Introduction
Liquid level measurement is a critical aspect of industrial process control, directly impacting operational safety and efficiency. Among the commonly used level gauges, glass tube level gauges and magnetic level gauges stand out due to their respective advantages and applications. However, in modern industrial settings, magnetic level gauges have become the preferred choice due to their enhanced durability, safety features, and automation capabilities. This article provides a detailed comparison between the two, highlighting why magnetic level gauges are increasingly favored in industries that require precision and safety.
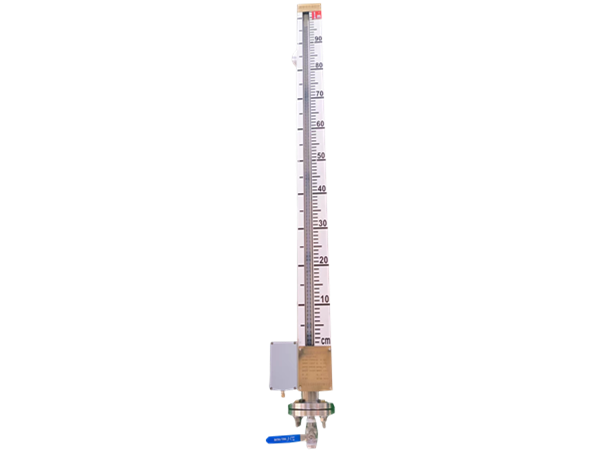
Comparison of Measurement Principles
Glass Tube Level Gauge
Glass tube level gauges operate based on the principle of communicating vessels, where the liquid level inside a transparent glass tube reflects the actual liquid level in the connected container. Operators visually observe the level through the glass tube, and some models come with a calibrated scale to enhance readability.
Magnetic Level Gauge
Magnetic level gauges function based on the buoyancy principle and magnetic coupling technology. A float equipped with a permanent magnet moves up and down within the measuring tube as the liquid level changes. This motion drives an external indicator with bi-color flaps, providing a clear and reliable level display. Additionally, modern magnetic level gauges can be integrated with remote transmitters (e.g., 4-20mA current loop, HART protocol), allowing seamless integration into automated monitoring systems for remote monitoring and alarms.
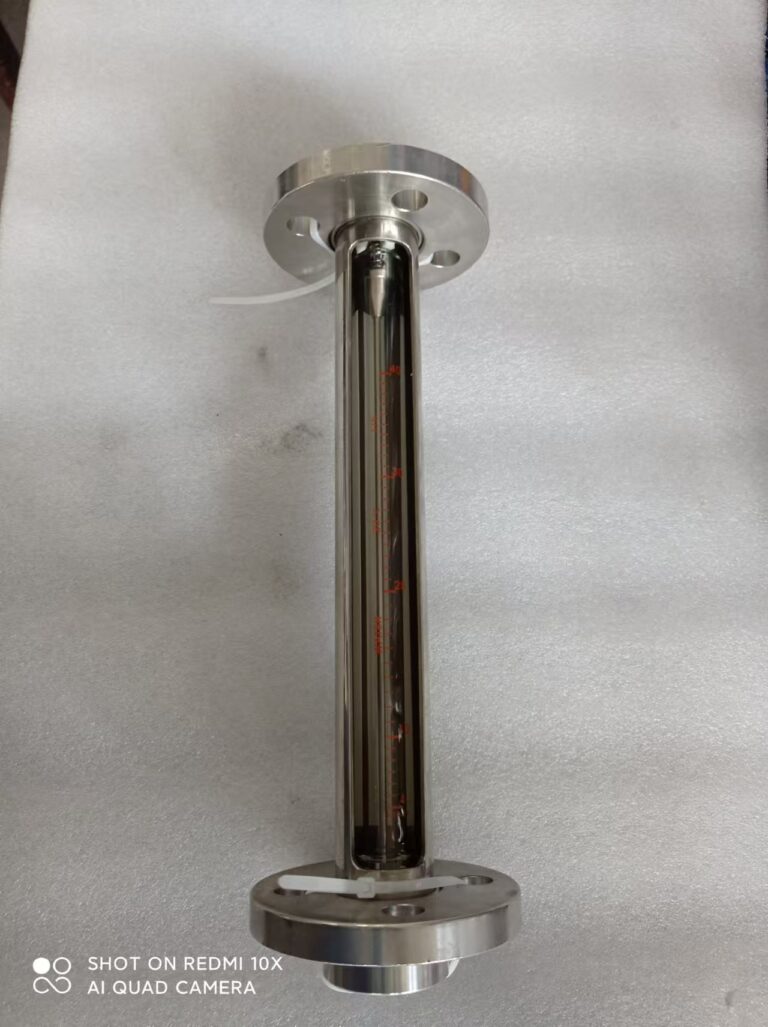

