Combustible gas detectors play a critical role in ensuring safety by detecting hazardous gas leaks in both industrial and domestic settings. A common question arises: Do these devices need periodic verification or calibration? The short answer is yes, in most cases, regular verification is essential to maintain their accuracy, reliability, and compliance with safety regulations. This article explores the reasons for periodic verification, the regulations surrounding it, and the recommended practices for ensuring the optimal performance of combustible gas detectors.

1. The Importance of Periodic Verification
1.1 Ensuring Accuracy and Sensitivity
Over time, combustible gas detectors can experience sensor drift, contamination, or wear and tear due to environmental factors. These issues can reduce the detector’s ability to accurately measure gas concentrations, potentially leading to undetected leaks or false alarms. Periodic verification ensures that the detector’s sensitivity and accuracy remain within acceptable limits.
1.2 Preventing Safety Hazards
Combustible gas leaks pose serious risks, including fires, explosions, and toxic exposure. A malfunctioning detector might fail to alert occupants in time, leading to catastrophic consequences. Regular verification minimizes the likelihood of such failures and enhances overall safety.
1.3 Regulatory Compliance
In many industries, combustible gas detectors are subject to stringent safety and performance standards. Regulatory authorities often mandate periodic verification and calibration as part of occupational safety and health requirements. Compliance ensures not only safety but also legal adherence.
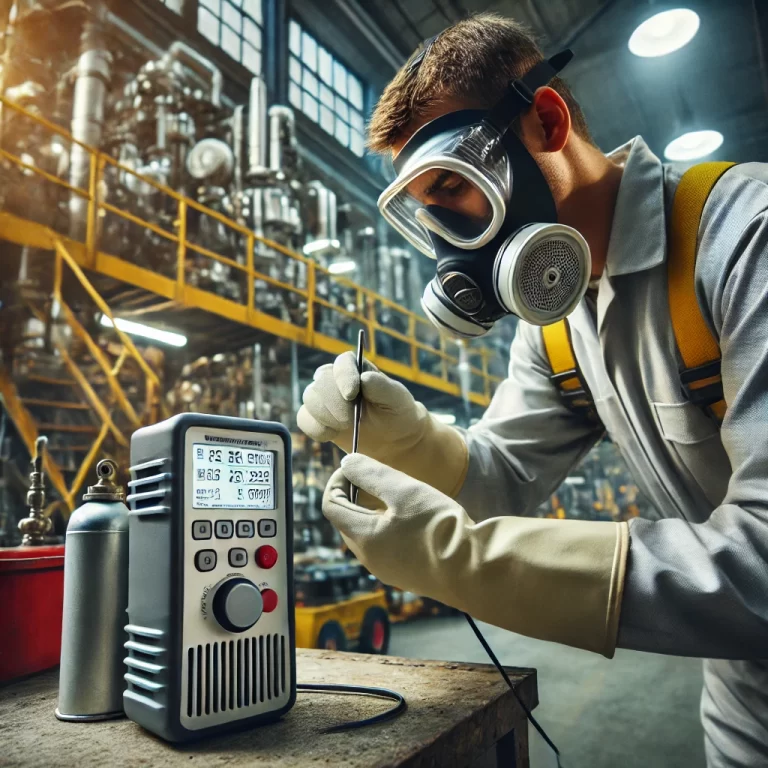

2. Regulatory Requirements
2.1 Standards and Guidelines
In countries like China, the United States, and the European Union, specific laws and guidelines govern the use and maintenance of combustible gas detectors. For example:
China: The “JJG693-2011 Combustible Gas Detection Alarm Device Verification Regulation” mandates annual verification for industrial detectors.
United States: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) recommend regular calibration for gas detection equipment in hazardous environments.
European Union: Standards such as EN 60079-29-2 provide guidance on the periodic maintenance and calibration of gas detection systems.
2.2 Frequency of Verification
Regulatory bodies typically recommend annual verification, but the frequency may vary based on:
The operating environment (e.g., temperature, humidity, and gas type).
Manufacturer’s recommendations.
Industry-specific requirements.
3. Verification Practices
3.1 Calibration vs. Bump Testing
Calibration involves adjusting the detector to ensure its readings align with a known gas concentration. This is a more comprehensive process and is usually performed by qualified professionals.
Bump Testing checks whether the detector can respond to a known gas sample. This quick test verifies functionality but does not adjust the sensor.
3.2 Professional Servicing
Periodic verification often requires specialized equipment and expertise. Many organizations contract authorized service providers or laboratories accredited for gas detector calibration to perform these tasks.
3.3 Documentation
Maintaining records of verification and calibration is crucial for regulatory compliance and operational tracking. Logs should include details such as calibration dates, results, and any adjustments made.

4. Industry-Specific Considerations
4.1 Industrial Applications
In industries like petrochemicals, mining, and manufacturing, gas detectors are often used in high-risk environments. These detectors are subject to mandatory annual or semi-annual verification to ensure safety compliance.
4.2 Domestic Applications
In residential settings, combustible gas detectors may not be subject to legal verification requirements. However, users should follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines and replace detectors as recommended (typically every 5-7 years).
4.3 Environmental Factors
Harsh environments with high humidity, temperature fluctuations, or airborne contaminants may require more frequent verification and calibration to maintain detector performance.

5. Conclusion
Periodic verification of combustible gas detectors is vital for ensuring safety, accuracy, and compliance with regulatory standards. While industrial settings often have mandatory verification requirements, residential users should also prioritize regular maintenance to safeguard against gas leaks. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and consulting authorized professionals for calibration and servicing are best practices to maximize the lifespan and reliability of these critical safety devices.
By staying proactive about maintenance, organizations and individuals alike can minimize risks, meet compliance standards, and protect lives and property from the dangers of combustible gas leaks.
