Introduction
When selecting cables for liquid level sensors, several common questions arise:
When does a liquid level sensor require a vented cable?
Does using a vented or non-vented cable affect measurement accuracy?
The choice of cable is crucial because the sensor must compensate for atmospheric pressure fluctuations to ensure accurate measurements. This article provides a detailed explanation of how cable selection impacts performance and the underlying principles behind it.
Understanding the Role of a Vented Cable
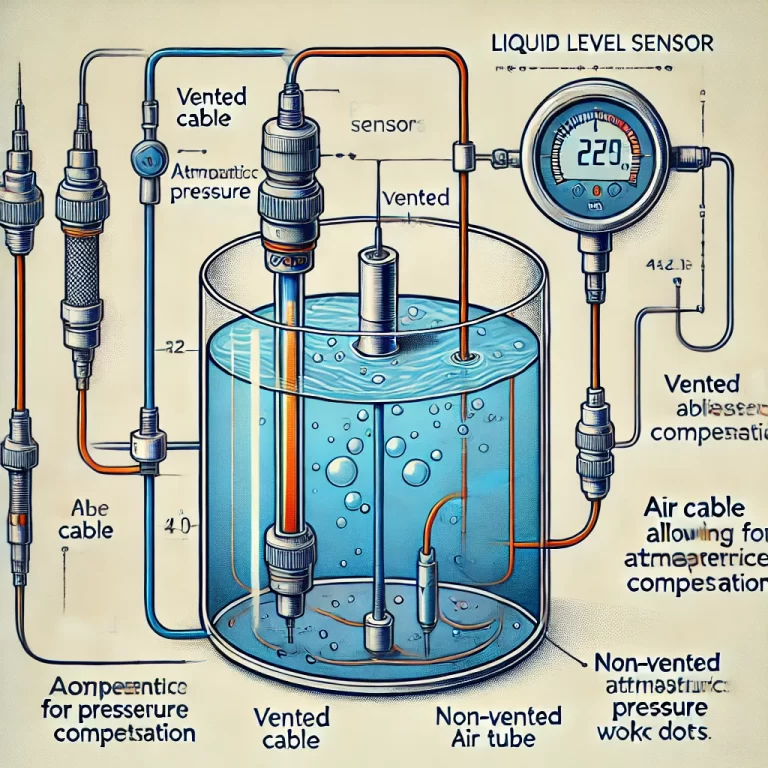
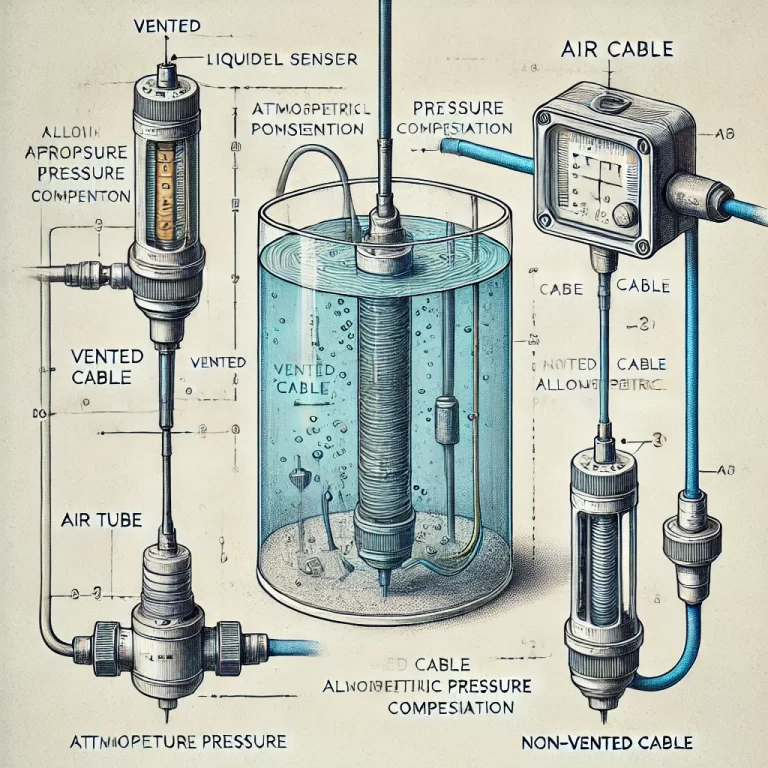
A liquid level sensor measures the pressure exerted by the liquid column above it. However, this pressure is influenced by the atmospheric pressure acting on the liquid surface. To compensate for this, some level sensors use vented cables that allow atmospheric pressure to reach the sensor’s reference side. This helps the sensor isolate the true hydrostatic pressure of the liquid.
For sensors with a range exceeding 160 meters, if their measurement accuracy is greater than the variations in atmospheric pressure, a non-vented cable may be used. Otherwise, a vented cable is necessary to maintain precision.

How a Vented Cable Works
When a liquid level sensor is submerged, the liquid exerts a pressure proportional to its depth. The sensor’s positive pressure chamber receives this pressure, while a vented cable allows external air pressure to reach the negative pressure chamber of the sensor.

Vented vs. Non-Vented Cables: When to Choose Which?
| Parameter | Vented Cable | Non-Vented Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Higher, as it compensates for atmospheric pressure | Slightly lower, as atmospheric pressure variations are not compensated |
| Depth Range | Suitable for shallow to deep applications | Suitable for very deep applications (160m+), where atmospheric variations are negligible |
| Maintenance | Requires protection against moisture ingress | Less maintenance needed |
| Application | Water wells, rivers, tanks, and environmental monitoring | Deep reservoirs, industrial applications with stable atmospheric conditions |
Conclusion
The choice between a vented and non-vented cable depends on the depth of measurement and the required accuracy. For most applications, vented cables are recommended to eliminate atmospheric pressure variations. However, in deep liquid level measurements where these variations are minimal, non-vented cables can be used. Understanding this distinction helps in selecting the right cable for optimal sensor performance.
