Introduction
Load cells are vital components in industrial automation, weighing systems, and process control. However, when used in harsh environments—such as dusty factories, outdoor installations, or corrosive chemical plants—load cells face challenges that can impact their accuracy, lifespan, and reliability.
This guide provides actionable best practices for installing load cells in demanding conditions to ensure long-term performance and safety.
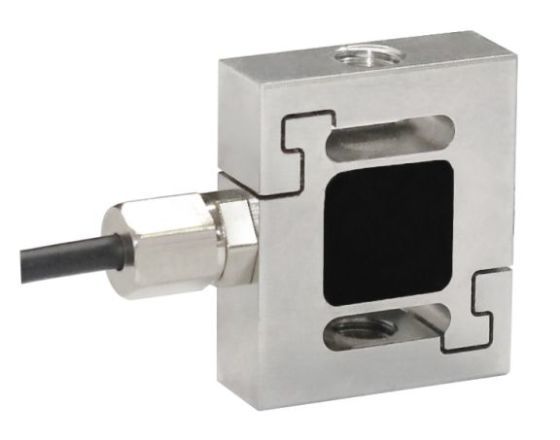

1. Understand the Environmental Hazards
Before selecting or installing a load cell, it’s crucial to assess the environmental risks at your installation site. These may include:
🌧️ Moisture & Water Ingress (e.g., rain, washdowns, humidity)
🧪 Chemical Exposure (e.g., acids, solvents, salt spray)
🌬️ Dust & Particulate Matter (e.g., cement, grain, metal shavings)
🌡️ Extreme Temperatures (e.g., furnaces, cold storage)
⚡ Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
⚙️ Mechanical Vibration & Shock
Each of these factors can degrade signal quality, damage sensor components, or lead to false readings over time.
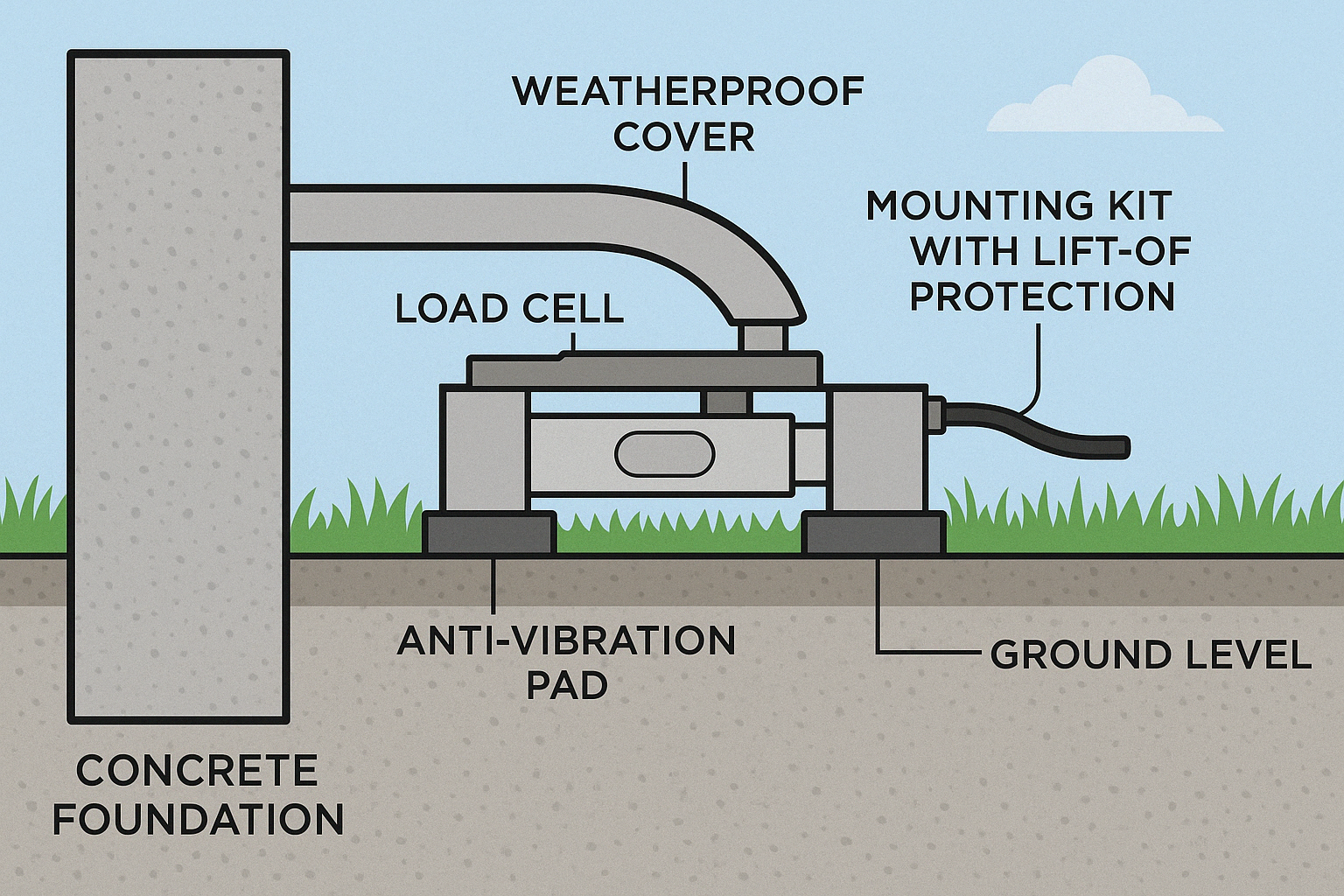
2. Choose the Right Load Cell Type and Materials
✅ Ingress Protection (IP) Rating
For harsh conditions, a minimum rating of IP65 is recommended. For wet, outdoor, or washdown applications, look for IP67 or IP68.
✅ Material Selection
Stainless steel load cells offer excellent corrosion resistance
Avoid aluminum models in chemical or marine environments
Use sealed models with welded construction where possible
✅ Temperature Compensation
Use temperature-compensated load cells for high or fluctuating temperatures to minimize signal drift.
3. Mounting and Installation Tips
Proper installation is just as important as the sensor itself. Follow these tips to protect performance:
