In industrial projects such as boilers, pressure vessels, and chemical processing equipment, the same material grade may be specified in different product forms (pipes, fittings, forgings, castings, and plates). To ensure consistency in design and procurement, engineers often need to cross-reference material standards. The following table provides an equivalency overview for commonly used American standards.
1. Alloy Steels
| Alloy Composition | Seamless Pipe (ASTM/ASME) | Fittings | Forgings | Castings | Plates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1¼Cr-½Mo | A335 P11 | A234 WP11 | A182 Gr.F11 | A217 Gr.WC6 | A387 Gr.11 |
| 2¼Cr-1Mo | A335 P22 | A234 WP22 | A182 Gr.F22 | A217 Gr.WC9 | A387 Gr.22 |
| 5Cr-½Mo | A335 P5 | A234 WP5 | A182 Gr.F5a | A217 Gr.C5 | A387 Gr.5 |
| 9Cr-1Mo | A335 P9 (creep resistant) | A234 WP9 | A182 Gr.F9 | A217 Gr.C12 | A387 Gr.12 |
| 9Cr-1Mo-V | A335 P91 (power plant grade) | A234 WP91 | A182 Gr.F91 | A217 Gr.C12A | A387 Gr.91 CL.2 |
| 9Cr-0.5Mo-1.8W-VNb | A335 P92 | – | – | – | – |
2. Carbon Steels
| Grade | Seamless Pipe | Fittings | Forgings | Castings | Plates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-Si | A106 B | A234 WPB | A105, A350 Gr.LF1 | A216 Gr.WCB, A352 Gr.LCB | A515 Gr.70 |
| C-Mn-Si | A106C | A234 WPC | A350 Gr.LF2 | A216 Gr.WCC | A516 Gr.70 |
| Low-temperature C-Si | A333 Gr.6 | A420 WPL6 | – | – | – |
3. Stainless Steels
| Type | Seamless Pipe | Fittings | Forgings | Castings | Plates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18Cr-8Ni (304) | A312 TP304 | A403 WP304 | A182 F304 | A351 CF8 | A240 Gr.304 |
| 18Cr-8Ni (304L) | A312 TP304L | A403 WP304L | A182 F304L | A351 CF3 | A240 Gr.304L |
| 16Cr-12Ni-2Mo (316) | A312 TP316 | A403 WP316 | A182 F316 | A351 CF8M | A240 Gr.316 |
| 16Cr-12Ni-2Mo (316L) | A312 TP316L | A403 WP316L | A182 F316L | A351 CF3M | A240 Gr.316L |
| 18-10Ni-Ti (321) | A312 TP321 | A403 WP321 | A182 F321 | A351 CF8T | A240 Gr.321 |
| 18-10Ni-Nb (347) | A312 TP347 | A403 WP347 | A182 F347 | A351 CF8C | A240 Gr.347 |
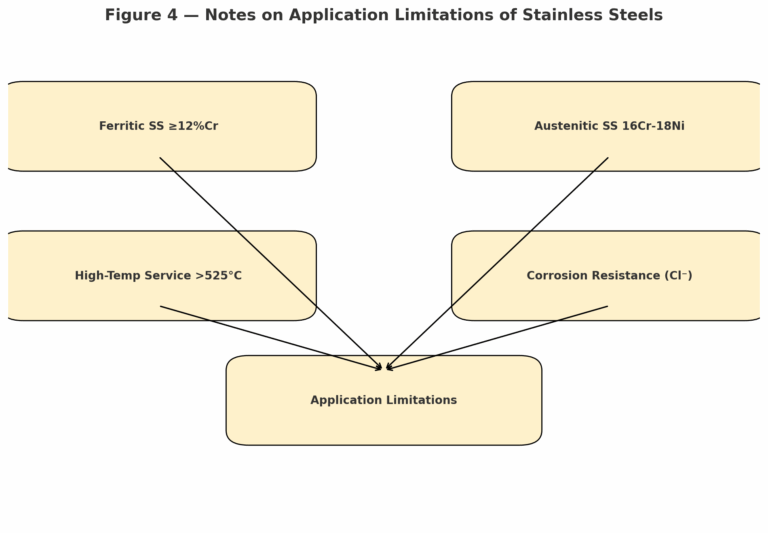
4. Notes on Application Limitations
Ferritic stainless steels with ≥12% Cr
Susceptible to embrittlement between 400–500 °C due to sigma-phase formation.
Maximum service temperature is generally ≤350 °C if C content is high.
Austenitic stainless steels with high Cr and Ni
Steels containing 16%Cr + 18%Ni may undergo embrittlement at 540–900 °C due to carbide precipitation.
High-temperature service
For use above 525 °C, stainless steels should contain >0.04% carbon.
Corrosion resistance
For chloride or aggressive environments, Type 316/316L is recommended.
5. Ranking of Pitting Corrosion Resistance
From lowest to highest resistance, the order is:
304 → 304L → 0Cr13 (410 equivalent) → 316 → 316L → 321 → 347
Conclusion
This cross-reference guide enables engineers to quickly identify equivalent ASTM/ASME standards for different product forms of alloy steels, carbon steels, and stainless steels. Proper material selection requires not only standard compliance but also consideration of service temperature, corrosion resistance, and fabrication conditions.
