Instrumentation junction boxes installed outdoors play a critical role in protecting sensitive electrical connections from harsh environmental conditions while ensuring the safe and efficient operation of equipment. This guide outlines detailed requirements for cable entry and exit to ensure reliability, safety, and ease of maintenance.
1. Selecting the Right Junction Box
When choosing an outdoor instrumentation junction box, consider the following:
- Ingress Protection (IP) Rating: The junction box should have an IP65 rating or higher to protect against dust and water ingress. For extreme conditions, such as heavy rain or submersion risks, opt for higher ratings (e.g., IP67 or IP68).
- Material Durability: Use materials such as stainless steel, aluminum alloy, or UV-resistant plastic to resist corrosion, temperature extremes, and weathering. The material should also comply with local or international standards for electrical enclosures (e.g., IEC 60529 or NEMA ratings).
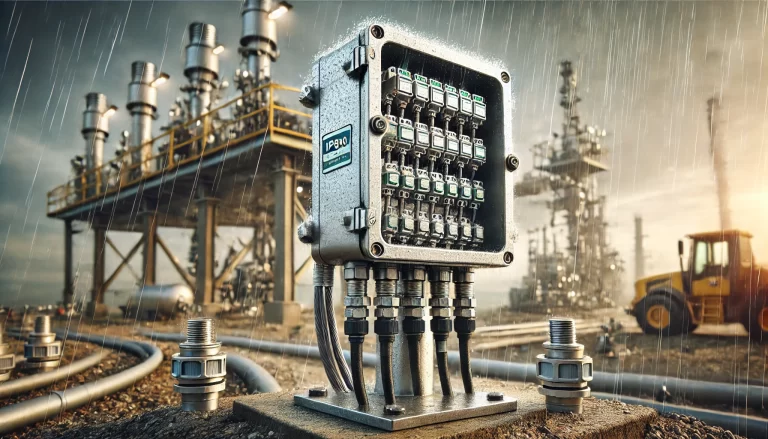

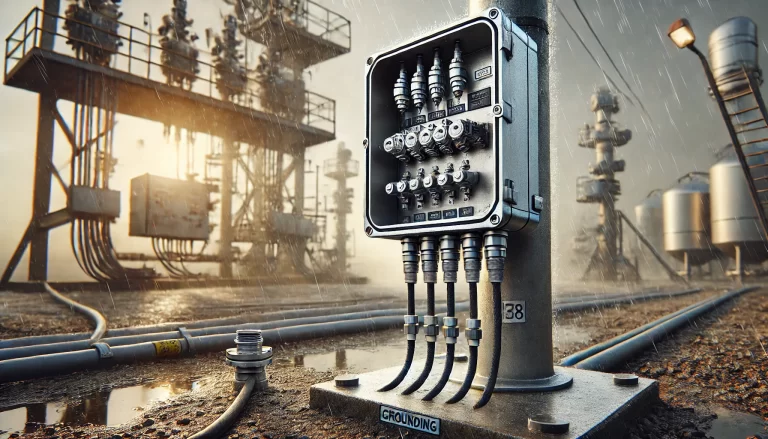
2. Cable Entry and Exit Requirements
Proper handling of cable entry and exit is essential for ensuring protection against environmental factors and electrical safety:
2.1. Sealing for Waterproofing
- Install gland seals or cable glands for all cable entries and exits to provide a secure and watertight connection.
- Choose glands with appropriate ratings, such as IP68-rated cable glands, to maintain box integrity.
- For unused cable entry holes, use sealed blanking plugs to maintain the box’s protection level.
2.2. Cable Entry Points
- Placement: Cable entry and exit points should be on the bottom or sides of the junction box. This minimizes water ingress caused by rain or condensation.
- Hole Sizes: Ensure the cable gland’s hole size matches the cable diameter to provide a snug fit without over-compression, which can damage the cable insulation.
3. Cable Routing and Management
Efficient cable management inside and outside the junction box is crucial for performance and maintenance:
- Bend Radius: Maintain the cable’s minimum bend radius as specified by the manufacturer to prevent stress or damage.
- Segregation: Separate cables into power, control, and communication lines. Avoid mixing high-voltage and low-voltage cables to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Protection from External Forces: Use conduits, armored cables, or cable trays to protect cables from mechanical damage.
4. Grounding and Bonding
Grounding plays a critical role in ensuring safety and protecting against electrical faults:
- Ground Connection: Ensure that the junction box itself is grounded using an external grounding terminal.
- Cable Shielding: For shielded cables, the shielding layer should be grounded at a single point—typically at the junction box entry or control panel—to avoid ground loops and signal interference.
5. Condensation Management
Outdoor installations are prone to condensation due to temperature fluctuations. To address this:
- Breather Valves: Install a breather or drain valve to equalize pressure and allow moisture to escape while maintaining the box’s IP rating.
- Desiccants: Place moisture-absorbing materials like silica gel packets inside the box to reduce humidity.
6. Protection from Environmental Factors
Outdoor environments can expose instrumentation junction boxes to additional challenges:
- UV Protection: Use UV-resistant paints or coatings for prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- Corrosion Resistance: In marine or chemical environments, ensure materials and fittings are corrosion-resistant (e.g., stainless steel 316).
- Temperature Extremes: For extreme hot or cold climates, consider enclosures with thermal insulation or integrated heating/cooling options.

7. Compliance with Electrical Standards
Follow international and regional standards to ensure compliance and safety:
- IEC Standards: Enclosures should comply with IEC 60529 for ingress protection and IEC 62208 for empty enclosures used in low-voltage switchgear and control gear assemblies.
- NEMA Ratings: In the U.S., adhere to NEMA standards to match enclosure types with environmental conditions.
8. Labeling and Maintenance
- Labeling: Clearly label all cables as they enter and exit the junction box to facilitate troubleshooting and future maintenance. Use weather-resistant labels for durability.
- Inspection and Testing: Periodically inspect cable glands, seals, and grounding connections for wear, corrosion, or leaks. Replace or repair components as needed.

Conclusion
Proper cable entry and exit in outdoor instrumentation junction boxes are vital for ensuring operational reliability, safety, and compliance with international standards. By adhering to these guidelines, industries worldwide can achieve robust, long-lasting installations suitable for diverse environments. Regular inspections and adherence to standards like IEC or NEMA will further safeguard these critical components, extending their service life and ensuring efficient maintenance.
