A glycerin-filled pressure gauge—also referred to as an oil-filled pressure gauge—is a type of mechanical pressure measuring device that enhances performance by filling the casing with damping liquid such as glycerin or silicone oil. It is widely used in industrial applications where vibration, pulsation, or corrosive conditions may affect the accuracy and lifespan of standard dry gauges.
1. Operating Principle and Construction
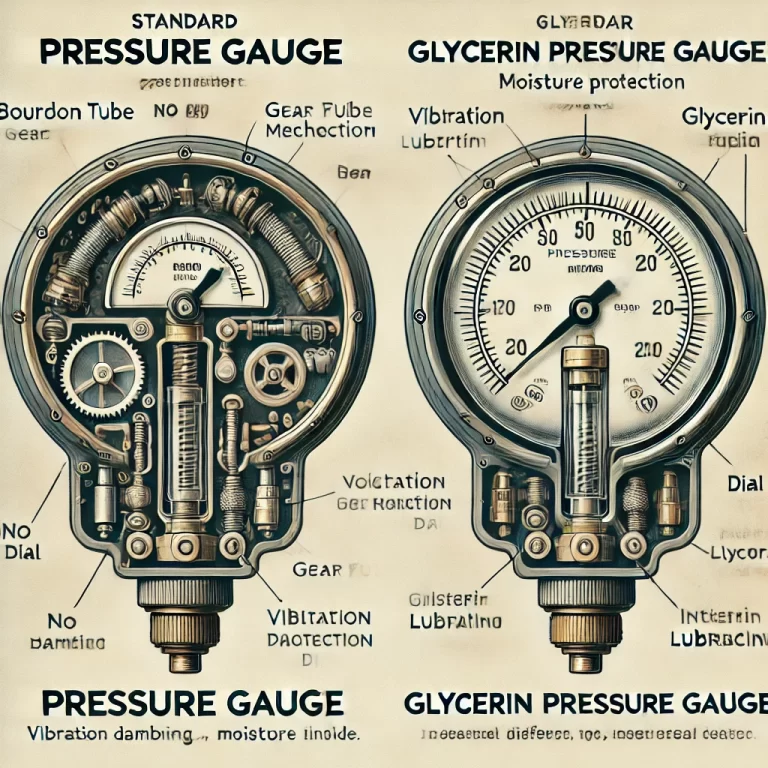
Structurally, an oil-filled gauge is similar to a conventional Bourdon tube pressure gauge. It consists of:
Bourdon tube
Gear movement mechanism
Dial and pointer
Liquid-filled case
When pressure is applied, the Bourdon tube deforms and transmits motion through the internal gear mechanism, moving the pointer across the scale. The damping fluid absorbs vibration energy, buffers mechanical shocks, and prevents the needle from fluctuating excessively—ensuring accurate and stable readings.
In addition, the liquid acts as a protective barrier against moisture and corrosive gases, effectively sealing the internal parts and extending the instrument’s operational life.

2. Key Advantages
✅ Superior Vibration Resistance
Ideal for equipment prone to severe vibrations, such as compressors, hydraulic systems, or heavy machinery. The fluid dampens movement and protects internal components.
✅ Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
The filled case prevents corrosive agents like acid vapors or moisture from penetrating the internal mechanisms—critical for chemical, petrochemical, and metallurgical environments.
✅ Lubrication and Heat Dissipation
The liquid medium lubricates moving parts, reducing friction wear, and aids in dissipating heat to maintain accuracy under elevated temperatures.
3. Common Application Areas
| Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Machinery & Manufacturing | Pressure monitoring for hydraulic and pneumatic systems, resilient to shock and vibration |
| Chemical & Petrochemical | Long-term stability in corrosive gas or liquid environments such as reactors and pipelines |
| Power Generation | Suitable for steam turbines, boilers, and high-temperature, high-pressure vessels |
| Water & Wastewater | Withstands impurities and surges, reliably monitoring pump and pipeline pressure |
4. Selection and Maintenance Guidelines
When selecting an oil-filled gauge, consider the following:
Process media compatibility
Pressure range
Operating temperature
Mounting type and connection
Regular maintenance involves checking for:
Leaks or fogging inside the case
Pointer sticking or erratic readings
Damaged seals or fluid loss
If any of these issues arise, timely replacement or servicing is advised to maintain measurement reliability.
5. Conclusion
With its dual advantages of mechanical stability and environmental protection, the glycerin-filled pressure gauge stands out as a dependable choice for demanding industrial environments. In settings where ordinary gauges fail due to vibration, corrosion, or thermal strain, it serves as a reliable sentinel guarding your equipment’s performance and safety.