Comparison of Application Conditions
The GB/T 21446-2008 standard provides specific guidelines for the usage of magnetic level gauges. These gauges are designed to withstand:
High temperatures exceeding 400°C
High pressures up to 10 MPa
Aggressive chemical environments with corrosive media
In contrast, glass tube level gauges are more limited in their applications:
Suitable for moderate temperature ranges (generally below 150°C, though special models can withstand up to 400°C)
Typically used in low-pressure systems (below 1 MPa)
Less effective for corrosive or volatile liquids due to material constraints
This distinction makes magnetic level gauges a superior choice for industries requiring reliable performance under extreme conditions, such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and heavy manufacturing.
Safety Considerations
Safety is a critical factor in liquid level measurement, particularly in industries dealing with hazardous chemicals, pressurized fluids, or extreme temperatures.
Glass Tube Level Gauge Safety Risks:
Fragile material: Glass tubes are prone to breakage, especially under high pressure or temperature fluctuations, increasing the risk of leaks and operator injury.
Potential spills: If the glass tube fractures, the liquid inside may leak, posing safety hazards, especially in chemical plants.
Some models incorporate protective enclosures (e.g., steel-wire mesh or double-layer glass) to mitigate risks, but these measures do not eliminate breakage concerns.
Magnetic Level Gauge Safety Features:
Completely sealed design: No direct exposure to liquid, eliminating breakage risks.
Ideal for hazardous and toxic substances: Suited for measuring flammable liquids, chemical solvents, and pressurized gases, significantly reducing the risk of leaks.
Minimal risk of operator injury: Operators do not need to come into direct contact with the liquid during measurement or maintenance.
Due to these safety advantages, magnetic level gauges are widely recommended in industries that prioritize process safety and operational reliability.

Readability and Remote Monitoring
Glass Tube Level Gauge:
Limited readability: The liquid level can only be accurately observed under adequate lighting and at close range.
Unsuitable for remote monitoring: Requires physical inspection, making it impractical for large industrial facilities with automated control systems.
Magnetic Level Gauge:
Highly visible display: Bi-color flaps provide clear visibility even in low-light conditions. Reflective coatings or auxiliary lighting can be added to improve readability in extreme environments.
Supports remote monitoring: Magnetic level gauges can be equipped with 4-20mA transmitters or HART communication modules, enabling integration with DCS (Distributed Control Systems) or SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition Systems). This feature allows for automated level monitoring and real-time alerts, reducing the need for manual inspection.
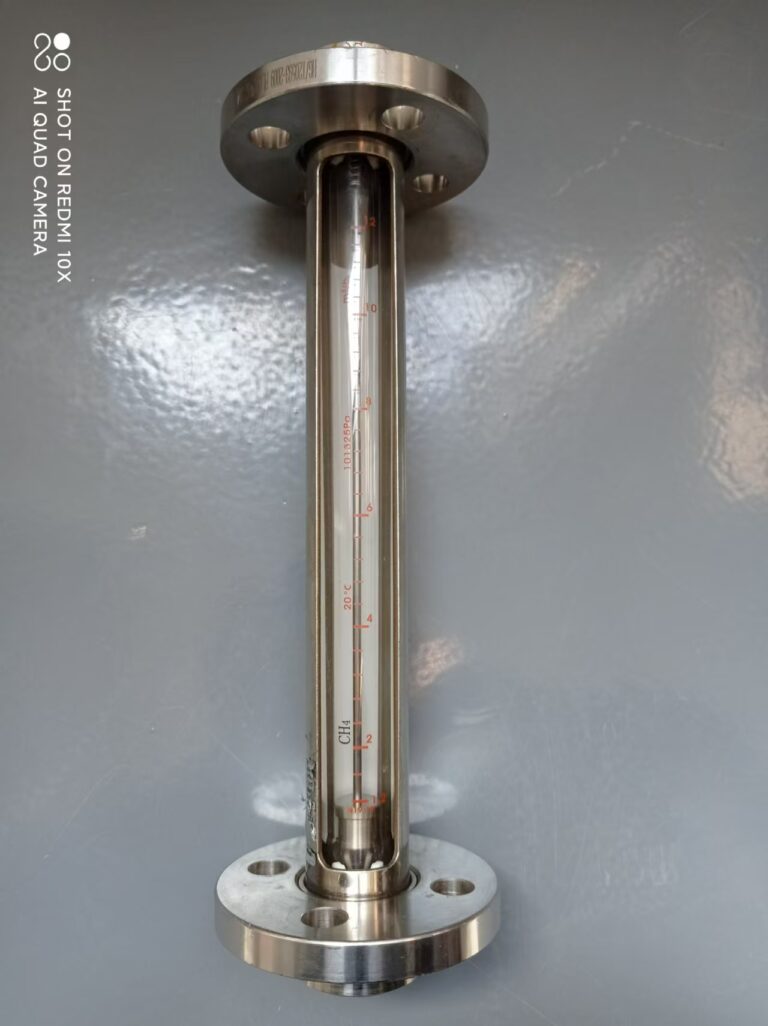

