The HART protocol can be said to be the most trusted communication protocol in the industry for more than 40 years. The HART Communication Foundation is an international, non-profit membership organization that supports and promotes the widespread use of HART communication protocol standards and technology.
1. Introduction to HART protocol
HART protocol (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer Protocol) was originally launched by Fisher-Rosemount Company in the 1980s as an open standard for fieldbus communication. It uses FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) frequency shift keying signals based on the Bell202 standard. Superimposing an audio digital signal with an amplitude of 0.5mA on the traditional 4~20mA analog signal for two-way digital communication, it is designed to solve the communication problem between industrial field intelligent instruments and control systems. HART communication will not interfere with the analog signals transmitted to the control system. , ensuring compatibility with existing analog systems, and is a transitional product in the process of transforming analog systems into digital systems.
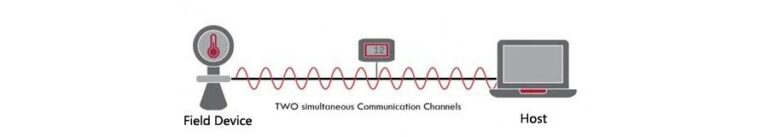
The HART protocol is a request-response (master/slave) communication protocol, which means that each communication is initiated by a request (or command) from the master device. The master device is typically a distributed control system (DCS), PLC, or PC-based asset management system. Slave devices are typically field measuring devices such as pressure, level, temperature, flow, or other types of transmitters. To ensure that any HART-enabled device from any vendor can communicate correctly and respond to commands with the correct information, command sets and types are clearly defined in the HART specification and implemented in all HART-registered devices.
The HART command set provides unified and standardized communication for all field devices. The host application can implement any commands required by the specific application. There are three main categories of HART command sets, and these three categories of commands can usually be found coexisting in a field device.

1. Universal Commands
Universal commands provide access to information useful in normal operation (e.g., reading host variables and units) and must be recognized and supported by all devices using the HART protocol.
2. Common Practice Commands
General behavior commands provide functions that can be implemented in many (but not necessarily all) field devices. Such commands include the function libraries of the most commonly used field devices.
3. Device Specific Commands
Device-specific commands represent functions unique to each field device. These commands access setup and calibration information, as well as information about the device’s construction. Information about device-specific commands is available from the device manufacturer.
2. HART protocol version
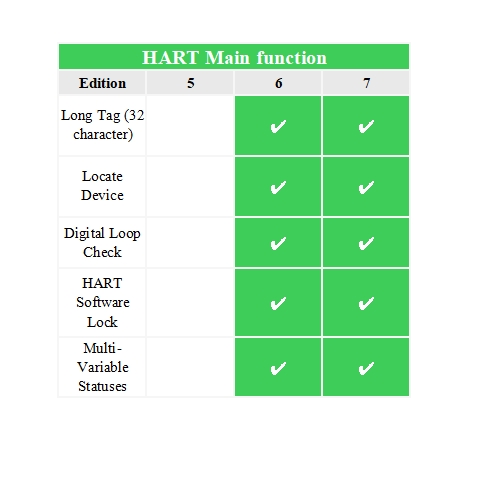
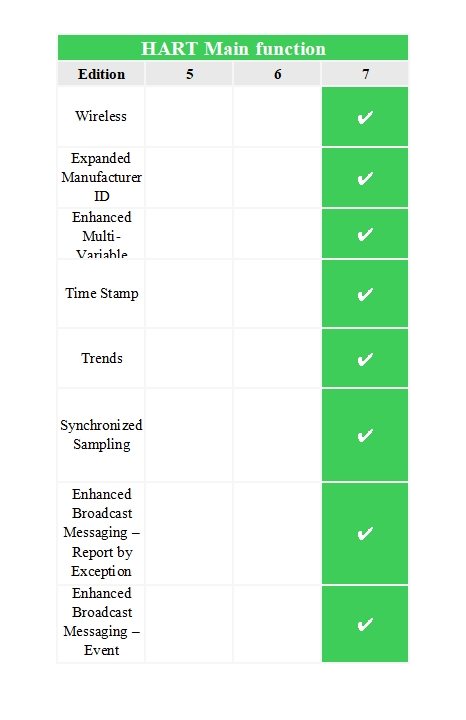
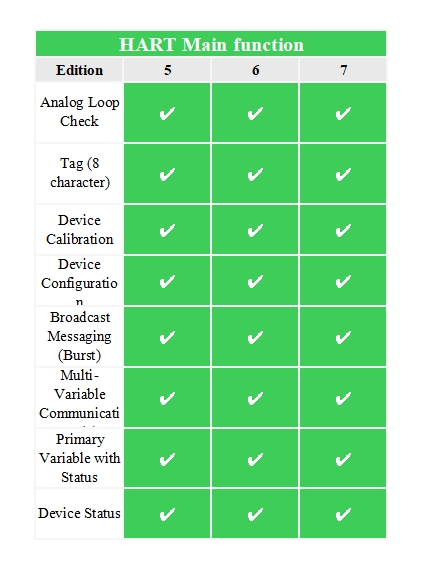
As an open, compatible, stable and reliable communication protocol, the HART protocol has been widely recognized and applied in the industrial field. After decades of continuous evolution, it has developed multiple versions of updates and improvements, each time The revision of the version brings new technologies and functions while being compatible with the previous version to meet the ever-changing development needs of industrial automation. The main functions and differences of the current mainstream versions HART 5, HART 6 and HART 7 are as follows:
Protocol before HART 5 version, physical layer: RS-485; link layer: token master-slave question and answer method; application layer: define some simple general commands.
HART 5 version protocol, physical layer: analog current + FSK, 1200bps; link layer: token master-slave question and answer type, adding a second master device, and adding a slave device burst mode; application layer: further enriched It contains general commands, ordinary commands and special commands, and the short address range is 0~15.
HART version 6 protocol, physical layer: increase current C8PSK, 9600bps specification; application layer: expand command content, use extended user ID, add device cluster command, short address range 0~63.
HART 7 version protocol, physical layer: added 2.4G DSSS O-QPSK 10dBm 250kbps specification; link layer: added time division multiple access (TDMA) link control method; network layer: added self-organization, multipath, mesh Network specification; application layer: expanded device cluster commands and added mesh network maintenance commands.