⚙️ Rigid and Aligned Mounting
Always install load cells on a flat, clean, and rigid surface
Misalignment can cause uneven stress and affect accuracy
🧽 Use of Mounting Kits or Modules
Load cell modules with built-in overload and lift-off protection are recommended for tanks, hoppers, and outdoor equipment
🛡️ Shield Against External Forces
Avoid side loads, torsion, and vibration—these cause false readings and mechanical wear
Use anti-vibration pads or isolators where appropriate

4. Electrical & Signal Wiring Best Practices
Use shielded cables and route them away from power lines or motors
Properly ground the shield to avoid EMI
Install cable glands or conduits to protect the cable entry point
Seal unused cable ends to avoid moisture ingress
5. Maintenance and Inspection Schedule
Establish a routine maintenance protocol:
🔍 Inspect for corrosion, cable damage, and mechanical looseness
🧪 Check for signal drift or loss of zero
📏 Recalibrate periodically based on operating cycles or compliance standards
6. Optional Protective Accessories
| Accessory | Function |
|---|---|
| Weatherproof Enclosure | Shields load cell from rain and sunlight |
| Cable Junction Box | Protects signal cables and enables calibration adjustment |
| Silica Gel Packets | Reduce moisture buildup inside enclosures |
| Load Cell Covers | Prevent dust and chemical splash |

Conclusion
Operating load cells in harsh environments requires thoughtful design, robust materials, and proper installation. By following the best practices above, you can significantly extend the service life of your sensors and maintain measurement integrity even in the toughest conditions.
Remember: prevention is cheaper than replacement. A well-installed load cell can deliver years of reliable service—even in the harshest conditions.
