Explosion-proof systems, especially in hazardous environments, demand a meticulous approach to ensure safety and compliance with regulations. This article outlines the essential principles for connecting explosion-proof distribution boxes with galvanized pipes, providing practical details and best practices for effective implementation.
1. Requirements for Explosion-Proof Piping Installation
The installation of explosion-proof pipelines requires higher standards compared to conventional open piping. The key requirements include:
Material: Thick-walled pipes, such as galvanized steel pipes, are mandatory to withstand high stress and provide added protection.
Connection Standards: All connections must adhere to specialized standards for explosion-proof environments, employing suitable components like explosion-proof junction boxes and switches.
2. Connection Between Pipes and Components
Pipes must be securely connected to junction boxes and switches using threaded connections. This ensures:
A tight, robust interface that enhances the explosion-proof capability of the system.
The use of explosion-proof-specific components, such as threaded junction boxes and switches, to prevent the leakage of explosive gases.
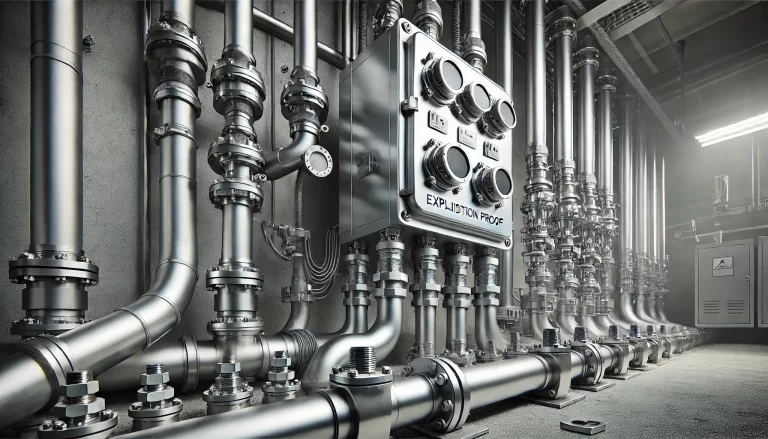
3. Pipe Strength and Thickness
The galvanized steel pipes used in explosion-proof installations must meet the following criteria:
A minimum wall thickness of 2.5 mm to ensure structural integrity and adequate protective strength.
Sufficient mechanical robustness to withstand environmental stress and potential impacts.
4. Secure Connections with Locknuts
When connecting pipes using clamps, the following measures are necessary:
Install locking nuts at connection points to prevent loosening of threads, which could compromise the explosion-proof barrier.
Avoid using soldered jumpers or painted connections at joints. Instead, use explosion-proof connectors when direct coupling is challenging.
5. Isolation and Sealing Requirements
When pipes transition from explosion-prone zones to areas with open flames or control rooms, isolation sealing boxes must be installed on both sides of the partition walls. This prevents explosive mixtures from entering the non-protected areas.
Position the isolation sealing boxes within 300 mm of the partition wall, ensuring no joints exist within this distance for optimal sealing performance.
For pipes passing through floors, install vertical isolation sealing boxes above the floors. Use drainable sealing boxes in areas prone to condensation to prevent internal pressure buildup during explosions.
6. Explosion-Proof Flexible Connectors
Flexible connectors are vital for applications where galvanized pipes require large curvature or need to connect electrical equipment:
Flexible connectors consist of metric threaded male fittings welded onto galvanized metal hoses at both ends.
Ensure that these connectors meet explosion-proof standards to maintain system integrity.
7. Grounding and Bonding Considerations
Galvanized pipes inherently have a zinc coating that can affect electrical conductivity. Proper grounding is critical:
Install dedicated grounding wires within the explosion-proof distribution box to ensure reliable grounding.
Use bridging wires between the distribution box and the galvanized pipe. Securely connect these wires to grounding screws inside the box and to grounding bars or other equipment as needed.
Ensure the grounding connections are tight and the wires are appropriately sized to prevent safety risks.
Step-by-Step Process for Bridging Wires
Select an appropriate grounding wire with sufficient cross-sectional area.
Inside the explosion-proof distribution box, connect the grounding wire to a dedicated grounding screw.
Extend the wire to the galvanized pipe and secure it tightly, ensuring both ends are fastened properly to provide an uninterrupted grounding path.
Verify the connections to ensure no loose or overly tight fittings, as these could compromise the system’s safety.
8. Material Selection for Explosion-Proof Distribution Boxes
The distribution box housing should be made from stainless steel (grade 304 or higher) for durability and resistance to environmental factors.
The box color should retain its natural stainless steel finish, with a minimum wall thickness of 4.0 mm to meet explosion-proof requirements.

Additional Notes on Sealing
Sealing is a critical aspect of explosion-proof systems:
Threaded connections alone do not provide adequate sealing. Use certified sealing compounds or fittings to prevent the ingress of explosive gases.
Regularly inspect seals to ensure they remain intact and effective over time, particularly in high-moisture or vibration-prone environments.
Conclusion
By adhering to these principles, the connection between explosion-proof distribution boxes and galvanized pipes can achieve high levels of reliability and safety. Proper attention to grounding, sealing, and material selection ensures compliance with safety standards and minimizes risks in hazardous areas. Incorporating these practices into your workflow will enhance the performance and longevity of your explosion-proof installations.
