Overview
In pressure vessels, pipeline systems, and high-temperature/high-pressure industrial equipment, flanged connections serve as crucial detachable joints. Bolts play a core role in transferring preload to the gasket, directly impacting sealing performance. Although austenitic stainless steel bolts such as 304 and 316 are sometimes used, many installations report frequent leakage. This document analyzes the reasons behind such failures and provides engineering recommendations.
1. Material Characteristics of 304/316 Austenitic Stainless Steel
1.1 Metallurgical Structure
Austenitic stainless steels (e.g., 304, 316) are non-magnetic, FCC-structured alloys with excellent corrosion resistance and ductility.
Commonly used for their chemical resistance, especially in neutral or mildly corrosive environments.
1.2 Mechanical Weaknesses
Low Yield Strength: Typically 170–210 MPa, lower than ferritic or martensitic steels.
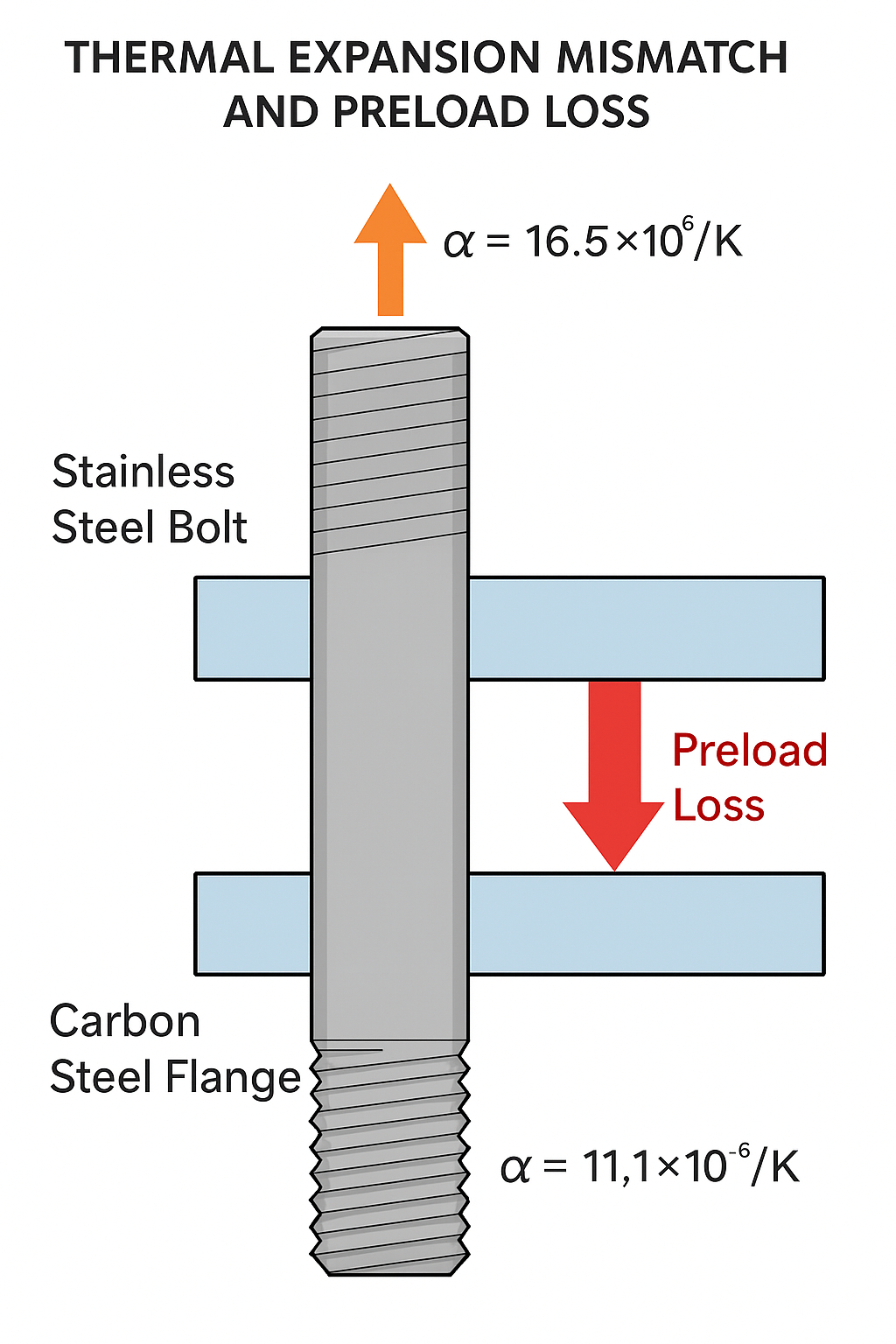
High Thermal Expansion Coefficient: Approx. 16.5 × 10⁻⁶ /K.
