Instrumentation construction drawing review is a critical step in ensuring safety, quality, and efficiency in engineering projects. A thorough review helps identify potential issues before construction begins, reducing errors, rework, and associated costs, and ensuring smooth project execution.
1. Preparatory Work Before Review
“Preparation is the foundation of success.” Before conducting a detailed review of instrumentation construction drawings, it is essential to complete several preparatory steps to ensure a comprehensive and effective process.
1.1 Collect Relevant Documentation
Gather all necessary design specifications, process flow diagrams (PFD), piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&ID), datasheets, and applicable international standards (e.g., IEC 61511, ISA 5.1).
Verify the completeness and accuracy of these documents.
1.2 Form a Multidisciplinary Review Team
Include professionals with expertise in instrumentation engineering, process engineering, electrical design, and safety.
Ensure team members have relevant experience and clear communication skills.
1.3 Develop a Detailed Review Plan
Define review scope, schedule, responsibilities, and documentation methods to ensure an organized process.
2. Seven Key Review Points
2.1 Equipment Selection: Matching Specifications with Application
Confirm that all instrumentation types, models, and specifications comply with design standards and project requirements.
Ensure compatibility with process conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and hazardous area classifications (e.g., ATEX, IECEx).
2.2 Layout Optimization: Ensuring Accessibility and Maintainability
Check that instrumentation is installed in accessible locations for operation, calibration, and maintenance.
Verify that sufficient space is provided around equipment to allow for future modifications and safe working conditions.
Assess the layout to ensure smooth process flow and compliance with ergonomic guidelines.
2.3 Piping and Cabling: Integrity of Connections
Examine the routing of process piping and signal cabling to avoid unnecessary bends, crossings, or interference.
Ensure proper segregation between power and signal cables to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Confirm that support and clamping systems comply with relevant standards (e.g., NEC, IEC 60364).
