1. Overview of Instrument Tube Fittings
Common fitting types:
Straight union
Elbow union
Tee union
Union with swivel nut
Adapter
Plug
Transition fitting
Pipe Thread Standards:
| Thread Type | Angle & Description | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| NPT | 60° tapered thread | ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 |
| PT | 55° tapered thread (Japanese standard) | JIS B 0203 |
| G | 55° parallel (non-sealing) thread | ISO 228 |
| 1/4″, 1/2″ | Nominal diameters (inches) | Conversion: 1 inch = 25.4 mm |
Note: Metric threads use millimeter-based sizing.
Sealing principle:
Metal-to-metal cone sealing with mechanical grip by ferrule.
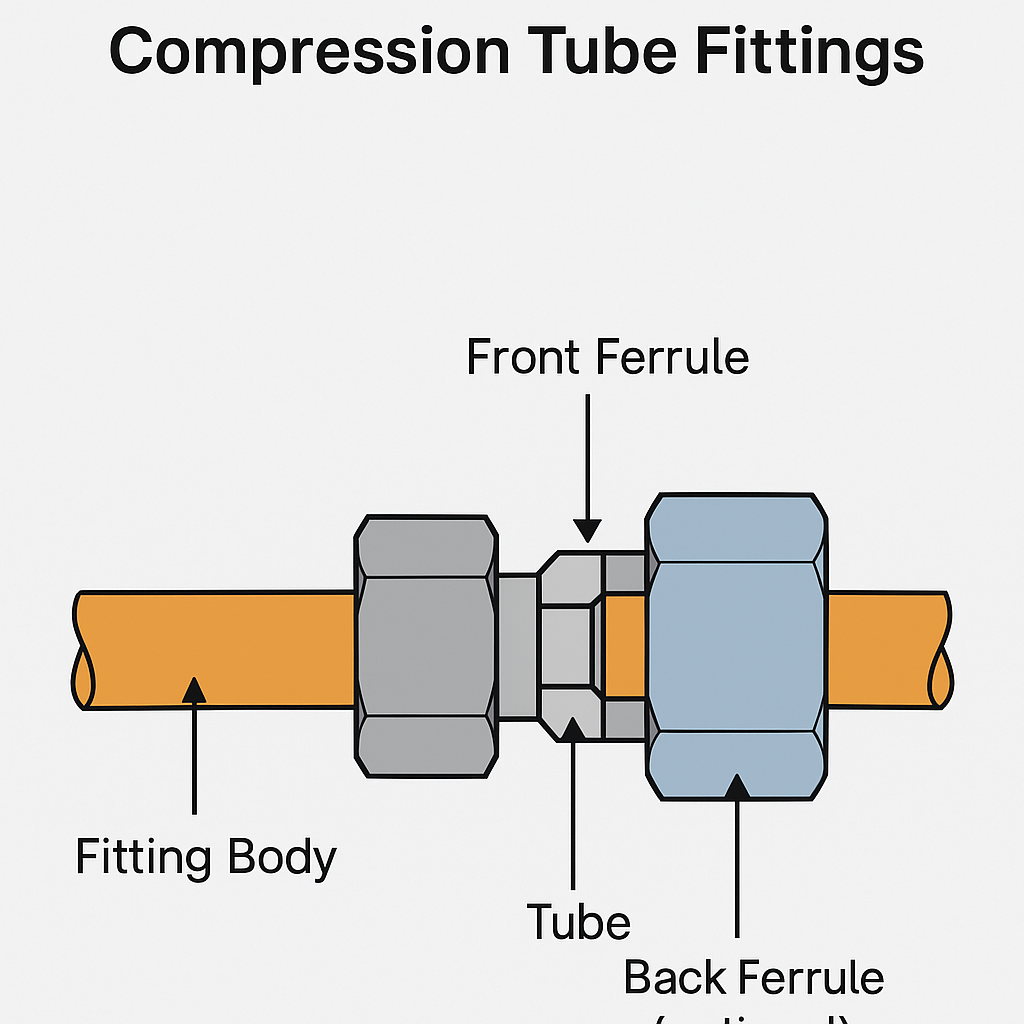
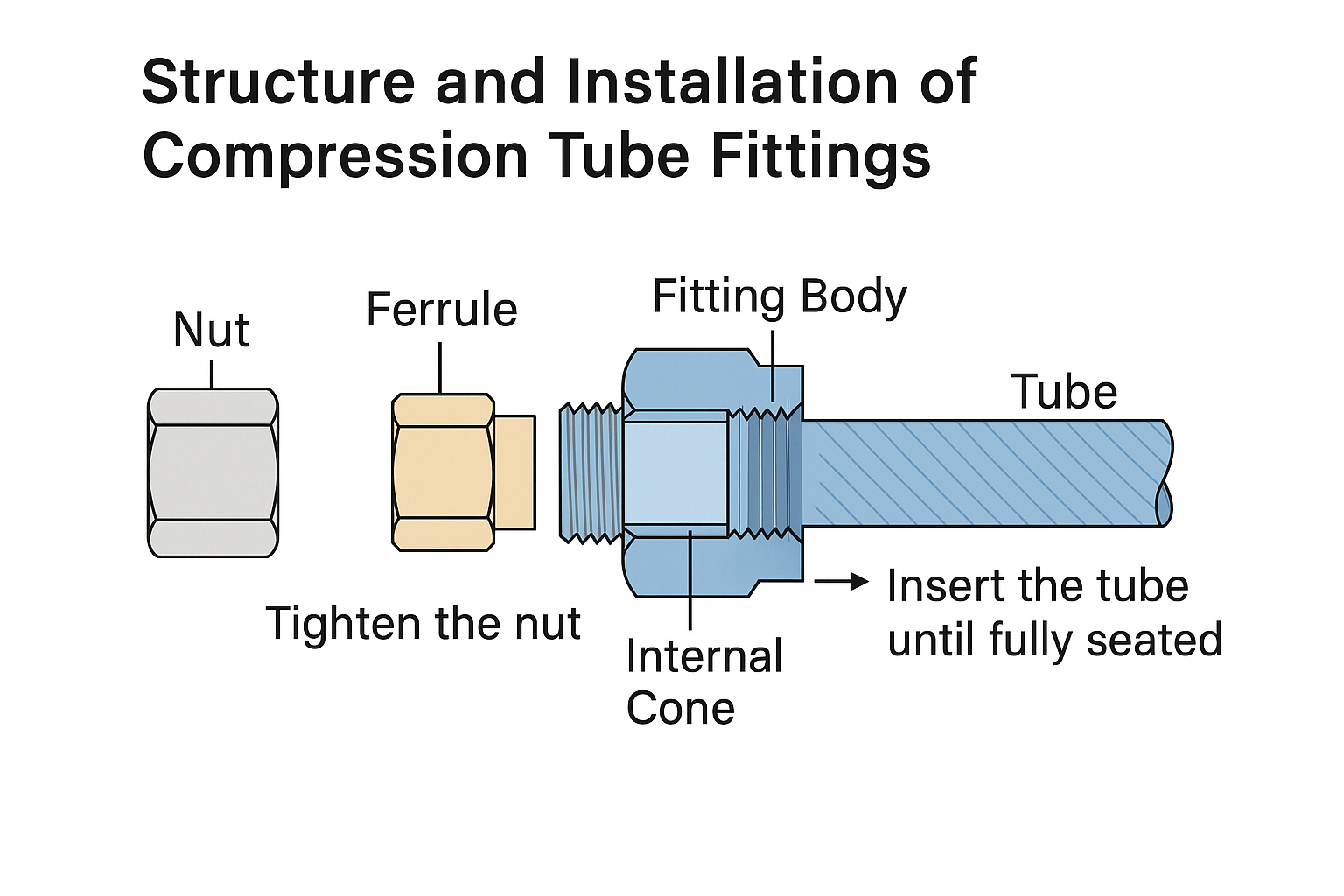
2. Structure and Installation of Compression Tube Fittings
Typical components:
Nut
Front ferrule (and optionally a back ferrule)
Fitting body
Tube
Installation steps:
Deburr the inner and outer tube ends, clean off oil, metal chips, or rust inhibitor.
Insert nut and ferrule(s) onto the tube (cutting edge of the ferrule should face the tube end).
Insert the tube into the fitting body until it bottoms out in the internal cone.
Hand-tighten the nut, then turn 3/4 to 1-1/4 turns using a wrench.
Sealing principle:
When tightened, the front ferrule is compressed into the fitting body, sealing against the cone surface and embedding slightly into the tube surface to create a secure mechanical seal.
3. Common Standards for Tube Fittings
ISO 8434-1: Metallic tube connections for fluid power and general use
DIN 2353: German standard for metric tube fittings
GB/T 3734: Chinese national standard for compression fittings
4. Quick Connector Installation and Removal
Installation:
Wrap PTFE tape around threaded ends (if applicable).
Tighten connector appropriately.
Cut the tubing end square using a proper tube cutter.
Push the tubing into the connector until fully seated.
Pull gently to confirm firm engagement.
Disassembly:
Ensure the medium flow is shut off.
Use fingers to press the collet toward the fitting while pulling the tube out.
