Temperature measurement is a fundamental part of many industrial processes. As the range of temperatures encountered in various fields continues to expand, the variety of temperature measurement instruments has also increased. Among these, the bimetallic thermometer stands out for its durability, accuracy, and ease of use. This article will provide a detailed overview of the bimetallic thermometer, its working principle, and its diverse applications.
What is a Bimetallic Thermometer?
A bimetallic thermometer is an instrument designed for the direct measurement of temperature in industrial settings. It consists of two metals with different coefficients of expansion, bonded together in a strip or coil. When subjected to temperature changes, the different rates of expansion cause the bimetallic strip to bend, and this movement is used to indicate the temperature on a calibrated dial.
Working Principle of a Bimetallic Thermometer
The working principle of a bimetallic thermometer relies on the physical property of metals to expand and contract at different rates when exposed to heat. The thermometer’s metal components, usually a combination of brass, steel, or other metals, are engineered to expand at different rates. As one side of the bimetallic strip heats up, it expands more than the other, causing the strip to bend. This bending motion drives a pointer on the thermometer dial, which displays the temperature.
The key advantages of this mechanism are that it does not require an external power source or complex electronics, making it reliable and easy to maintain. It is ideal for situations where temperature monitoring needs to be constant and stable, such as in manufacturing environments.
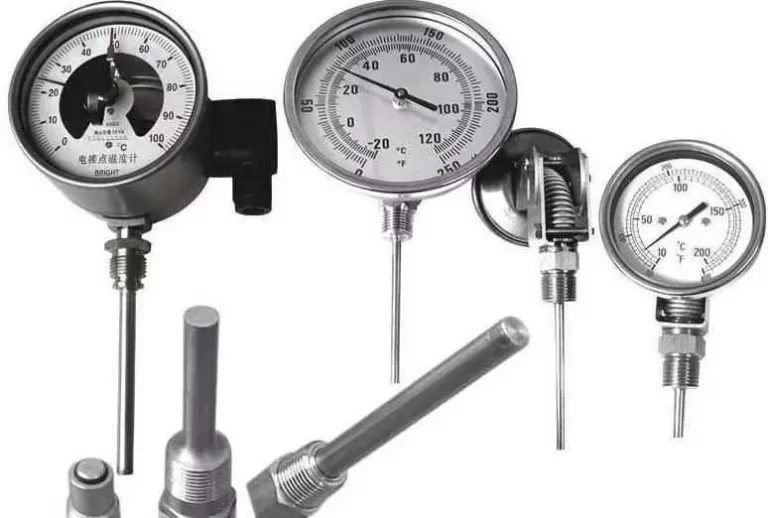

Temperature Measurement Range
Bimetallic thermometers are capable of measuring temperatures over a wide range. Typically, these thermometers can measure temperatures from -80°C to +500°C, making them versatile for many industrial applications. They are widely used to monitor the temperature of liquids, gases, and vapors during production processes. This broad range of measurement ensures that bimetallic thermometers can be used in both low and high-temperature environments, providing accurate readings across different conditions.
Applications of Bimetallic Thermometers
The versatility of bimetallic thermometers makes them invaluable in many industries. They are commonly used in the following fields:
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries: Bimetallic thermometers are often employed to monitor the temperature of liquids and gases during chemical reactions and pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. Accurate temperature control is critical in these industries to ensure product quality and safety.
Food and Beverage: In the food processing industry, precise temperature measurement is essential for ensuring proper pasteurization and food safety. Bimetallic thermometers are frequently used in this sector due to their reliability and durability.
HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems rely on temperature sensors to maintain proper indoor climate conditions. Bimetallic thermometers are used in HVAC systems to measure air and fluid temperatures accurately.
Automotive and Aerospace Industries: In these high-performance sectors, where temperature fluctuations can affect engine performance and safety, bimetallic thermometers are used to monitor temperatures in various components.
Power Plants: Bimetallic thermometers are widely used in power generation facilities to measure the temperature of steam, water, and other fluids involved in the energy production process.
Advantages of Bimetallic Thermometers
Bimetallic thermometers offer several distinct advantages:
No Power Supply Required: Since they operate based on mechanical movement, they do not require an external power source or batteries, making them reliable in locations without electrical access.
Durability: Built to withstand harsh industrial environments, bimetallic thermometers are resistant to vibration and shock, making them highly durable even in demanding settings.
Ease of Use: Bimetallic thermometers are simple to install and read, making them user-friendly in a variety of environments. The dial can be easily read from a distance, providing quick and accurate temperature readings.
Cost-Effective: Bimetallic thermometers are often more affordable compared to electronic temperature sensors, especially for applications that require basic temperature monitoring without complex features.

Conclusion
Bimetallic thermometers continue to be a reliable and cost-effective solution for temperature measurement across a broad range of industries. Their robust design, ease of use, and wide temperature range make them indispensable tools in industrial applications, including chemical production, food processing, HVAC systems, automotive, and power plants. As temperature monitoring becomes more critical in production and manufacturing, the importance of bimetallic thermometers will only continue to grow.
