1. Overview
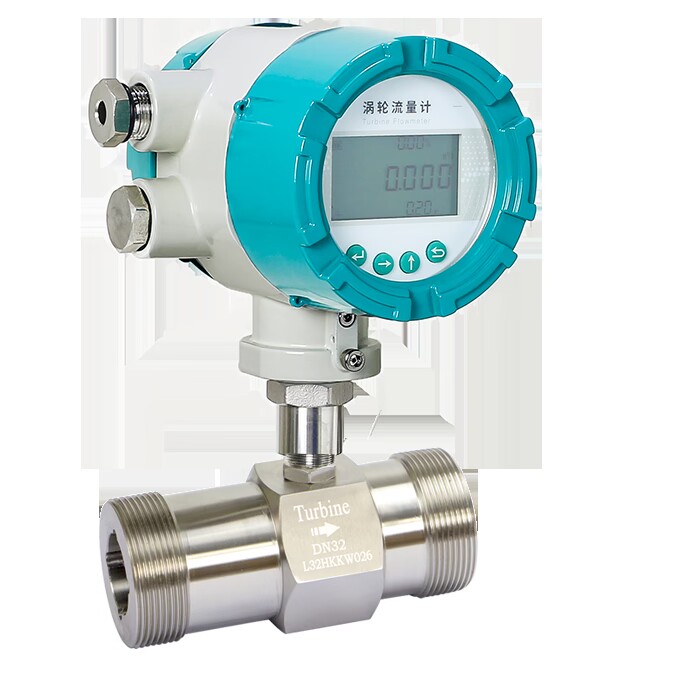
The LWS series sanitary turbine flowmeter is a type that can be widely used in manufacturing pharmaceutical, food, beverage, and other industries, for measurement, ingredients, control, and finished product filling.
Flow metering instruments for installation and other purposes. The instrument housing is made of stainless steel (316L), the movement part is made of special materials and has good anti-corrosion, corrosion, and rust prevention capabilities. The entire watch structure breaks through traditional craftsmanship and adopts foreign advanced structures.
The structural optimization design greatly improves the accuracy and repeatability of the instrument. Specifically designed for the pharmaceutical and beverage industries, it adopts a quick-install connection structure for easy cleaning.
LWS series sanitary turbine flowmeter has reached the international level of similar products.
It is an ideal instrument for the health industry.
2. Features
- Measurement is not affected by the variation of flow density, viscosity, temperature, pressure and conductivity. High accuracy measurement is guaranteed according to the linear measurement principle.
- No obstacle in the pipe, no pressure-loss and lower requirement for straight pipeline.
- DN 6 to DN2000 covers a wide range of pipe size. A variety of liners and electrodes are available to satisfy different flow characteristic.
- Programmable low frequency square wave field excitation, improving measurement stability and reducing power consumption.
- Implementing 16 bits MCU, providing high integration and accuracy; Full-digital processing, high noise resistance and reliable measurement; Flow measurement range up to 1500:1.
- High definition LCD display with backlight.
- RS485 or RS232 interface supports digital communication.
- Intelligent empty pipe detection and electrodes resistance measurement diagnosing empty pipe and electrodes contamination accurately.
- SMD component and surface mount technology (SMT) are implemented to improve the reliability.
3. Working principle
When the liquid to be measured flows through the sensor, under the action of the fluid, the impeller rotates.
It rotates under force, and its rotation speed is proportional to the average flow rate of the pipe. The rotation of the impeller dynamically and periodically changes the reluctance value of the magnetic circuit to detect the magnetic flux in the coil.
Subsequently, a periodic change occurs with the same frequency as the blade rotation frequency. The induced electromotive force is amplified, converted, and processed.