Sensitive to Creep: Deformation under stress at elevated temperatures over time.
Non-hardenable by heat treatment.
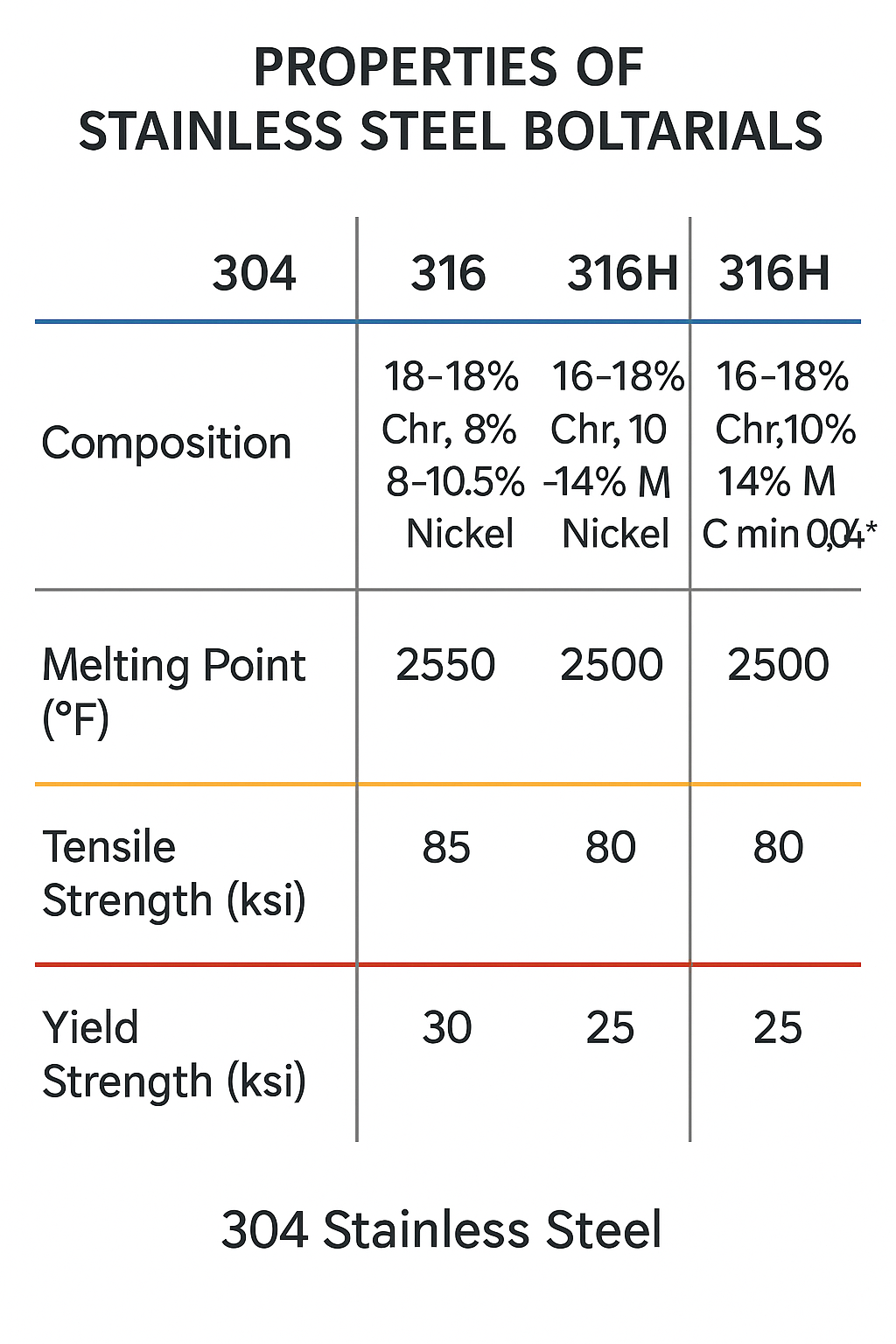
1.3 Comparison of Chemical and Mechanical Properties
| Material | Grade | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Mo (%) | Thermal Expansion (×10⁻⁶/K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | B8 Cl.1 | ~205 | ~515 | – | 16.5 |
| 316 | B8M Cl.1 | ~210 | ~520 | 2-3 | 16.5 |
| B8 Cl.2 | Cold-worked 304 | ≥690 | ≥860 | – | 16.5 |
| A193 B7 | Alloy Steel | ≥720 | ≥860 | – | ~12.5 |
| Inconel 718 | Ni-based alloy | >1000 | >1250 | >3 | ~13 |
2. Failure Mechanisms in Flanged Applications
2.1 Inadequate Mechanical Strength
Bolt stress must achieve 70% of the yield strength to seal metal or spiral wound gaskets.
304/316 bolts may yield prematurely or fracture under required torque.
Not suitable for:
High-pressure flanges (PN25 and above)
High gasket stress applications
Installations lacking torque control tools
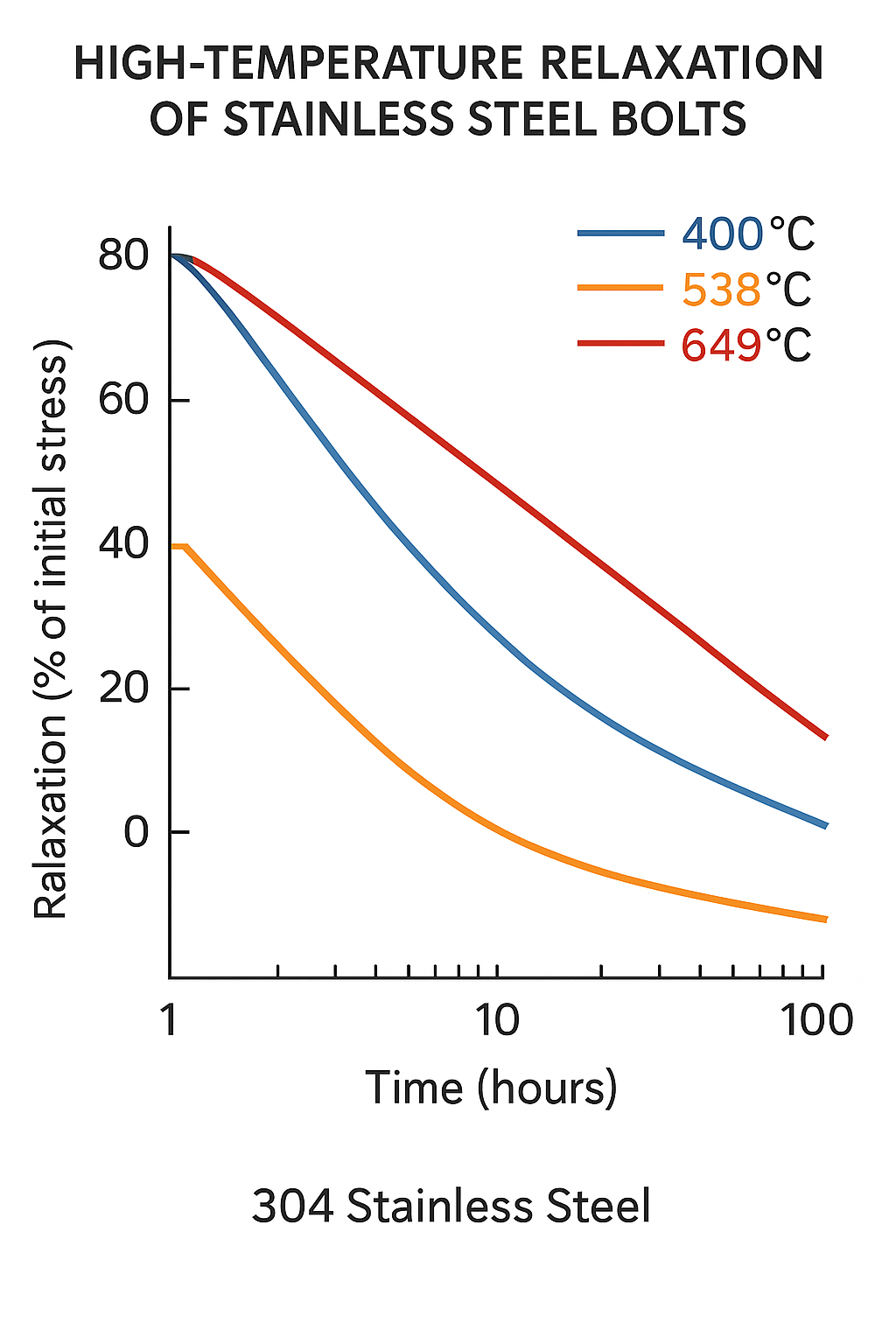
2.2 Stress Relaxation and Creep