Maintenance and Service Life
Glass Tube Level Gauge Maintenance Challenges:
Frequent cleaning required: Glass tubes are susceptible to scale buildup, which can impair visibility and measurement accuracy.
Regular replacement needed: Seals and gaskets degrade over time, and glass tubes may break, leading to higher long-term maintenance costs.
Magnetic Level Gauge Advantages:
Low maintenance requirements: No glass components, eliminating the risk of breakage.
Highly durable design: Sealed construction minimizes wear and tear, requiring only periodic inspections of the float and indicator.
Extended service life: Magnetic level gauges can last over 10 years, significantly reducing operational costs compared to glass tube level gauges.
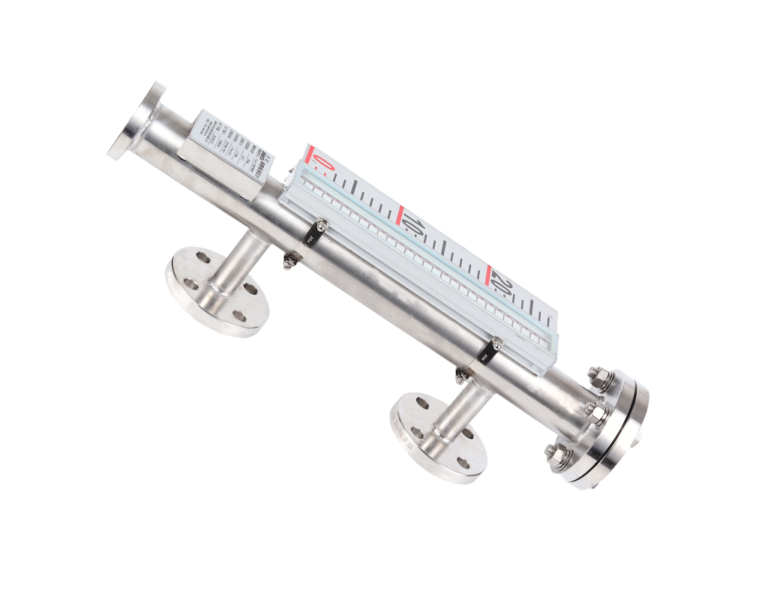

Conclusion: Why Magnetic Level Gauges Are the Superior Choice
According to GB/T 21446-2008, magnetic level gauges offer higher safety, better adaptability to harsh conditions, remote monitoring capabilities, and lower maintenance costs, making them the dominant choice in modern industrial measurement applications.
However, glass tube level gauges still have their place in situations where:
Cost efficiency is a priority: For applications with low-pressure, non-corrosive liquids, glass tube level gauges remain an economical option.
Simplicity and direct visual observation are essential: Industries like food and pharmaceuticals may still prefer glass tube level gauges for certain applications where easy cleaning and visibility are necessary.

Future Industry Trends
While API 2350 does not mandate magnetic level gauges as the exclusive choice for safe level measurement, industries are increasingly transitioning towards automation and safer technologies. As a result, magnetic level gauges are becoming the preferred solution, particularly in petrochemicals, chemicals, metallurgy, and high-risk industrial sectors.
Case Study: Magnetic Level Gauge in Real-World Applications
A prime example is the adoption of Zero Instrument Flap-11 Magnetic Level Gauge at Dezhou Shihua Chemical Plant, where its superior reliability and safety features have contributed to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs.
Final Verdict:
For industries seeking a long-term, reliable, and automated liquid level measurement solution, magnetic level gauges stand out as the optimal choice. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions, ensure safety, and integrate with automated systems makes them a future-proof investment in industrial liquid level monitoring.
