Differential pressure (DP) flow meters occasionally show no flow indication despite normal system operation. This article analyzes two real-world case studies and summarizes practical troubleshooting steps for diagnosing such issues.
📘 Case Study 1: No Indication in Ortho-Xylene Feeding Line
Background:
After restarting a benzene workshop post-maintenance, the DP flowmeter for ortho-xylene feeding consistently showed no indication, while the corresponding rotameter indicated stable flow. Process data (oxidizer temperature) also suggested that material was indeed flowing into the reactor.
Investigation:
The transmitter and orifice system were thoroughly checked—no faults found.
After discharging the transmitter’s drain valve, the indicator temporarily recovered, but soon returned to zero.
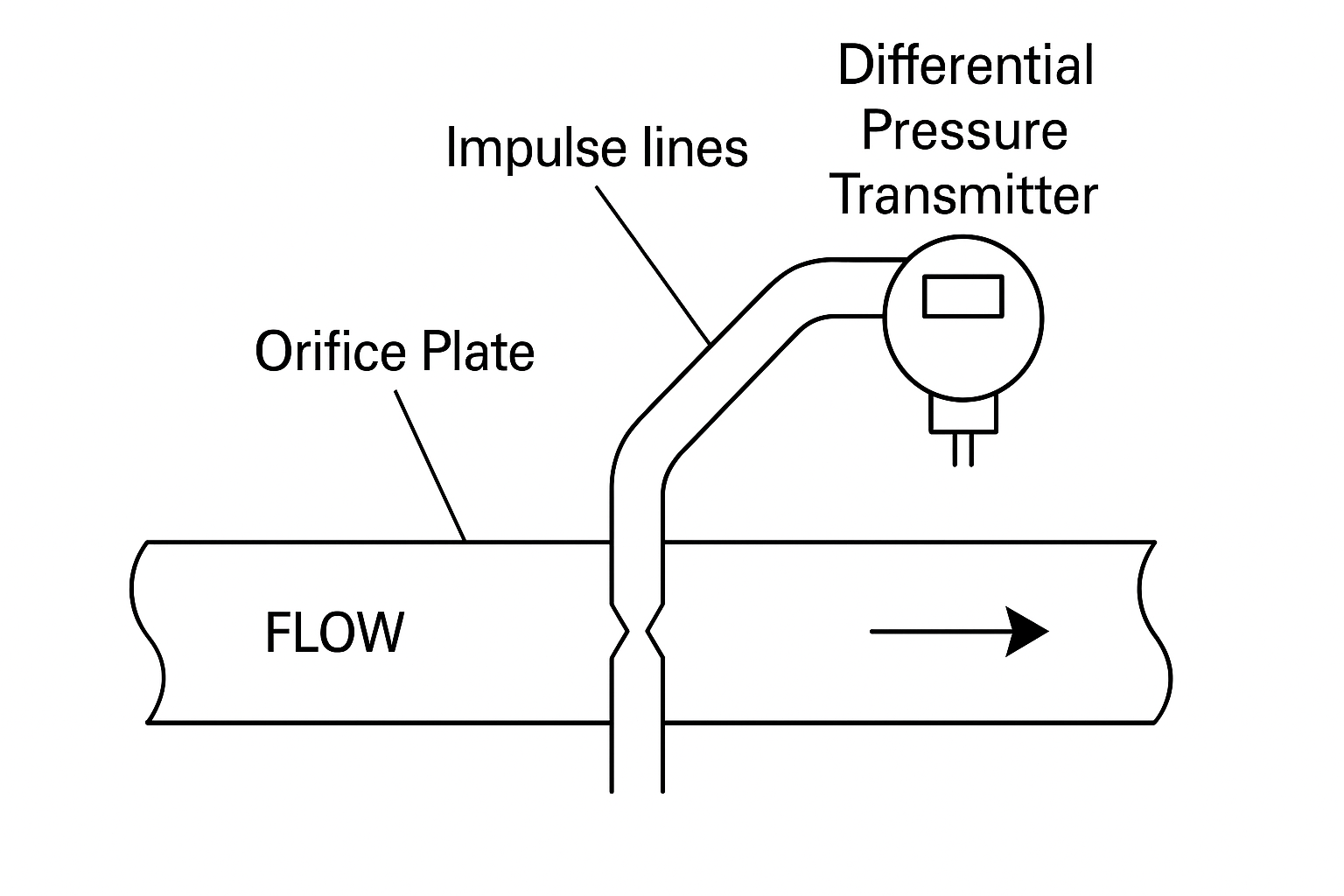