Under sustained loads and temperatures (>300°C), preload decays due to:
Creep deformation
Thermal fatigue from cycling temperatures
Studies show B8 Cl.1 bolts can lose >50% of clamping force after 10,000 hours in service.
2.3 Thermal Expansion Mismatch
304 bolts expand more than carbon steel flanges during heating cycles:
Leads to preload loss
Critical in cyclic or batch process plants
2.4 Corrosion and Hydrogen Embrittlement Risks
Pitting and intergranular corrosion in high-chloride or acidic environments
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) above 60°C in tensile-stress + corrosive media
Hydrogen embrittlement may occur under specific electrochemical conditions
3. Code and Standard Guidance
3.1 International Standards
ASME B16.5 / B31.3: Recommend B8 Cl.2 or higher for high-pressure systems
ASME Section II Part A: Limits use of 304/316 for temperatures >538°C
API 6A / 17D: Suggests Inconel or alloy steel for HPHT environments
3.2 Chinese National Standards
GB/T 150.3-2021:
Allows S30408/S31608 (B8 Cl.2, B8M Cl.2) for medium-duty service
Recommends against S30400/S31600 (B8 Cl.1, B8M Cl.1) in HPHT scenarios
GB/T 38343-2019:
High gasket stress requires medium/high strength bolts
Recommends torque-stress conversion charts and tensioning tool
4. Engineering Recommendations
4.1 Preferred Bolt Materials for Flanged Connections
B8 Cl.2 / B8M Cl.2 (Cold-worked stainless steel)
A193 B7 (Chromium-molybdenum alloy steel)
35CrMo (for high strength applications)
Inconel 718 (for extreme temperatures and corrosion)
4.2 Installation Best Practices
Use torque wrenches or hydraulic tensioners
Apply lubrication to minimize friction variance
Implement load monitoring washers or ultrasonic preload testers if applicable
5. Conclusion
While 304 and 316 stainless steel bolts offer superior corrosion resistance, their low yield strength, high creep rate, and mismatch in thermal expansion make them unsuitable for high-temperature, high-pressure, or cyclic load flanged applications. For enhanced reliability and safety, high-strength, stable-performance bolts should be selected, combined with proper installation techniques to ensure long-term seal integrity.
