The electrical interfaces of field instruments have many specifications and sizes depending on the manufacturer and application scenarios… Domestic and foreign, metric, imperial, sealed and non-sealed, who is not confused when encountering them? This article mainly introduces the two specifications of M20×1.5 and 1/2″NPT that are often encountered by instrument engineers and are easily confused. I guarantee that you can understand them at once!
M20×1.5 metric cylindrical thread
The complete thread mark consists of the thread feature code, size code, tolerance zone code and other individual information that requires further explanation.
The characteristic code of ordinary threads is represented by the letter “M”. The size code of single-thread threads is “nominal diameter × pitch”. The unit of nominal diameter and pitch is millimeters. For coarse threads, the standard pitch item can be omitted.
Metric threads are cylindrical threads with a thread angle of 60 degrees. They can be divided into coarse threads and fine threads. The top of the thread is flat for easy processing, and the bottom of the thread is arc-shaped to increase the strength of the thread. Expressed as M20×1.5. (M: code, 20: nominal diameter, 1.5: pitch).
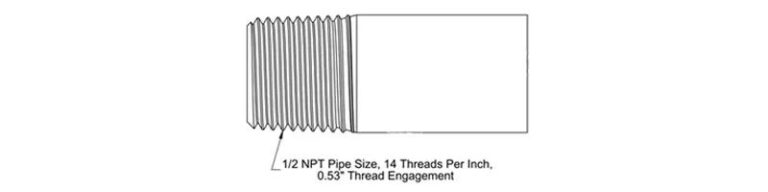
1/2"NPT American standard conical thread
NPT is the abbreviation of National (American) Pipe Thread, which belongs to the American national pipe thread standard. The standard thread is a conical thread, the thread angle is 60 degrees, and the pitch is expressed in the number of threads per inch. It is mainly used in North America.
The Chinese national standard certification can For comparison, please refer to GB/T12716-2011. 1/2″NPT means: 1/2″ tapered pipe thread, 14 teeth per inch (standard pitch can be omitted in the mark), taper is 1:16, bevel angle is 1 °47′24″. It has the advantages of small pitch, small rising angle, good self-locking performance, firm connection and good sealing.
In general, it is easy to quickly identify two pipe fittings if they are put together:

The picture above shows the M20×1.5 – 1/2″NPT adapter. Do you see the difference?
M20×1.5 is a cylindrical thread, a straight thread, the threaded part looks like a cylinder, and the maximum outer diameter is equal to 20mm.
1/2″NPT is a tapered thread. The thread part looks conical and the maximum outer diameter is greater than 20mm.
