Industrial bimetallic thermometers are precision instruments designed to measure temperatures ranging from -50°C to 500°C. These thermometers are widely utilized in various industries, including industrial equipment, petrochemical plants, heating systems, pipelines, power plants, marine applications, and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. To ensure accurate temperature measurements and extend the operational lifespan of these instruments, regular maintenance and inspection are essential.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the recommended maintenance cycle and key inspection checkpoints for industrial bimetallic thermometers.
1. Maintenance Cycle
Under normal operating conditions, it is generally recommended that industrial bimetallic thermometers undergo a full inspection and maintenance at least once a year. This period is based on standard industry practices and manufacturer recommendations. However, in extreme working environments, such as high-vibration areas or chemically aggressive atmospheres, more frequent inspections may be necessary.

2. Key Inspection Points
When performing routine inspections, the following four aspects should be carefully examined:
2.1 Accuracy and Stability of Temperature Indication
Verify that the temperature readings remain accurate by comparing the thermometer’s readings with a calibrated reference thermometer or other reliable temperature measurement device.
Check for any fluctuations or instability in the readings that may indicate internal mechanical issues.
Ensure that the installation location does not expose the thermometer to excessive vibrations, which could cause significant pointer oscillations and impact reading stability.
2.2 Certification and Compliance Check
Confirm that the thermometer is accompanied by a valid calibration certificate.
Check the certification date to ensure that the thermometer is still within the valid calibration period. If the certificate has expired, recalibration should be performed by an accredited laboratory or according to company standards.
2.3 Physical and Structural Integrity
Inspect all components of the thermometer to ensure they are firmly assembled and free from corrosion or wear that might compromise measurement accuracy.
Examine the protective glass or transparent cover on the dial. It should be free of cracks, discoloration, or any defects that might obscure readings.
Verify that all mounting and connection parts are secure and not loose or damaged, which could lead to inaccurate readings or mechanical failures.
2.4 Dial Markings and Readability
Ensure that the scale markings, numerical values, and unit symbols (℃) are complete, clearly visible, and legible.
Confirm that the precision class (accuracy rating), production date, and manufacturer details are properly labeled and readable.
Any worn-out or faded dial markings should be corrected or replaced to avoid misinterpretations of the readings.
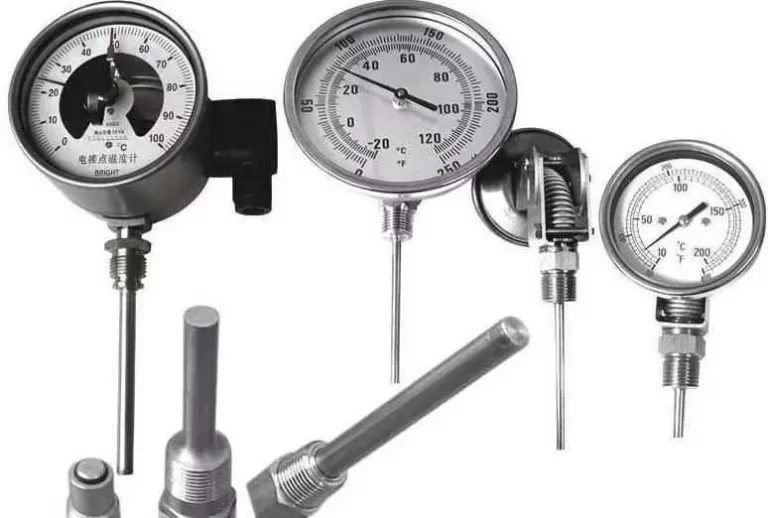

3. Documentation and Maintenance Records
Once the inspection is complete, it is crucial to update and maintain inspection records. This should include:
Inspection date and time
Inspection results and findings
Any necessary repairs, recalibrations, or component replacements
Next scheduled maintenance date
Proper documentation ensures compliance with industry regulations and helps in predictive maintenance by identifying trends in instrument performance over time.
4. Conclusion
Regular inspections and maintenance of industrial bimetallic thermometers are essential to maintaining their accuracy, reliability, and longevity. By adhering to an annual inspection cycle and following the detailed inspection guidelines outlined above, industries can minimize measurement errors, prevent costly equipment malfunctions, and ensure the smooth operation of critical temperature monitoring systems.
By implementing a proactive maintenance strategy, businesses can enhance safety, improve efficiency, and extend the lifespan of their bimetallic thermometers, ultimately contributing to more effective industrial temperature control and monitoring.