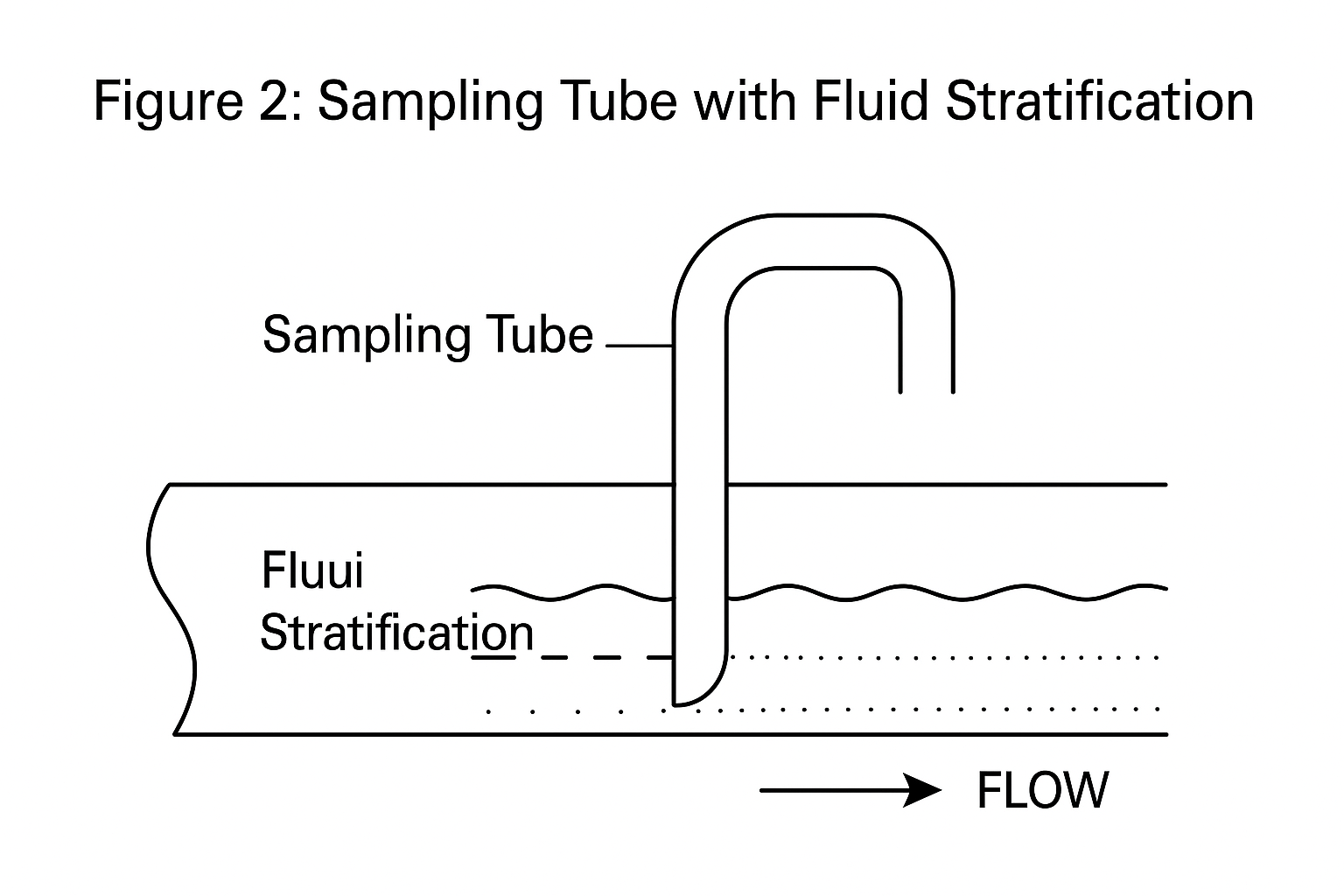
Sample taken from the orifice impulse line showed obvious stratification.
Lab results indicated over 30% water content in the ortho-xylene feed.
Root Cause:
The high density difference between water and ortho-xylene (~100 g/L), combined with long impulse lines (~4 m), caused the hydrostatic head to offset the pressure differential, resulting in no reading.
Solution:
Notified the process department to resolve the raw material issue. After switching to qualified feedstock, the flowmeter returned to normal operation.
📘 Case Study 2: No Indication in Fluidized Bed Water Refill Line
Background:
Operators reported no indication from the flowmeter monitoring water refill to a fluidized bed gas buffer, although tank level and reactor temperature suggested active flow.
