1. Measurement Principle
- Radar Level Meter: Uses radar waves to measure the distance between the sensor and the material surface. It is a non-contact method where high-frequency electromagnetic waves are emitted and reflected back from the surface, calculating the liquid level based on the time delay.
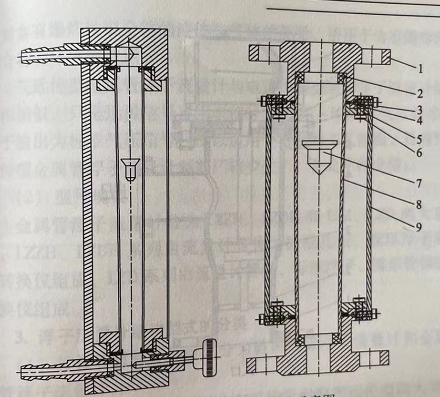
- Glass Tube Level Meter: A traditional mechanical method where the liquid level inside a transparent glass tube directly reflects the level of liquid in a tank or vessel through visual observation.
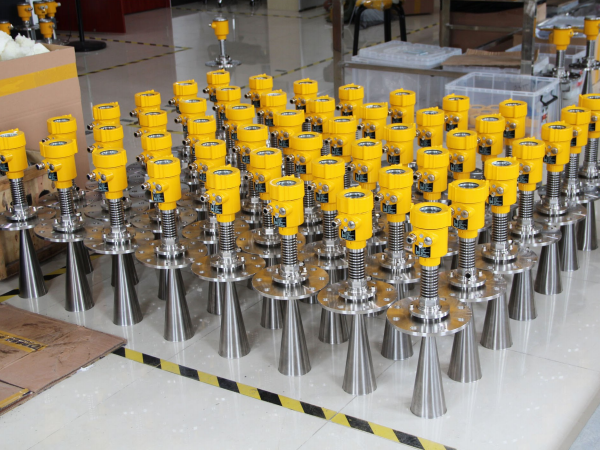

2. Application Range
- Radar Level Meter: Suitable for a wide range of applications, including challenging environments such as high temperature, high pressure, corrosive substances, and tanks with foam or steam. It is widely used in industries like chemical, oil, gas, and food processing.
- Glass Tube Level Meter: Typically used in simpler and less demanding applications, such as in water tanks, boilers, and small vessels. It is mainly suited for clear, non-corrosive liquids.
3. Accuracy and Sensitivity
- Radar Level Meter: Offers high accuracy and is less influenced by temperature, pressure, or liquid properties (such as viscosity or density). It can accurately measure even in the presence of foam, turbulence, or vapors.
- Glass Tube Level Meter: While generally accurate for basic applications, its performance can be compromised by liquid viscosity, fouling, or condensation on the tube, and it is less effective in turbulent conditions.
4. Safety and Durability
- Radar Level Meter: Since it is non-contact, it is safer for hazardous, toxic, or corrosive liquids. Radar meters can be made with corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to operate in extreme environments, offering a longer lifespan and low maintenance.
- Glass Tube Level Meter: More vulnerable to breakage, especially under high pressure or in the presence of corrosive substances. Regular cleaning and maintenance are required to keep the tube clear for visual inspection, and the material may need frequent replacement in harsh environments.
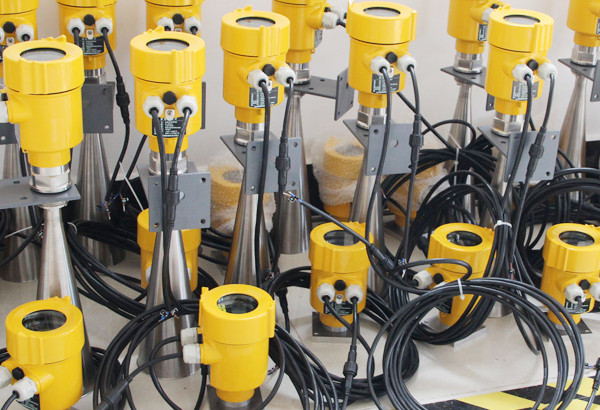

5. Cost and Installation
- Radar Level Meter: Generally more expensive due to its advanced technology and robustness. Installation may require calibration and professional setup, particularly in complex industrial settings.
- Glass Tube Level Meter: More cost-effective and simpler to install. It requires minimal technical knowledge for installation and is a common choice for smaller-scale operations or where cost is a primary concern.

6. Advantages and Limitations
- Radar Level Meter:
- Advantages: High accuracy, non-contact measurement, suitable for extreme conditions, low maintenance.
- Limitations: Higher initial cost, requires expertise for setup and calibration.
- Glass Tube Level Meter:
- Advantages: Cost-effective, simple design, easy visual observation, and no complex electronics.
- Limitations: Fragile, requires regular maintenance, not suitable for high-pressure or corrosive environments, limited accuracy in complex conditions.

Conclusion
Radar level meters are ideal for industrial applications requiring high precision, safety, and durability in complex or extreme conditions. In contrast, glass tube level meters remain a practical and economical solution for simpler applications where conditions are stable and visibility is sufficient. The choice between the two depends on factors like environmental conditions, required accuracy, and budget.
