The radar velocity meter and radar flow meter are two widely used industrial measuring instruments. Although they share similar names and both employ radar technology for flow measurement, there are significant differences in their functions, applications, and principles. Let’s delve into these differences and highlight the unique characteristics of each.

From a conceptual standpoint, the radar velocity meter is primarily used to measure the velocity of fluids. It detects changes in the surface speed of water by transmitting and receiving microwave signals. This instrument is suitable for environments such as rivers, streams, and pipelines, providing real-time monitoring of fluid velocity with high frequency and accuracy.
In contrast, the radar flow meter focuses on measuring the total volume of fluid, i.e., the flow rate through a specific cross-section over a unit of time. It not only determines velocity but also calculates total flow by combining it with the cross-sectional area, making it more widely applicable in fields such as water supply, drainage, and wastewater treatment.
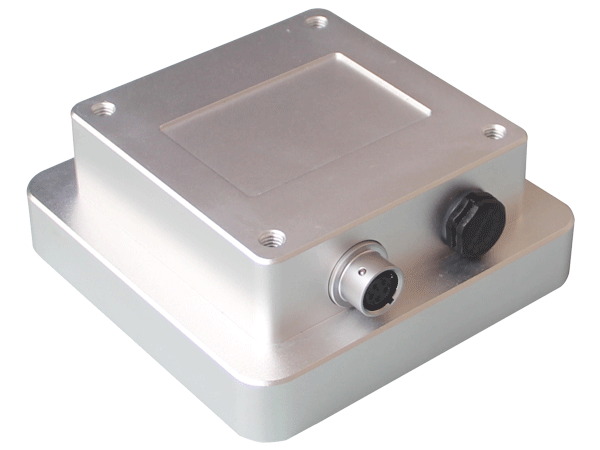

Analyzing from the perspective of measurement principles, the radar velocity meter typically operates based on the Doppler effect. This effect causes a change in the frequency of the reflected radar wave when it encounters a moving object. By detecting the frequency shift, the radar velocity meter can accurately calculate the fluid’s velocity. On the other hand, radar flow meters often employ the time-of-flight method or the frequency difference method.
The time-of-flight method calculates velocity and flow rate by measuring the time it takes for radar waves to travel through the fluid, while the frequency difference method uses the difference in propagation speeds of two microwaves with different frequencies in the fluid to calculate the flow rate. These methods enable the radar flow meter to provide both velocity and flow rate data simultaneously.
In terms of application scenarios, the radar velocity meter, with its non-contact measurement feature, is particularly suitable for complex environments, such as liquids containing a large amount of suspended solids or bubbles, as well as areas sensitive to mechanical instruments.
On the other hand, the radar flow meter is better suited for scenarios requiring precise measurement, such as water resource management and industrial process optimization. In these cases, the radar flow meter can provide highly accurate data, helping managers make informed decisions based on scientific insights.

Although the radar velocity meter and radar flow meter differ in principles and applications, they both showcase the powerful potential of radar technology in the field of flow measurement. Whether it’s monitoring water flow velocity or calculating total flow, these two instruments play critical roles in their respective domains.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect these instruments to become more intelligent and precise, bringing greater convenience and benefits to industrial and environmental monitoring.
