Level measurement is critical in industrial applications, ensuring operational safety, efficiency, and compliance. Two commonly used technologies are magnetostrictive level gauges and magnetic flip board level gauges. Both rely on magnetic coupling principles but differ significantly in design, functionality, and application. This article provides a comprehensive comparison, including selection guidance, case studies, and market trends.
1. Working Principle Comparison
| Level Gauge Type | Working Principle |
|---|---|
| Magnetostrictive Level Gauge | Uses a magnetostrictive waveguide wire and a magnetic float to generate torsional waves. The measurement is based on time-of-flight calculations, providing non-contact, continuous output. |
| Magnetic Flip Board Level Gauge | A float moves up and down with the liquid level, flipping magnetic plates to change colors, indicating the level visually. This is a mechanical contact-based, discrete output system. |
Illustrative Example
A petrochemical plant uses magnetostrictive level gauges for high-precision measurement in large storage tanks, integrating them into remote monitoring systems.
A water treatment facility employs magnetic flip board level gauges for local tank level indication where budget constraints apply.

2. Core Performance Comparison
| Criteria | Magnetostrictive Level Gauge | Magnetic Flip Board Level Gauge |
| Measurement Type | Continuous digital measurement (Resolution: 0.1mm, Accuracy: ±0.05% FS) | Discrete visual or switch-based measurement (Accuracy: ±5-10mm) |
| Output Signal | Supports 4-20mA, HART, RS-485, Modbus | Only switch alarm signals or no output |
| Multi-Parameter Capability | Can measure liquid level, interface, and temperature | Only liquid level indication |
| Environmental Adaptability | High-pressure (≤40MPa), extreme low temperatures (-196°C), strong corrosive media | Suitable for normal pressure, moderate temperature (-40°C to +150°C), and non-corrosive environments |
| Maintenance Needs | Low (No mechanical parts, lifespan >10 years) | Medium (Requires periodic cleaning of flip boards and float) |
| Cost | High (Advanced precision measurement) | Low (Economical, on-site indication) |
3. Typical Application Scenarios
| Scenario | Magnetostrictive Level Gauge Suitability | Magnetic Flip Board Level Gauge Suitability |
| Trade Measurement | ✔️ Ideal for high-precision custody transfer of crude oil and LNG tanks (±1mm accuracy) | ❌ Not suitable due to low accuracy |
| Chemical Reactors | ✔️ Suitable for highly corrosive media (HCl, H₂SO₄), providing continuous monitoring | ❌ Only applicable to non-corrosive media |
| Food & Pharmaceutical Tanks | ✔️ Sanitary design (Tri-Clamp interface), supports CIP/SIP cleaning | ✔️ Suitable for basic tank level indication (requires manual monitoring) |
| Wastewater Treatment Plants | ✔️ Capable of oil-water interface detection (multi-float design) | ✔️ Cost-effective for simple level indication |
| Explosive Hazardous Areas | ✔️ Intrinsic safety and explosion-proof certification (Ex ia/Ex d) | ✔️ Some models support explosion-proof certification (for budget-sensitive cases) |
4. Selection Guidelines
When to Choose a Magnetostrictive Level Gauge:
✅ High precision continuous measurement is required (e.g., custody transfer applications).
✅ Multi-parameter output is needed (level + interface + temperature).
✅ The environment involves high pressure, extreme temperatures, or corrosive substances.
✅ Remote monitoring or industrial IoT (IIoT) integration is required.
When to Choose a Magnetic Flip Board Level Gauge:
✅ Only on-site visual indication or simple switch-based alerts are needed.
✅ Budget constraints exist, and the application is straightforward (normal pressure, non-corrosive environments).
✅ Routine manual inspection is feasible.
5. Maintenance and Cost Analysis
| Maintenance Aspect | Magnetostrictive Level Gauge | Magnetic Flip Board Level Gauge |
| Routine Maintenance | Clean float (every 6 months), annual calibration | Clean flip boards (every 3 months), check float mobility |
| Failure Rate | Low (Electronic components, failure rate <1%) | Medium (Mechanical parts, prone to jamming, failure rate 5-10%) |
| Life-Cycle Cost | High initial investment, but low long-term maintenance cost | Low upfront cost, but higher maintenance and replacement frequency |
6. Market Trends and Innovations
Advancements in Magnetostrictive Technology:
🔹 Increasing integration with industrial IoT (IIoT) for real-time remote monitoring.
🔹 Adoption in LNG storage and hydrogen energy applications, driven by global energy transitions.
🔹 Improved sensor miniaturization to enable use in smaller process tanks.
Innovations in Magnetic Flip Board Level Gauges:
🔹 Emerging hybrid designs incorporating digital sensors for remote level monitoring.
🔹 Enhanced materials (ceramic-coated floats) to improve corrosion resistance.
🔹 New self-cleaning mechanisms to reduce maintenance efforts.
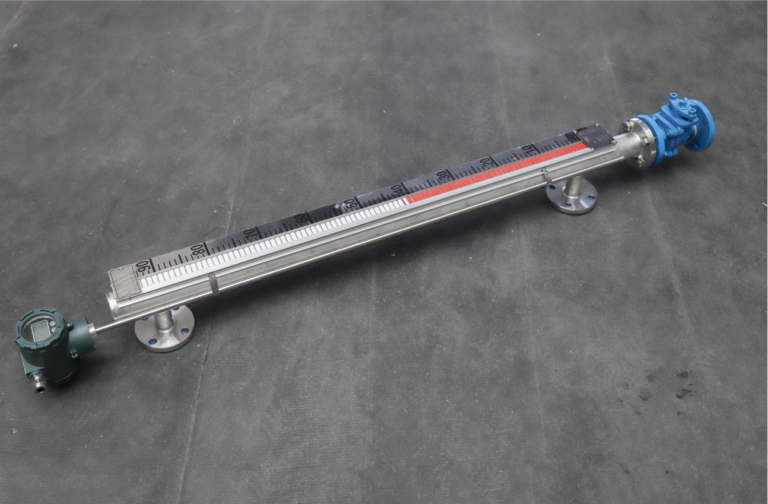

7. Conclusion
🔹 Magnetostrictive Level Gauges are best for high-precision, smart automation, and extreme conditions, making them ideal for petrochemicals, LNG storage, and nuclear power applications.
🔹 Magnetic Flip Board Level Gauges are suitable for cost-sensitive, simple visual indication applications, such as water treatment, food processing, and small storage tanks.
Key Decision Factors:
✅ Measurement Accuracy Needs
✅ Budget Considerations
✅ Environmental Conditions
✅ Automation and Remote Monitoring Requirements
By considering these factors, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize both performance and cost efficiency.

Final Thought:
For industries aiming to upgrade their measurement systems, investing in magnetostrictive technology ensures long-term accuracy and automation benefits. However, where budget and simplicity are priorities, magnetic flip board gauges remain a cost-effective choice.
