Introduction
Although PF and G threads may appear similar at first glance, important distinctions exist between them regarding standards, practical applications, and detailed technical specifications. Understanding these differences ensures appropriate selection and compatibility in plumbing and piping systems.
Main Differences
1. Standardization
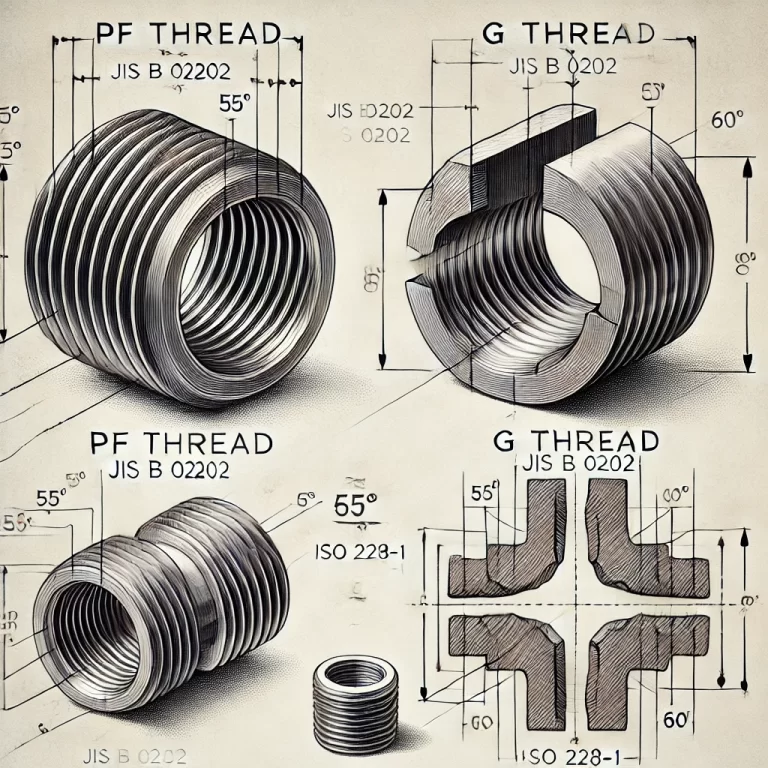
PF Thread: Defined by the Japanese Industrial Standard JIS B 0202, primarily used in Japan and certain parts of Asia.
G Thread: Defined by the ISO 228-1 international standard, widely adopted in Europe, North America, and many other regions globally.
2. Thread Angle Differences
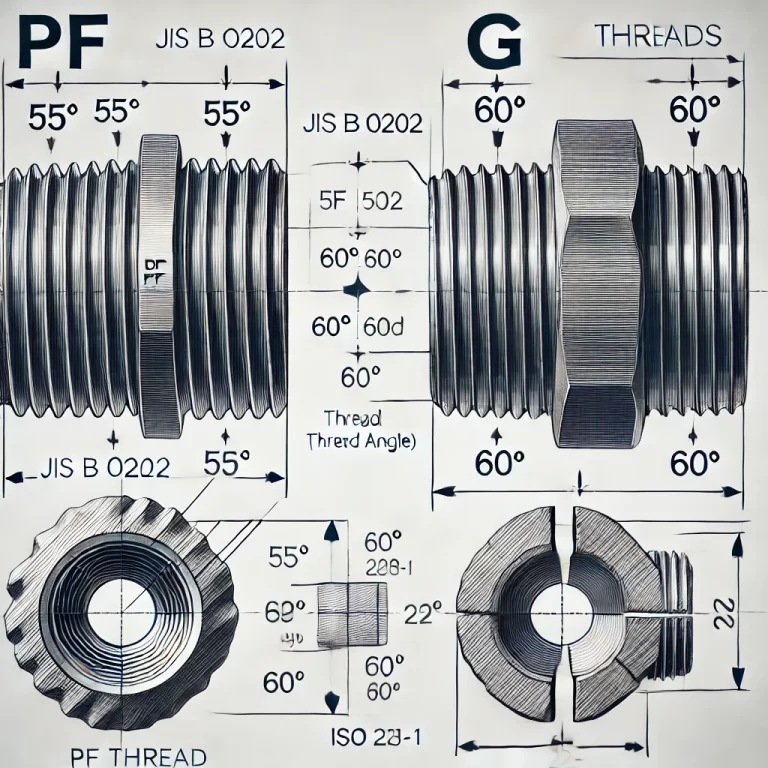
PF Thread: Has a thread angle of 55°, conforming to the Whitworth threading profile.
G Thread: Features a thread angle of 60°, aligning with common international standards.
This seemingly minor difference in thread angle can significantly impact sealing effectiveness, particularly in high-precision or pressure-sensitive applications. Even though both threads belong to the parallel pipe thread family (BSPP), this angular variance should not be overlooked in specialized installations.
Similarities
1. External Shape and Dimensions
Both PF and G threads are parallel pipe threads (BSPP), sharing identical external diameters and pitch. This similarity enables limited interchangeability in certain non-critical applications or where sealing requirements are less stringent.
2. Sealing Requirements
Neither PF nor G threads possess self-sealing capabilities. Both types of threads necessitate the use of sealing elements such as gaskets, O-rings, or sealing washers to achieve proper sealing integrity.
Practical Implications
When selecting thread types for applications, understanding the precise requirements of your piping system is crucial:
For International Applications: Prefer G threads, compliant with ISO 228-1, ensuring compatibility with internationally sourced fittings and components.
For Japanese or Compatible Equipment: Opt for PF threads to align with JIS standards and existing infrastructure.
In high-pressure, precision-sensitive scenarios, the subtle differences between these threads may lead to performance degradation or sealing failure if mismatched.
Conclusion
Although PF and G threads are dimensionally similar and can sometimes interchange, the critical differences in standards and thread angles mean they are not identical. Proper selection depends on geographical standards, intended application precision, and sealing requirements. Careful consideration ensures reliability, efficiency, and safety in piping installations.
