In industrial settings, effective debugging and communication are crucial for ensuring smooth operation and troubleshooting issues across various equipment and control systems. Specialized debugging cables facilitate efficient communication between devices, computers, and controllers, allowing engineers and technicians to monitor, configure, and troubleshoot machinery and control systems. Here are some of the most commonly used types of debugging cables in industrial environments, along with their features and applications.
1. RS-232 Debugging Cable
- Overview: The RS-232 serial cable is one of the oldest and most widely used debugging cables in industrial environments, specifically for serial communication between devices.
- Features: RS-232 is limited in terms of speed and distance but provides reliable point-to-point communication. It is typically used for distances of up to 50 feet (15 meters) and at speeds of up to 115 Kbps.
- Applications: Ideal for PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), microcontrollers, sensors, and control equipment, RS-232 cables are usually paired with DB9 connectors. The simplicity of the RS-232 cable makes it suitable for environments where short-range, low-speed communication is required.
2. RS-485 Debugging Cable
- Overview: The RS-485 cable is an advanced option compared to RS-232 and is designed for multi-point communication over longer distances, which makes it ideal for industrial applications requiring more nodes in the network.
- Features: RS-485 cables support distances up to 4,000 feet (1,200 meters) and have high resistance to electrical interference, which is beneficial in electrically noisy industrial environments. They also support multiple devices on the same line.
- Applications: RS-485 cables are frequently used in SCADA systems, industrial automation, and environments where devices are spaced far apart. It is commonly seen in systems with modems, PLCs, and data loggers.
3. Ethernet (RJ45) Debugging Cable
- Overview: Ethernet cables, commonly referred to as RJ45 cables, are widely used for network debugging in modern industrial environments. They support high-speed data transmission, making them suitable for TCP/IP network communications.
- Features: Ethernet cables come in several categories (e.g., Cat5, Cat6) that support different speeds and distances. They offer high-speed connections (up to 10 Gbps in some cases) and can be used over distances of up to 328 feet (100 meters) without repeaters.
- Applications: Ethernet cables are preferred in applications where multiple devices are networked, such as industrial PCs, PLCs, HMIs (Human Machine Interfaces), and other networked industrial control devices.
4. USB Debugging Cable
- Overview: USB debugging cables are primarily used to connect computers with other devices over USB ports. They are widely recognized for their ease of use and plug-and-play capability.
- Features: USB supports high data transfer rates and can provide power to connected devices. However, it is limited to shorter distances, usually around 16 feet (5 meters) without extenders.
- Applications: USB debugging cables are common in embedded systems, single-board computers, and industrial devices that require simple, direct connection to a PC for configuration or data extraction.
5. CAN Bus Debugging Cable
- Overview: The CAN (Controller Area Network) bus cable is widely used for high-speed communication in environments where robustness and reliability are essential.
- Features: CAN bus cables provide excellent resistance to interference and can support multiple devices on a single network. They are highly reliable and can transmit data up to 1 Mbps over distances of approximately 131 feet (40 meters).
- Applications: The CAN bus is used extensively in automotive, aerospace, and industrial automation. It is ideal for applications where a large number of microcontrollers and sensors need to communicate reliably.
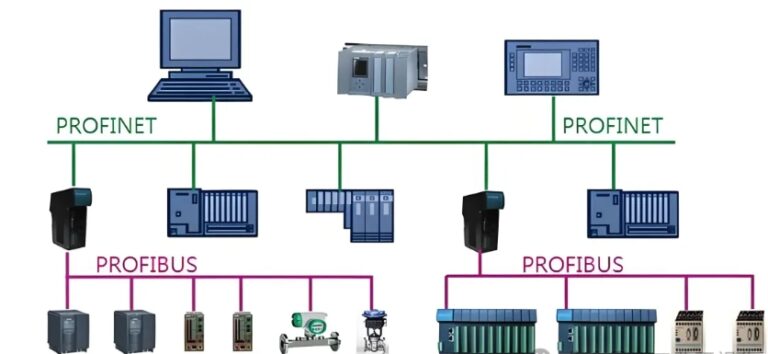
6. PROFIBUS Debugging Cable
- Overview: PROFIBUS (Process Field Bus) is a standard for fieldbus communication in automation technology, developed for connecting devices such as sensors and actuators to a central controller.
- Features: PROFIBUS cables are designed for robust industrial environments and support data transmission speeds of up to 12 Mbps. They also feature high noise immunity, which is beneficial in environments with high electromagnetic interference.
- Applications: PROFIBUS is commonly used in process and factory automation, especially in systems that require real-time communication between control systems and field devices.
7. Fieldbus Debugging Cable (e.g., Modbus)
- Overview: Fieldbus debugging cables, such as those for Modbus, are frequently used in industrial automation for establishing communication between control systems and field devices.
- Features: Modbus cables support different physical layers, such as RS-232, RS-485, and TCP/IP, making them versatile for various communication needs.
- Applications: Modbus cables are often used in data acquisition, device monitoring, and control applications. They are commonly found in distributed control systems (DCS) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems.

8. Wireless Debugging Devices (e.g., Wi-Fi, Bluetooth)
- Overview: Wireless debugging options, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, provide flexibility in settings where wired connections may be inconvenient.
- Features: Wireless debugging devices are convenient for remote access but can be prone to interference and security concerns. They offer flexibility for mobile or temporary setups but may not be suitable for applications requiring stable, high-speed connections.
- Applications: Wireless debugging is popular in situations requiring mobility or where running physical cables is impractical. It is often used in machine diagnostics, data logging, and condition monitoring in industrial IoT setups.

Choosing the Right Debugging Cable
Selecting the appropriate debugging cable depends on several factors, including the required communication distance, environmental conditions, the number of devices, and the speed of data transmission. Here are some general guidelines for choosing the right cable:
Distance: For long-distance communication, RS-485, CAN bus, and Ethernet are preferred, while USB and RS-232 are better suited for short-range applications.
Interference Resistance: In environments with high electromagnetic interference, CAN bus, RS-485, and PROFIBUS are ideal due to their high resistance to interference.
Network Complexity: For applications requiring multi-point connections or a large number of devices, RS-485, CAN bus, and Ethernet are suitable as they support multi-device networks.
Portability: If portability is essential, USB and wireless debugging devices like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth provide flexibility, though they are best suited for short-range or low-priority debugging tasks.
Using the right debugging cable can optimize communication and improve reliability in industrial operations, ensuring efficient troubleshooting and reducing downtime.
