applications in Gas Measurement
Residential Use:
Diaphragm gas meters are commonly installed in homes to measure daily gas consumption. This helps households monitor usage and manage their gas bills efficiently.
Commercial Use:
Small commercial establishments, such as restaurants and cafes, rely on diaphragm gas meters for accurate measurement to avoid billing discrepancies.
Utility Companies:
Gas supply companies use diaphragm gas meters to track consumption patterns, ensuring precise billing and operational efficiency.
Technical Considerations:
Diaphragm meters are typically used for gas pressures ranging between 5kPa and 20kPa and gas flow rates up to 40m³/h.
For higher flow rates exceeding 100m³/h, other types of meters, such as rotary or turbine meters, are recommended.
Emerging Technologies:
Modern diaphragm gas meters are increasingly integrated with IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities.
Features like remote meter reading, temperature compensation, and automated data logging improve efficiency and reduce manual errors.
Visual Aid Suggestion: Include charts comparing diaphragm gas meters with other types (e.g., rotary, ultrasonic meters) in terms of flow capacity, accuracy, and cost.
4. Selection Guide for Diaphragm Gas Meters
When selecting a diaphragm gas meter, consider the following factors:
Measurement Range:
Choose a meter with a measurement range suitable for your gas consumption requirements.
Accuracy Level:
Ensure the meter meets the required accuracy standards for your application.
Operating Environment:
Take into account temperature, humidity, and pressure conditions where the meter will be installed.
Manufacturer Reputation:
Opt for well-known brands with proven reliability and good after-sales support.
Compliance with Standards:
Ensure the selected meter complies with local and international gas metering regulations.
Visual Aid Suggestion: A checklist or table summarizing these selection criteria would enhance clarity.
5. Future Trends and Innovations
The integration of smart technologies, such as remote metering and advanced data analytics, is revolutionizing diaphragm gas meter systems.
Innovations in materials, such as enhanced synthetic membranes, are improving durability and precision.
Sustainability efforts are driving the development of energy-efficient and environmentally friendly metering solutions.
Conclusion
Diaphragm gas meters remain an essential tool in residential and small commercial gas measurement due to their accuracy, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. With technological advancements, these meters are becoming even smarter and more efficient.
When choosing a diaphragm gas meter, understanding your specific needs, considering environmental conditions, and selecting a reputable manufacturer are key steps to ensuring optimal performance.
By embracing innovations and smart technologies, diaphragm gas meters will continue to play a vital role in the energy sector for years to come.
Suggested Next Steps:
Explore case studies of successful diaphragm meter implementations.
Compare leading brands in the market.
