1. Introduction
Adverse weather conditions are a major contributing factor to road traffic accidents. To mitigate these risks, highway traffic weather stations have been developed, integrating various sensor technologies and automated control systems. These stations enable comprehensive data collection and analysis of climatic conditions across highway sections, allowing for earlier, more accurate travel planning and reducing accident rates.
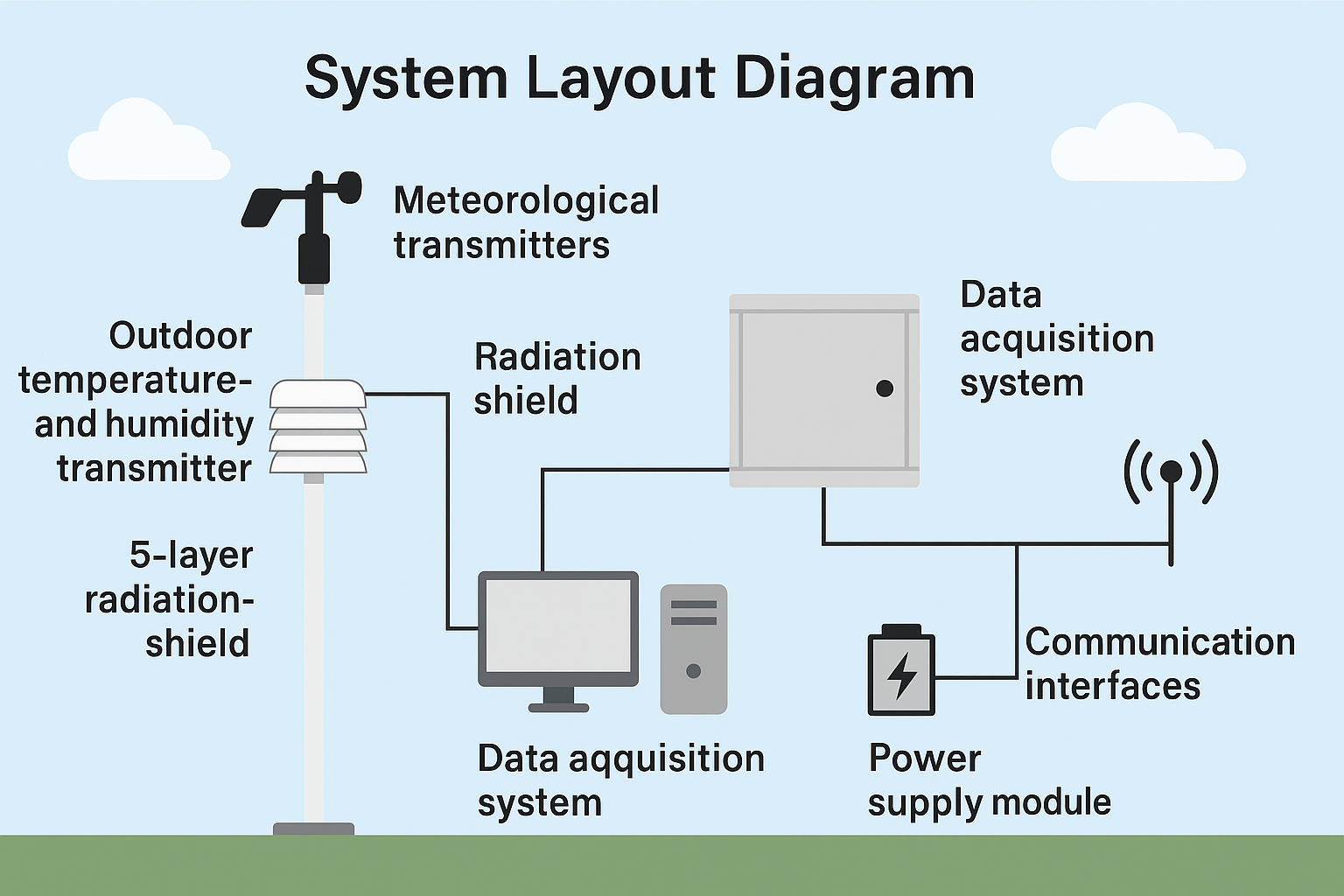
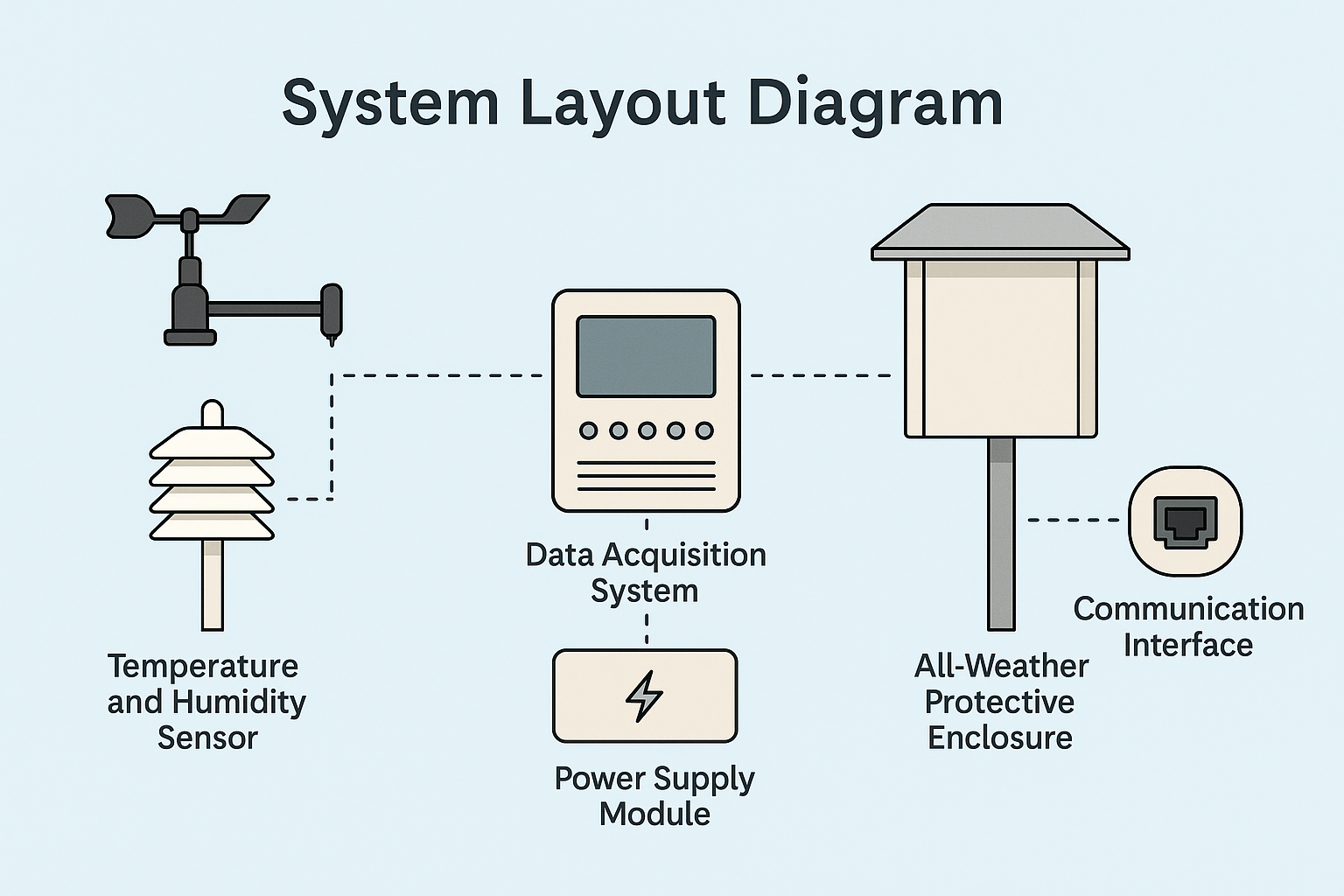
2. System Components of Highway Traffic Weather Stations
A standard highway traffic weather station typically consists of the following components:
Meteorological transmitters (temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind speed, and wind direction sensors)
Data acquisition systems
Power supply modules
Radiation shields and ventilation systems
All-weather protective enclosures
Meteorological mounting structures
Communication interfaces and peripheral equipment
These systems work together to continuously monitor environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind direction, and precipitation in real time.
3. Role of Temperature and Humidity Transmitters
Temperature and humidity are critical parameters for assessing road conditions. In highway traffic meteorological stations, outdoor temperature and humidity transmitters are commonly used. These devices are typically equipped with five-layer radiation shields (similar to lightweight louvered shelters), which serve multiple functions:
Protection against rain, direct sunlight, and UV radiation
Ensuring accurate sensing of ambient temperature and humidity
Adjustable height to suit different installation requirements
The radiation shield is made from specialized materials that effectively block solar radiation and precipitation, ensuring the sensor can function reliably in harsh outdoor environments.
4. Installation Considerations for Temperature and Humidity Transmitters
Proper installation is critical for obtaining accurate measurements. Key guidelines include:
Vertical Positioning: The transmitter must be installed vertically to prevent rainwater ingress.
Location Selection: Avoid installing transmitters in areas prone to heat transfer (such as near metal surfaces or concrete structures) which could create localized temperature differentials, leading to inaccurate readings.
Electromagnetic Interference: Keep transmitters away from high-power electrical devices (such as variable frequency drives or large motors) to minimize measurement errors caused by electromagnetic interference.
By following these best practices, the highway traffic weather stations can deliver highly reliable real-time environmental data, contributing to safer and more efficient road management.
