In differential pressure flow measurement, the orifice plate, flow nozzle, and Venturi tube are the most commonly used primary elements. All three belong to the category of standard differential pressure devices, as defined in GB/T 2624, where their flow coefficients and discharge characteristics are well-established and can be used without individual calibration when designed and installed correctly.
However, when measuring erosive, corrosive, or dirty process fluids, the performance and reliability of these devices can be significantly different. Selecting the right element is essential to ensure long-term accuracy and stable operation.

1. Standard vs Non-Standard Differential Pressure Devices
Standard differential pressure devices have well-verified calculation formulas and coefficient charts. They can be used directly without flow calibration, as long as manufacturing and installation follow standards.
Non-standard differential pressure devices require individual calibration after fabrication due to insufficient test data support.
Standard devices defined in GB/T 2624 include:
Orifice plate
ISA 1932 flow nozzle
Venturi tube
Typical pressure tapping methods:
| Device | Pressure Tapping Method |
|---|---|
| Orifice Plate | Corner tapping, Flange tapping, D and D/2 tapping |
| ISA 1932 Nozzle | Corner tapping only |
| Long-radius Nozzle | Radius (distance) tapping |
| Venturi Tube | Pressure tapping at throat and upstream sections |

2. Structural Characteristics and Performance Comparison
| Device | Cost | Pressure Loss | Erosion Resistance | Suitable for Dirty Fluids | Flow Coefficient Stability | Application Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orifice Plate | Low | Highest | Weak (sharp edge wears easily) | Poor | Medium | Best for clean gas, steam, and liquids |
| Flow Nozzle | Medium | Medium | Good | Medium | Good | Suitable for high-velocity steam and fluids with small particle content |
| Venturi Tube | High | Lowest | Excellent | Excellent | Very stable | Ideal for large pipelines, slurry, high solids content fluids |
Key Conclusions
Pressure loss: Orifice > Nozzle > Venturi
Erosion resistance: Venturi > Nozzle > Orifice
Flow capacity (same diameter & ΔP): Venturi > Nozzle > Orifice
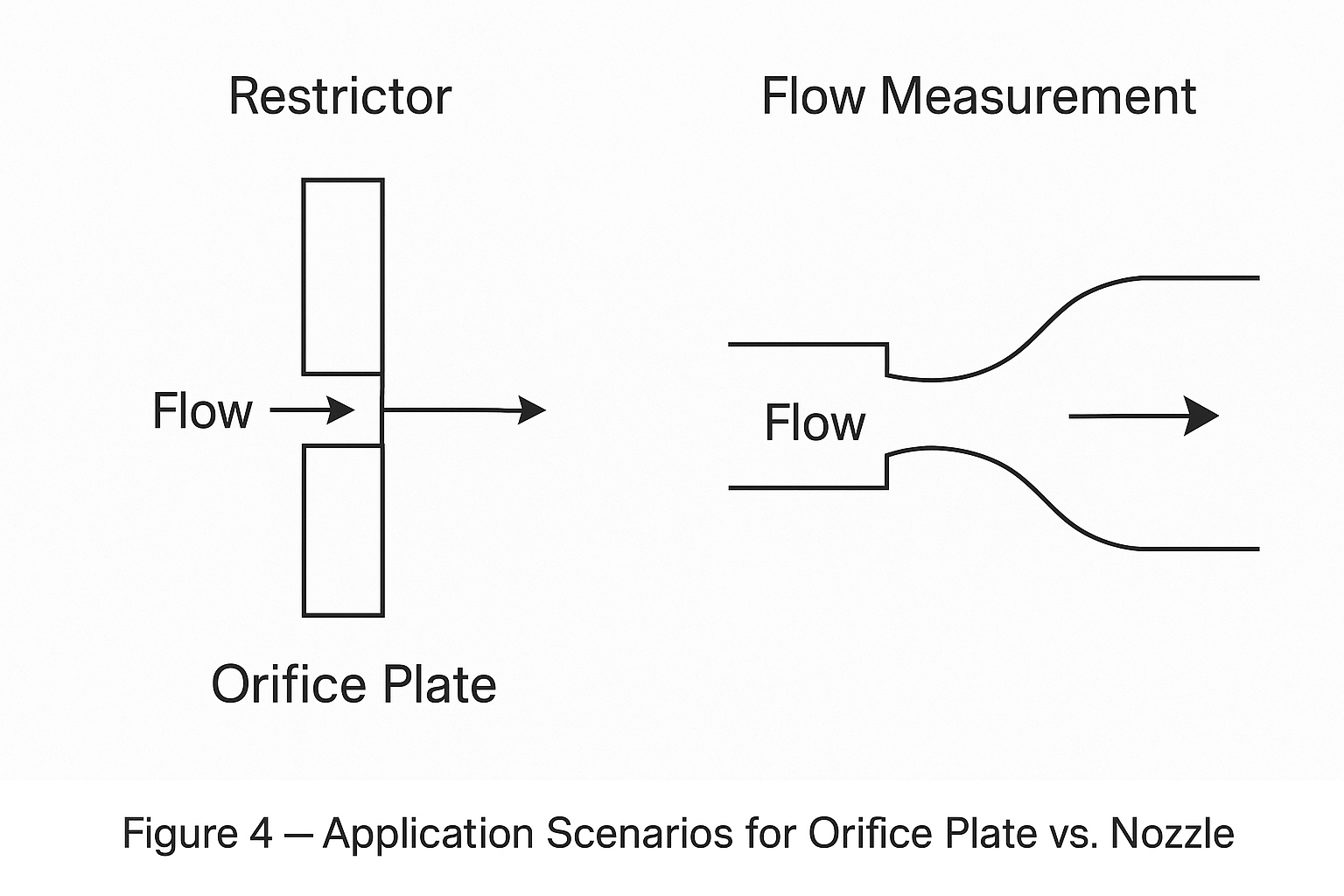
3. Why Erosive Fluids Matter
When measuring abrasive fluids (e.g., slurry, sand-laden water, catalytic cracking media), the sharp edge of an orifice plate wears quickly, causing the flow coefficient to drift, which leads to measurement error increasing over time.
The nozzle and Venturi tube, having smooth, rounded inlet contours, are less affected by edge wear, maintaining measurement accuracy for longer service cycles.
4. Application Guidance
| Application Scenario | Recommended Device | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Clean gas, steam, general liquid | Orifice Plate | Low cost, simple installation |
| High-temperature steam, high velocity flow | Nozzle | Stable coefficient, better erosion resistance |
| Slurry, dirty fluids, high-solid content, large pipeline systems | Venturi Tube | Low pressure loss, best long-term accuracy and durability |
5. Special Variants of Orifice Plates
| Type | Feature | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Dual Orifice Plate | Two plates in series | High-viscosity or low-flow fluids |
| Concentric Orifice Plate | Standard design | General measurement, widely used |
| Eccentric Orifice Plate | Hole offset from center | Fluids containing particles (solids settle away from opening) |
| Segmental (Segment) Orifice Plate | Opening is arc-shaped | Fluids containing gas bubbles or heavy contamination |
6. Summary and Selection Rule
For erosive or dirty fluids:
Venturi Tube is the first choice
Flow Nozzle is acceptable in medium conditions
Orifice Plate should be avoided unless the fluid is clean and cost is a priority
A simple selection mnemonic:
Clean & economical → Orifice
High velocity steam → Nozzle
Slurry / Erosive / Large pipeline → Venturi