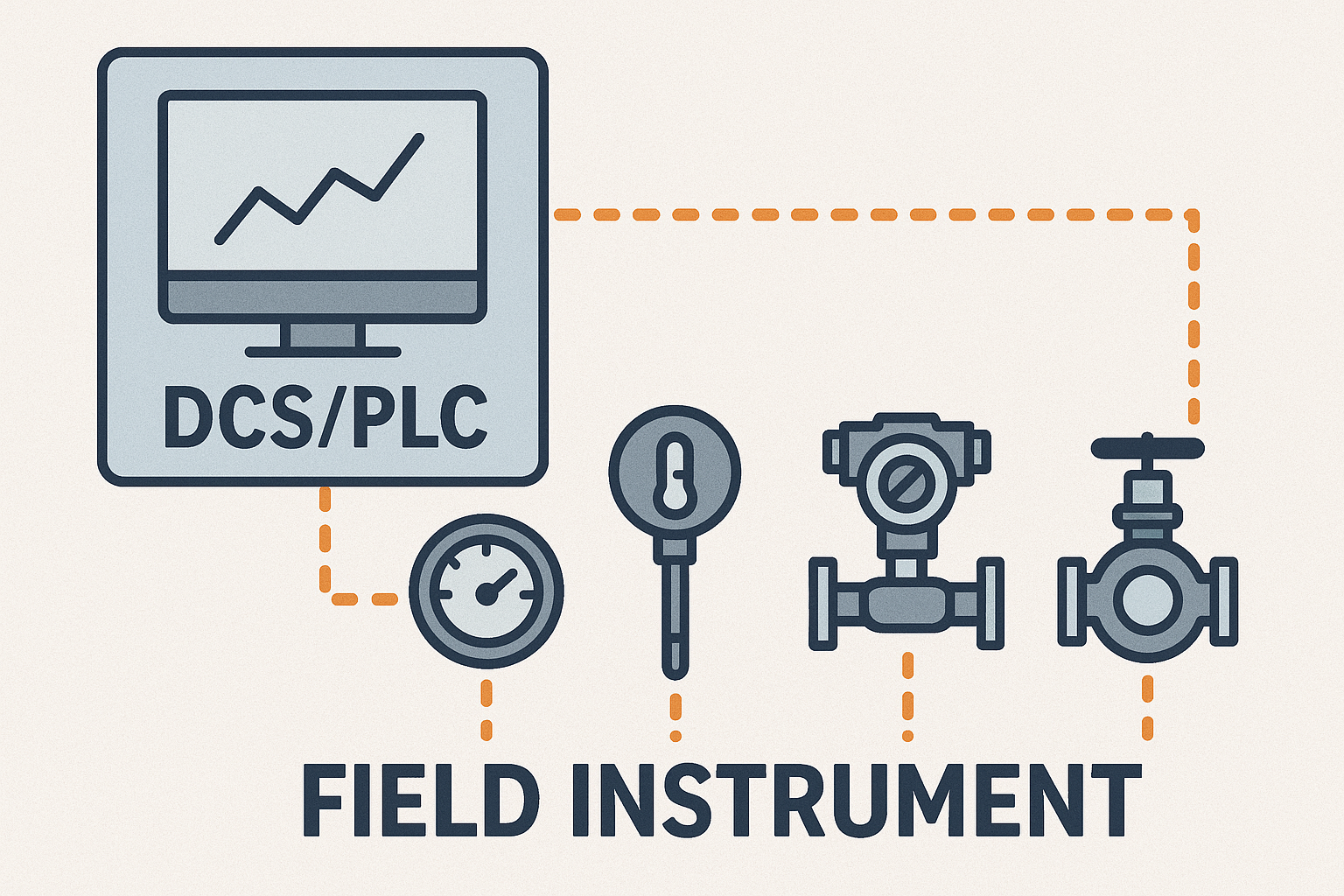
2.4 Signal Consistency: Reliable System Communication
Verify that signal types (4-20 mA, HART, Modbus, Profibus, etc.) are consistent throughout the system.
Assess potential signal degradation, impedance mismatches, or conversion issues.
Ensure clarity in signal display and control interfaces for operator interpretation.
2.5 Safety Compliance: Prioritizing Protection Measures
Check for proper implementation of explosion-proof, fireproof, waterproof, and grounding measures.
Ensure adherence to applicable safety standards (e.g., IEC 60079 for hazardous areas, NEC for US installations).
Confirm that emergency shutdown (ESD) and safety instrumented system (SIS) components are correctly integrated.
2.6 Electrical Connections: Following Best Practices
Review wiring diagrams for accuracy, including terminal numbering, wire sizing, and grounding.
Ensure compliance with electrical standards (e.g., IEC 60204, NEC Article 430).
Verify proper labeling and documentation to aid troubleshooting and future maintenance.
2.7 System Testing and Commissioning: Ensuring Functional Integrity
Confirm that functional, performance, and stability tests are defined in the documentation.
Assess the inclusion of pre-commissioning and commissioning procedures to verify system readiness.
Check that validation protocols cover all critical parameters, including accuracy, response time, and fail-safe behavior.

3. Review Best Practices and Recommendations
3.1 Maintain a Rigorous and Methodical Approach
Use standardized checklists and reference international best practices.
3.2 Document All Findings and Actions
Record comments, decisions, and revisions clearly to provide traceability.
3.3 Foster Collaboration Across Disciplines
Engage in regular coordination meetings with design, construction, and safety teams to resolve conflicts early.
3.4 Leverage Digital Tools for Enhanced Efficiency
Utilize 3D modeling, clash detection software, and digital markups to streamline the review process.

4. Conclusion
Reviewing instrumentation construction drawings is a cornerstone of successful project delivery. By addressing the key considerations outlined above, engineering teams can ensure compliance with technical standards, improve system reliability, and enhance overall project safety and efficiency.