Investigation:
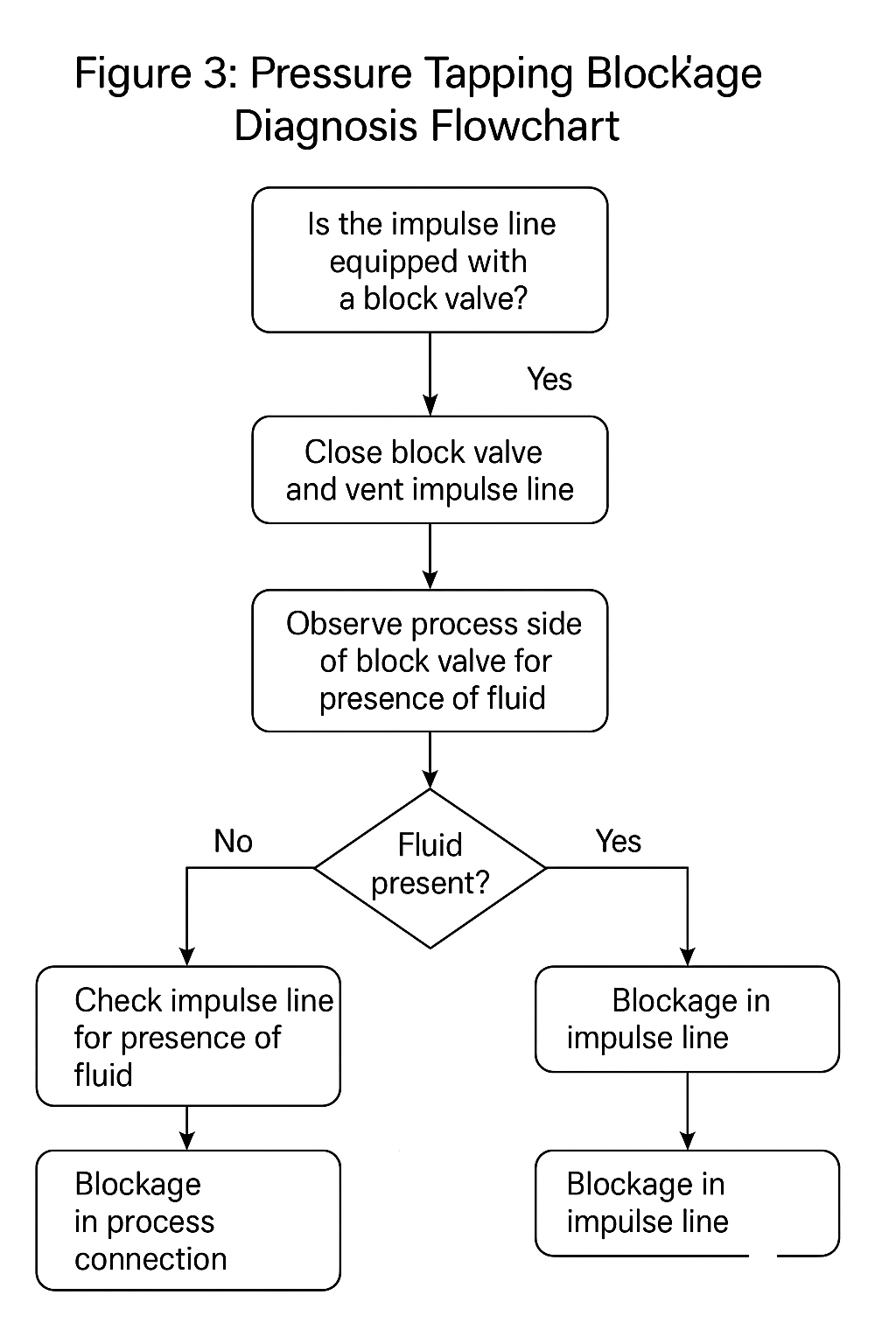
The negative pressure side of the transmitter showed output; positive side seemed blocked.
Step-by-step air purging indicated the blockage was located in the primary needle valve or the orifice tap chamber.
