Radar level gauges focus on measuring the height of liquid in storage containers or open surfaces. The device transmits a microwave signal and calculates the time required from the transmission to the reception of the reflected signal to derive the height of the liquid. This process relies on the property of microwaves reflecting from the liquid surface, making radar level gauges ideal for precise measurement in chemical, water treatment and other industries that require level measurement.
In contrast, the core function of a radar flow meter is to determine the flow rate of a fluid in a pipe, river or other water channel. It assesses the flow rate by emitting radar waves and capturing the signals reflected back from particles in the fluid.
Unlike a level meter, a flow meter focuses more on the measurement of fluid dynamic parameters, which is particularly important in fields such as hydrological monitoring, sewage treatment and pipeline flow control.
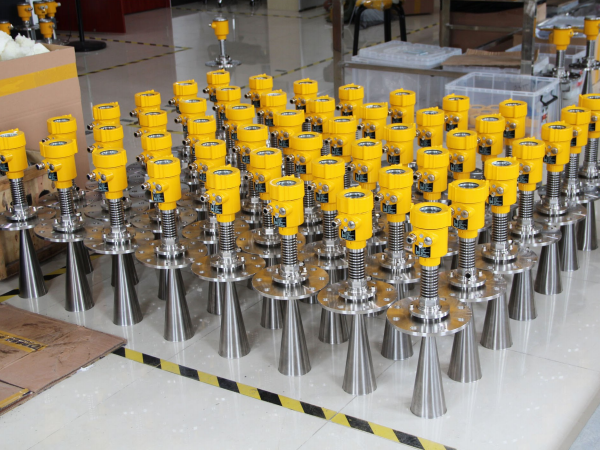

In terms of working principle, radar level meters usually use pulse wave or frequency modulated continuous wave technology. Pulse wave technology determines the distance by sending short microwave pulses and measuring their round-trip time.
Frequency modulated continuous wave technology sends microwaves with varying frequencies and calculates the distance by evaluating the frequency changes of reflected waves. These methods ensure accurate measurement even in the presence of steam, dust or low dielectric constant media.
Radar flow meters mostly use the principle of Doppler effect, that is, flow velocity information is obtained by measuring the frequency changes of reflected signals. When radar waves encounter moving fluid particles, the reflected waves will experience a frequency shift, which is proportional to the fluid velocity.
Using this principle, radar flow meters can accurately measure the velocity of the fluid, and this method is insensitive to changes in the composition and density of the fluid. In terms of structural design, radar level meters are usually designed to be top-mounted, which can be directly installed on the top of the storage tank or installed through a waveguide.
This installation method helps to maintain the cleanliness of the equipment and reduce the impact of environmental factors. Radar flow meters may be installed in an insertable manner, directly inserted into the fluid for measurement, or in a non-contact manner, such as fixed to the outside of the pipe to monitor the fluid.
In practical applications, choosing the right equipment has a significant impact on improving production efficiency and cost control. For example, in the application of urban drainage systems, radar level meters can be used to monitor water levels to prevent overflows; while radar flow meters can be used to monitor the discharge rate of rainwater to ensure the efficient operation of the drainage system.
In summary, although radar level meters and radar flow meters are both based on radar technology, they have their own advantages in function, principle and structural design.
Understanding their different characteristics and applicable occasions can help people make more wise choices in practical applications, thereby achieving accurate measurement and efficient management.