Solution:
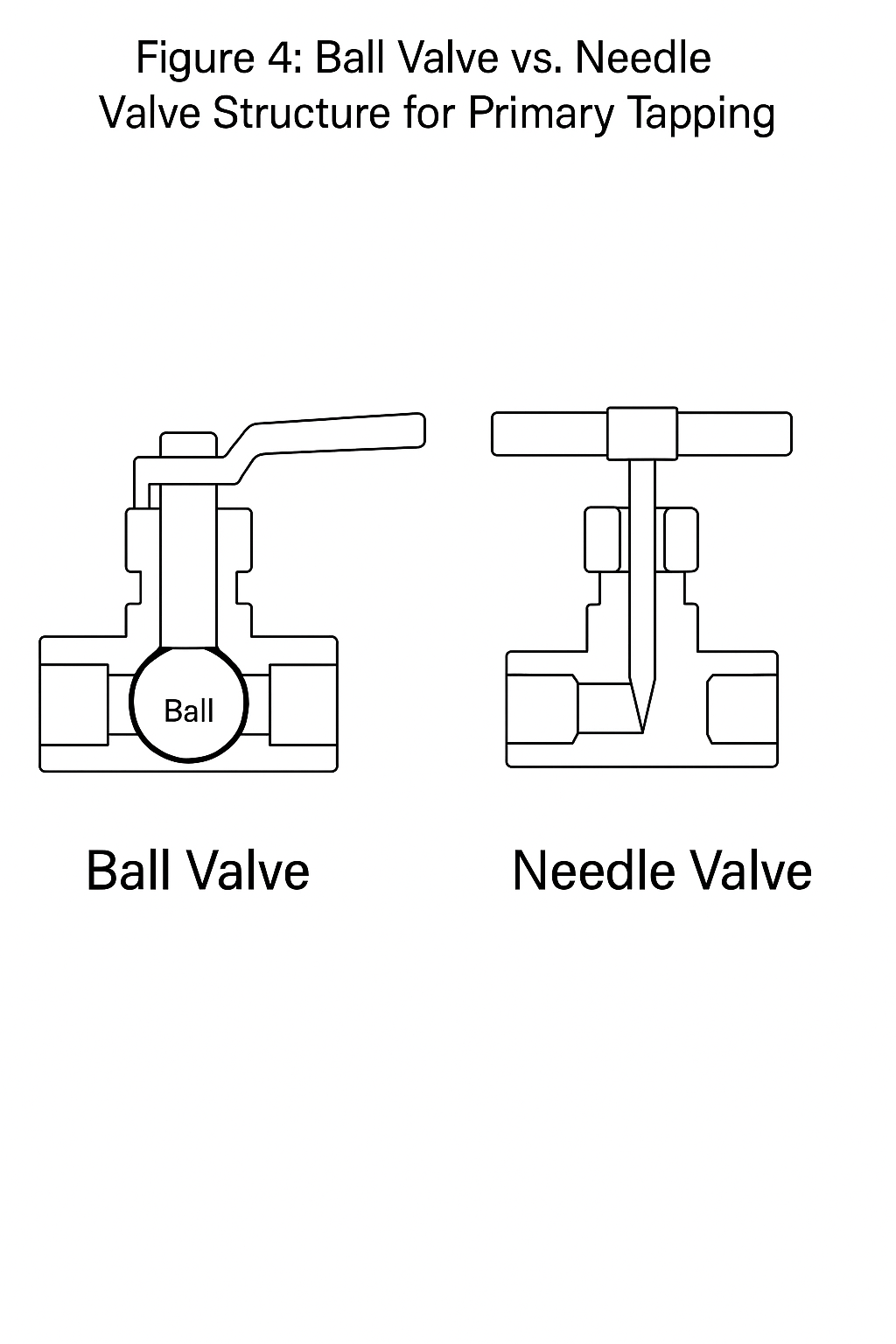
The needle valve could not be cleared due to its structure. A temporary shutdown was arranged, and the valve was replaced with a ball valve, restoring normal function.
📌 Recommendation: Ball valves are preferable for primary taps in water service orifice installations to ease maintenance.
🛠 Common Causes of “No Indication” in DP Flowmeters
| Category | Possible Cause | Diagnostic Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Signal/Electrical | No power supply or broken cable | Check transmitter and loop voltage (18–23V DC) |
| Transmitter set to fixed 4 mA output | Review settings via HART or configuration tool | |
| Impulse Line Issues | Blocked or partially blocked impulse lines | Open vent/drain valves and test with air |
| Condensate not fully drained (steam service) | Ensure proper trap or condensate pot functioning | |
| Installation/Operation | Sample or isolation valve not opened | Check all valves in measurement loop |
| Orifice orientation or tapping error | Compare to installation drawings | |
| Transmitter Problems | Damaged sensor or incorrect range setting | Check span, zero, and calibration parameters |
🔧 Recommended Troubleshooting Steps
Power Check
Inspect if display or output is zero.
Measure loop voltage: 18–23 VDC is typical.
Use a multimeter to confirm loop current.
Signal Path Validation
Check terminal connections for looseness or corrosion.
Inspect surge protectors or safety barriers if present.
Impulse Line Flushing
Rapidly open/close drain valves to create pressure impulse.
If indication changes, blockage or air pockets are likely.
Transmitter Configuration
Ensure correct range and operating mode (e.g., not fixed output).
For smart transmitters, use configuration tools to verify zero/span settings.
Conclusion:
Loss of indication in a DP flowmeter is not always due to hardware failure. Medium properties, impulse line design, installation errors, and electrical issues can all play a role. A systematic approach—starting from signal verification to process fluid analysis—ensures efficient diagnosis and resolution.
